Earth`s Shape
... a. The altitude (height or angle made between the observer’s eyea and the observer’s horizon) of Polaris is equal to the observer’s latitude (only in the northern hemisphere). ...
... a. The altitude (height or angle made between the observer’s eyea and the observer’s horizon) of Polaris is equal to the observer’s latitude (only in the northern hemisphere). ...
One way to measure distance
... • Consider Figure 0.18 on page 16 in your text. This figure shows solar eclipse paths over a world map. As a group, write a description of which eclipse your group would most like to observe together, where and when you would go to observe it, and fully explain why you selected the date and site you ...
... • Consider Figure 0.18 on page 16 in your text. This figure shows solar eclipse paths over a world map. As a group, write a description of which eclipse your group would most like to observe together, where and when you would go to observe it, and fully explain why you selected the date and site you ...
Corresponding Angles and Distances forvJarded expressly for
... star 51 Librce. The early measures of this pair were considered by Admiral Smyth (see Cycle, vol. ii. p. 3 52) to indicate a circular orbit; but the stars, which have latterly been gradually approaching, have within the last two years closed up so rapidly as to be in the early part of the current ye ...
... star 51 Librce. The early measures of this pair were considered by Admiral Smyth (see Cycle, vol. ii. p. 3 52) to indicate a circular orbit; but the stars, which have latterly been gradually approaching, have within the last two years closed up so rapidly as to be in the early part of the current ye ...
Chapter 14 - Heritage Christian School
... only tool was the unaided eye. Ancient peoples had their own ideas about the universe and because it was mysterious, they developed superstitions and religions centered on the sun, moon and stars. True science began when men began to track the movements of these heavenly lights. As result very compl ...
... only tool was the unaided eye. Ancient peoples had their own ideas about the universe and because it was mysterious, they developed superstitions and religions centered on the sun, moon and stars. True science began when men began to track the movements of these heavenly lights. As result very compl ...
LAB1_1SEP09
... A sextant is used to measure the angle between the horizon and sun, moon, Venus, or North Star Used (before GPS) for navigation, especially at sea. Latitude can be determined directly (at noon) Longitude requires accurate timekeeping. ...
... A sextant is used to measure the angle between the horizon and sun, moon, Venus, or North Star Used (before GPS) for navigation, especially at sea. Latitude can be determined directly (at noon) Longitude requires accurate timekeeping. ...
Measuring the Sun - Faculty Web Sites
... Sun Facts •Earth-Sun Distance: 150,000,000 kilometers (93,000,000 miles) = 1 A.U. (Astronomical Unit) •Mass: Sun contains 99%+ of the solar system mass. ...
... Sun Facts •Earth-Sun Distance: 150,000,000 kilometers (93,000,000 miles) = 1 A.U. (Astronomical Unit) •Mass: Sun contains 99%+ of the solar system mass. ...
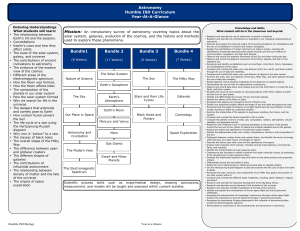
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... through the use of data and modeling. • Compare and contrast the scale, size, and distance of objects in the solar system. • Examine the scale, size, and distance of the stars, Milky Way, and other galaxies through the use of data and modeling. • Relate apparent versus absolute magnitude to the dist ...
... through the use of data and modeling. • Compare and contrast the scale, size, and distance of objects in the solar system. • Examine the scale, size, and distance of the stars, Milky Way, and other galaxies through the use of data and modeling. • Relate apparent versus absolute magnitude to the dist ...
Overview - School District of La Crosse
... A. Astrophysics- the use of atomic physics to explain how various forms of radiation are created. 1. a stars radiation is the summation of all the radiation given off by the individual atoms of the star( quantum mechanics). a. the interaction of gravity holding the atoms together in the star and und ...
... A. Astrophysics- the use of atomic physics to explain how various forms of radiation are created. 1. a stars radiation is the summation of all the radiation given off by the individual atoms of the star( quantum mechanics). a. the interaction of gravity holding the atoms together in the star and und ...
DOC
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) Dr. Iffat Sardharwalla ...
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) Dr. Iffat Sardharwalla ...
