* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Shape
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
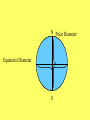
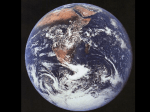
Aim: What is the shape of the Earth? I. Shape of the Earth A. The Earth is NOT a perfect sphere, but it is close!!!!! B. Oblate spheroid – the true shape of earth in which its equatorial diameter is slightly larger than its polar diameter. 1. Polar Diameter (measured from N.Pole to S. Pole) – 12,714 Km 2. Equatorial Diameter – 12,757 Km N Polar Diameter Equatorial Diameter S C. Evidence of Earth’s Shape 1. Photographs of Earth from outer space show that Earth is round 2. Years ago, sailors noticed that ships slowly disappeared or appeared over the horizon. 3. Gravity measurements a. Gravity is the force of attraction between any two objects. b. The Law of Gravitation – the gravitational force is proportional to the square of the distance between the two centers of attracted objects. Gravitational Force Distance Between two objects c. If Earth was a perfect sphere, then the force of gravity would be the same anywhere on the surface. But, the force of gravity is actually greater at the poles than at the equator. Thus, the distance from the poles to the center of the Earth is less than the distance from the equator to the center of the Earth!!!!! 4. Altitude of Polaris (North Star) a. The altitude (height or angle made between the observer’s eyea and the observer’s horizon) of Polaris is equal to the observer’s latitude (only in the northern hemisphere).