Chapter 6 Study Guide
... 15. The times when day and night are of equal length are called ______________________. 16. The force that pulls the moon toward Earth is called ___________________________. 17. If you are in a car that stops suddenly, your body keeps moving because it has ...
... 15. The times when day and night are of equal length are called ______________________. 16. The force that pulls the moon toward Earth is called ___________________________. 17. If you are in a car that stops suddenly, your body keeps moving because it has ...
Space
... The Sun is the most prominent feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible ...
... The Sun is the most prominent feature in our solar system. It is the largest object and contains approximately 98% of the total solar system mass. One hundred and nine Earths would be required to fit across the Sun's disk, and its interior could hold over 1.3 million Earths. The Sun's outer visible ...
Problems 4 File
... (ii.) The period of the planet’s orbit (in Earth years), τ . Problem 4.2 ”I see myself as a huge fiery comet, a shooting star. Everyone stops, points up and gasps ”Oh look at that!” Then whoosh, and I’m gone... and they’ll never see anything like it ever again... and they won’t be able to forget me ...
... (ii.) The period of the planet’s orbit (in Earth years), τ . Problem 4.2 ”I see myself as a huge fiery comet, a shooting star. Everyone stops, points up and gasps ”Oh look at that!” Then whoosh, and I’m gone... and they’ll never see anything like it ever again... and they won’t be able to forget me ...
Geocentric System
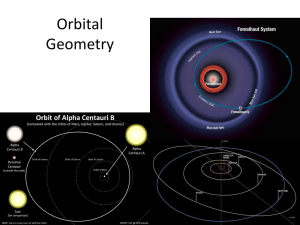
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury (once every 10 years) and Venus (Once every century), using triangulation ...
... Astronomical unit: mean distance from Earth to Sun First measured during transits of Mercury (once every 10 years) and Venus (Once every century), using triangulation ...
Distance Light travels in ONE year!
... Metric System: 1000m = 1km Astronomical Unit (AU): Earth to sun = 1 AU (1.496 x 1011 m) ...
... Metric System: 1000m = 1km Astronomical Unit (AU): Earth to sun = 1 AU (1.496 x 1011 m) ...
Gravitation Worksheet
... 4. Discuss the variation in ‘g’ with altitude and depth. 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. ...
... 4. Discuss the variation in ‘g’ with altitude and depth. 5. Derive expression for escape velocity. 6. State and prove Kepler’s second and third law of planetary motion 7. How much faster than its present rate should earth rotate about its axis so that the weight of a body at equator becomes zero? 8. ...
proposed another geocentric _ _ _ _ _.
... Kepler (1571-1630) supported Copernicus’s _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ model and applied mathematics to the observations of _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ who proceeded him. He proposed three theories to explain the _ _ _ _ _ _ of planets. His theories are now Kepler’s Laws. Kepler’s First Law describes the motio ...
... Kepler (1571-1630) supported Copernicus’s _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ model and applied mathematics to the observations of _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ who proceeded him. He proposed three theories to explain the _ _ _ _ _ _ of planets. His theories are now Kepler’s Laws. Kepler’s First Law describes the motio ...
Section 2
... is if it was the standard distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
... is if it was the standard distance from the earth. temperature is based on the color of the star • Blue or blue white is the hottest and red is the coolest ...
KS2 Earth and Space
... huge the distances involved are. Pupils will learn about how gravity keeps our solar system together. We then focus in to the Earth with pupils exploring the rotation of the Earth, day, night and shadows by getting hands-on with globes and torches. Pupils can see at first hand why it is that differe ...
... huge the distances involved are. Pupils will learn about how gravity keeps our solar system together. We then focus in to the Earth with pupils exploring the rotation of the Earth, day, night and shadows by getting hands-on with globes and torches. Pupils can see at first hand why it is that differe ...
Solar System - U
... The four inner or terrestrial planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four in ...
... The four inner or terrestrial planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates, which form their crusts and mantles, and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four in ...
PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES HOMEWORK
... The mean distance from the Sun to Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars and Jupiter are 0.39, 0.72, 1.0, 1.5, and 5.2 AU. Assume that the density, solar wind speed, total magnetic field, and temperature at the base of the corona are 20x104 #/cc, 450 km/sec, 2,5x106 oK, radial (Br) component of magnetic field ...
... The mean distance from the Sun to Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars and Jupiter are 0.39, 0.72, 1.0, 1.5, and 5.2 AU. Assume that the density, solar wind speed, total magnetic field, and temperature at the base of the corona are 20x104 #/cc, 450 km/sec, 2,5x106 oK, radial (Br) component of magnetic field ...
Year 7 Gravity and Space
... Students do not have to remember planetary information. They need to remember the order of the planets and they need to know how to use data to find patterns and trends ...
... Students do not have to remember planetary information. They need to remember the order of the planets and they need to know how to use data to find patterns and trends ...
aphelion
... The spin of a body on its axis. The motion of a body that travels around another body in space. A large cloud of gas and dust in interstellar space where stars are born. A dark, cooler area of the photosphere of the sun with a strong magnetic field. The outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere. When ...
... The spin of a body on its axis. The motion of a body that travels around another body in space. A large cloud of gas and dust in interstellar space where stars are born. A dark, cooler area of the photosphere of the sun with a strong magnetic field. The outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere. When ...
Earth at Aphelion 2015
... Institute announce that at 3 p.m. EDT on Tuesday, July 6, the Earth, in its annual orbit around the sun will be at it farthest point from the Sun. Astronomers call this point aphelion. The average distance of the earth from the sun is about 92,918,000 miles. However, the earth’s orbital path around ...
... Institute announce that at 3 p.m. EDT on Tuesday, July 6, the Earth, in its annual orbit around the sun will be at it farthest point from the Sun. Astronomers call this point aphelion. The average distance of the earth from the sun is about 92,918,000 miles. However, the earth’s orbital path around ...
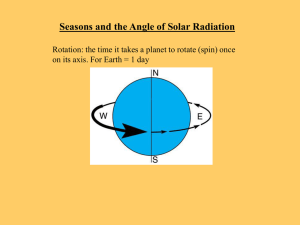
Seasons
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
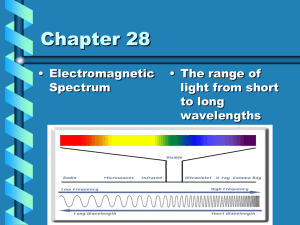
Topic E: Astrophysics
... 103 – 105 light years across Each star is approx. 1 ly apart Andromeda is about 2.5x106ly away ...
... 103 – 105 light years across Each star is approx. 1 ly apart Andromeda is about 2.5x106ly away ...
Gravity in the Solar System Quiz
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
... 9) If you are on the top of a mountain and drop an apple, it will fall to the ground, even though the apple is gravitationally attracted to you. Why? a) Earth is larger and has a much stronger gravitational pull. b) Apples always fall down. c) Centrifugal forces pull the apple to the Earth and that ...
File
... away, indicating heliocentric model • Calculated distances to other planets based on an astronomical unit (AU) • Showed that the universe was much, much larger than thought. People began thinking other stars might be suns with other planets orbiting them. ...
... away, indicating heliocentric model • Calculated distances to other planets based on an astronomical unit (AU) • Showed that the universe was much, much larger than thought. People began thinking other stars might be suns with other planets orbiting them. ...
Gravity
... 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the Sun? 3. What did Galileo see in his telescope that confirmed that planets orbit the Sun? 4. How did Tycho Brahe attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? 5. What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Su ...
... 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the Sun? 3. What did Galileo see in his telescope that confirmed that planets orbit the Sun? 4. How did Tycho Brahe attempt to test the ideas of Copernicus? 5. What paths do the planets follow as they move around the Su ...