Models of the Solar System
... What is the Center of the Solar System? • The early scientists, in their attempt to answer this fundamental question created various models of the solar system. • Models, which placed Earth at the center, are called Earth-centered, or geocentric, models. ...
... What is the Center of the Solar System? • The early scientists, in their attempt to answer this fundamental question created various models of the solar system. • Models, which placed Earth at the center, are called Earth-centered, or geocentric, models. ...
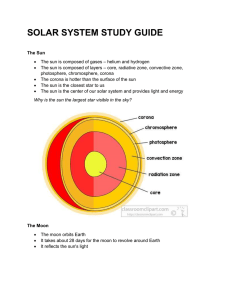
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
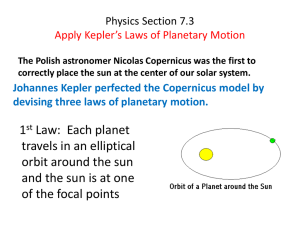
Physics Section 7.3 Apply Kepler*s Laws of Planetary
... correctly place the sun at the center of our solar system. ...
... correctly place the sun at the center of our solar system. ...
Chapter3 - The Science of Astronomy-ppt
... • 24 hour day – the time it takes the Sun to circle our sky. • Month – comes from the lunar cycle. • Calendar Year – Based on the cycle of the seasons. • Days of the week – named after the seven “naked-eye” objects that appear to move among the constellations. (Sun, Moon and five planets) • At night ...
... • 24 hour day – the time it takes the Sun to circle our sky. • Month – comes from the lunar cycle. • Calendar Year – Based on the cycle of the seasons. • Days of the week – named after the seven “naked-eye” objects that appear to move among the constellations. (Sun, Moon and five planets) • At night ...
Astronomy word grid
... 40. The largest planet 42. The line in the sky along which the Sun and the planets move Down 1. An object with an escape velocity greater than the speed of light 2. A huge cloud of low density gas sometimes shining 3. A huge collection of some hundred thousand million stars 5. A ball of ice and rock ...
... 40. The largest planet 42. The line in the sky along which the Sun and the planets move Down 1. An object with an escape velocity greater than the speed of light 2. A huge cloud of low density gas sometimes shining 3. A huge collection of some hundred thousand million stars 5. A ball of ice and rock ...
Name: _ Period: _______ Date: _______ Astronomy Vocabulary To
... 23. Background Radiation – The leftover debris, dust, and radiation (energy) from the initial big bang explosion that is found in every area of our universe. 24. Eccentricity – ratio of the distance between the foci to the length of the major axis; defines the shape of a planet’s orbit (more ellipti ...
... 23. Background Radiation – The leftover debris, dust, and radiation (energy) from the initial big bang explosion that is found in every area of our universe. 24. Eccentricity – ratio of the distance between the foci to the length of the major axis; defines the shape of a planet’s orbit (more ellipti ...
Set 2
... In 1786 James Bradley, the 3rd Astronomer Royal, noticed that the apparent positions of stars on the night sky shift slightly relative to their real positions as the Earth orbits the Sun. This effect is due to the combined effect of the finite speed of light and the motion of the Earth around its or ...
... In 1786 James Bradley, the 3rd Astronomer Royal, noticed that the apparent positions of stars on the night sky shift slightly relative to their real positions as the Earth orbits the Sun. This effect is due to the combined effect of the finite speed of light and the motion of the Earth around its or ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The sun, mass 2.0X1030kg, revolves around the center of thee galaxy with a radius of 2.2X1020 m. The period of one rotation is 2.6X108 years. a. Find the approximate mass of the galaxy. b. Assume the average star in the galaxy has the mass of the sun, find the number of ...
... of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The sun, mass 2.0X1030kg, revolves around the center of thee galaxy with a radius of 2.2X1020 m. The period of one rotation is 2.6X108 years. a. Find the approximate mass of the galaxy. b. Assume the average star in the galaxy has the mass of the sun, find the number of ...
Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name:
... The largest refracting telescope was built at the Yerkes Observatory near the end of the nineteenth century. With it, Gerald Kuiper discovered methane gas on Saturn’s moon, Titan, and two new moons of Uranus. ...
... The largest refracting telescope was built at the Yerkes Observatory near the end of the nineteenth century. With it, Gerald Kuiper discovered methane gas on Saturn’s moon, Titan, and two new moons of Uranus. ...