WK8revised
... “Perhaps the greatest anomaly in this situation is the incredibly weak scientific case for the whole scenario of cosmic evolution. There can be no "experiments" or "observations" of stars evolving, in the very nature of the case, so it cannot be scientific, though it may be naturalistic - all based ...
... “Perhaps the greatest anomaly in this situation is the incredibly weak scientific case for the whole scenario of cosmic evolution. There can be no "experiments" or "observations" of stars evolving, in the very nature of the case, so it cannot be scientific, though it may be naturalistic - all based ...
Introducing the Sun-Earth
... • Our sun is just an “average star” and one of 100 billion or so stars in our galaxy. Joined by billions of other galaxies in the universe. • The term “average star” is how astronomers classify stars by temperature, luminosity, and mass. The sun is not unusually hot or cold, old or young, or large o ...
... • Our sun is just an “average star” and one of 100 billion or so stars in our galaxy. Joined by billions of other galaxies in the universe. • The term “average star” is how astronomers classify stars by temperature, luminosity, and mass. The sun is not unusually hot or cold, old or young, or large o ...
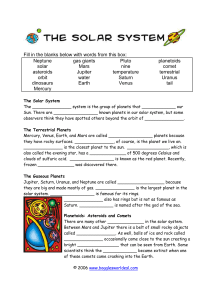
Solar System Notes
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
... Solar System Notes Solar System- A group of planets, moons and other satellites that orbit around a star. The Sun-the most important object in our solar system. Our sun provides light and heat for earth Our sun is a star When the sun rises and sets it looks like it is moving but it is not actually m ...
Planetary Motions - LathamWHS13-14
... Measures time interval from noon on one day to noon on the next day Noon occurs when the sun is at the highest point in the sky ...
... Measures time interval from noon on one day to noon on the next day Noon occurs when the sun is at the highest point in the sky ...
Chapter 2
... 1. The following diagram shows the relative position of some galaxies (2.5 Mly = 2.5 million light years). The location labeled "X" is the observation point. ...
... 1. The following diagram shows the relative position of some galaxies (2.5 Mly = 2.5 million light years). The location labeled "X" is the observation point. ...
Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 1. Describe the three types of plate boundaries and characteristic features associated with them. 2. Know the 3 types of faults, what causes them, and what occurs along them. 3. Describe the agents of ...
... 1. Describe the three types of plate boundaries and characteristic features associated with them. 2. Know the 3 types of faults, what causes them, and what occurs along them. 3. Describe the agents of ...
UNIT 4 STUDY GUIDE Objectives
... What is the difference between the penumbra and the umbra? What causes the tides? How many high & low tides are there per day? What is the difference between a neap tide and a spring tide? What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three law ...
... What is the difference between the penumbra and the umbra? What causes the tides? How many high & low tides are there per day? What is the difference between a neap tide and a spring tide? What’s the difference between heliocentric & geocentric models of the solar system? What are Kepler’s three law ...
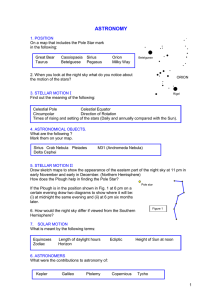
Astronomy work sheet
... the night sky which planets are closer to the Sun than the Earth? 11. ASTRONOMICAL TERMS What is meant by the following: Galaxy Magnitude Red Shift Black Hole ...
... the night sky which planets are closer to the Sun than the Earth? 11. ASTRONOMICAL TERMS What is meant by the following: Galaxy Magnitude Red Shift Black Hole ...
SNC1P - The Study of the Universe Exam Practice Questions
... 9. What causes tides on Earth? Tides are caused by the gravitational pull that the Earth and the moon exert on one another 10. Which planet has the coldest average surface temperature? Neptune (-235oC) 11. Which planets are the gas giants? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 12. Which planet is one ast ...
... 9. What causes tides on Earth? Tides are caused by the gravitational pull that the Earth and the moon exert on one another 10. Which planet has the coldest average surface temperature? Neptune (-235oC) 11. Which planets are the gas giants? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune 12. Which planet is one ast ...
Geocentric vs. Heliocentric Models of the Solar System
... A. a way to measure angles B. a way to measure the baseline C. a way to measure distances D. only useful for astronomical objects greater than a few hundered light years away. ...
... A. a way to measure angles B. a way to measure the baseline C. a way to measure distances D. only useful for astronomical objects greater than a few hundered light years away. ...
Fermi Quiz Instructions
... standing shoulder to shoulder and toe to toe on the surface of a newly discovered exo-planet, what would be the radius of the planet? ...
... standing shoulder to shoulder and toe to toe on the surface of a newly discovered exo-planet, what would be the radius of the planet? ...
Early history of astronomy
... Two primary motions • Revolution • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imagin ...
... Two primary motions • Revolution • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imagin ...
Solar System
... Simple Facts • Our solar system consists of nine planets orbiting around one sun. • Measurement in space: 1 astronomical unit (AU) = 150 million kilometers. ...
... Simple Facts • Our solar system consists of nine planets orbiting around one sun. • Measurement in space: 1 astronomical unit (AU) = 150 million kilometers. ...
Section 26.1 - CPO Science
... While the Ptolemaic model could predict the positions of the planets, Nicholas Copernicus found that its predictions became less and less accurate over the centuries. In Copernicus’ model, the Sun was at the center of the solar system and the planets orbited in circles around the Sun. ...
... While the Ptolemaic model could predict the positions of the planets, Nicholas Copernicus found that its predictions became less and less accurate over the centuries. In Copernicus’ model, the Sun was at the center of the solar system and the planets orbited in circles around the Sun. ...
Earth, Sun and Moon
... • By measuring the ages of lunar rocks, we know that the moon is about 4.6 billion years old, or about the same age as Earth. • The distance between the Earth and its moon averages about 238,900 miles (384,000 kilometers). The diameter of the moon is 2,160 miles (3,476 kilometers). The moon's mass—t ...
... • By measuring the ages of lunar rocks, we know that the moon is about 4.6 billion years old, or about the same age as Earth. • The distance between the Earth and its moon averages about 238,900 miles (384,000 kilometers). The diameter of the moon is 2,160 miles (3,476 kilometers). The moon's mass—t ...
Astronomy In the News Parallax Class demos: Parallax
... • Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point Which “move” more- closer or farther objects? ...
... • Your right eye is the Earth in June Watch the apparent motion of your thumb against a distant reference point Which “move” more- closer or farther objects? ...
Studying Space
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...
... Parallax of stars • Aids scientists in measuring distance. • It is the apparent shift of a star over a 6 month period. • It is just like when you shut 1 eye & look at an object; then open the other & the object appears to have moved. ...