stars-notes
... as seen from Earth. The absolute magnitude is the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth. • If all stars were the same distance away, their absolute magnitudes would be the same as their apparent magnitudes. ...
... as seen from Earth. The absolute magnitude is the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth. • If all stars were the same distance away, their absolute magnitudes would be the same as their apparent magnitudes. ...
Lecture 11
... • The Sun is not massive enough to form a Black Hole. However, lets say that by some mysterious process it suddenly collapses to form a Black Hole of exactly 1 solar mass. What would happen to Earth’s orbit after the Sun became a Black Hole? ...
... • The Sun is not massive enough to form a Black Hole. However, lets say that by some mysterious process it suddenly collapses to form a Black Hole of exactly 1 solar mass. What would happen to Earth’s orbit after the Sun became a Black Hole? ...
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
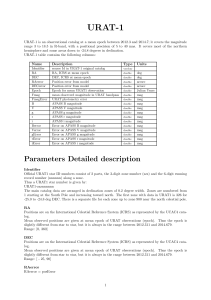
... URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 starting at the South Pole and increasing toward north. The first zone with data in URAT1 is 326 for -25.0 to -24.8 deg DEC. There is a separate file for each zone up to zone 900 ne ...
... URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 starting at the South Pole and increasing toward north. The first zone with data in URAT1 is 326 for -25.0 to -24.8 deg DEC. There is a separate file for each zone up to zone 900 ne ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by their D ...
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by their D ...
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
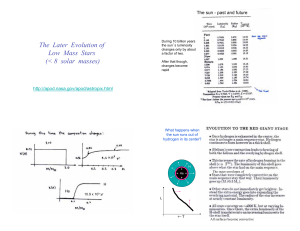
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
Participant Handout - Math Machines Home
... discovered that temperature (measure in kelvin) is inversely proportional to the wavelength of a star’s peak emission as described by the equation: λmax T= 3,000,000 nm K The actual brightness (luminosity) of a star is determined by the star’s size and temperature. In addition to having a more blui ...
... discovered that temperature (measure in kelvin) is inversely proportional to the wavelength of a star’s peak emission as described by the equation: λmax T= 3,000,000 nm K The actual brightness (luminosity) of a star is determined by the star’s size and temperature. In addition to having a more blui ...
Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
Stellar Masses
... velocities are lower than the actual velocities. If it is in the plane of observation then twice per orbit the stars will pass in front of each other and the total luminosity will dim.[Eclipsing Binary] Sufficient visual or eclipsing binaries are known to check the mass-luminosity relationship deriv ...
... velocities are lower than the actual velocities. If it is in the plane of observation then twice per orbit the stars will pass in front of each other and the total luminosity will dim.[Eclipsing Binary] Sufficient visual or eclipsing binaries are known to check the mass-luminosity relationship deriv ...
- Lowell Observatory
... We checked the old observations obtained between 1955 and 1962 in Radcliff Observatory, South Africa. Fig. 2 below shows the comparison between the spectra obtained in 1961 and 2005. The similarity is striking. At that time, star A was a WN6 star as it is now. We do not see any absorption lines and ...
... We checked the old observations obtained between 1955 and 1962 in Radcliff Observatory, South Africa. Fig. 2 below shows the comparison between the spectra obtained in 1961 and 2005. The similarity is striking. At that time, star A was a WN6 star as it is now. We do not see any absorption lines and ...
PPT
... Energy gradually leaks out of the radiation zone in the form of randomly bouncing photons. The photons bounce off electrons and make a “random walk”. It can take over 100,000 years for a photon to reach the surface. ...
... Energy gradually leaks out of the radiation zone in the form of randomly bouncing photons. The photons bounce off electrons and make a “random walk”. It can take over 100,000 years for a photon to reach the surface. ...
Famous Constellations
... Orion, the Hunter, famous constellation named from Greek Mythology It is most easily recognized constellation https://img1.etsystatic.com/009/1/5742776/il_570xN.411934929_a84j.jpg Ursa Major is also famous and very important because it points to North Star Ursa Major means Big Bear in Latin http://3 ...
... Orion, the Hunter, famous constellation named from Greek Mythology It is most easily recognized constellation https://img1.etsystatic.com/009/1/5742776/il_570xN.411934929_a84j.jpg Ursa Major is also famous and very important because it points to North Star Ursa Major means Big Bear in Latin http://3 ...
dtu7ech01 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Ancient constellations were imaginary pictures outlined by familiar patterns of stars. ...
... Ancient constellations were imaginary pictures outlined by familiar patterns of stars. ...
Talk
... Teff and log(g) obtained from the fit to the whole spectrum were select the “hot” or “cold” solutions from the line profiles ...
... Teff and log(g) obtained from the fit to the whole spectrum were select the “hot” or “cold” solutions from the line profiles ...
Stella Finger Prints
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
Astronomy 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... E. Estimate Main-Sequence Life of Sun. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of the Sun: i.e., how long the Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You wi ...
... E. Estimate Main-Sequence Life of Sun. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of the Sun: i.e., how long the Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You wi ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... evolution can not be studied by observing individual stars as most changes occur over millions and billions of years. Astrophysicists observe numerous stars at various stages in their evolutionary history to determine their changing properties and probable evolutionary tracks across the H-R diagram. ...
... evolution can not be studied by observing individual stars as most changes occur over millions and billions of years. Astrophysicists observe numerous stars at various stages in their evolutionary history to determine their changing properties and probable evolutionary tracks across the H-R diagram. ...
Star Finder
... Find the Big Dipper Asterism and note the three stars of the handle (The middle star is shown as a double whose visibility was used by the ancient Egyptians as an “eye” exam for civil service). Image follow the arc of the handle away from the four stars of the cup portion of the Big Dipper. The arc ...
... Find the Big Dipper Asterism and note the three stars of the handle (The middle star is shown as a double whose visibility was used by the ancient Egyptians as an “eye” exam for civil service). Image follow the arc of the handle away from the four stars of the cup portion of the Big Dipper. The arc ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.