3 - MrFuglestad
... Larger mass stars can become Red Giants several times over the course of their lifetimes as each sourc e of fuel is used up. The star expands and then pressure in the core “ignites” the next element in the succession of fusion from Hydrogen to Iron. Stars that end up with mass less than 1.5 times ou ...
... Larger mass stars can become Red Giants several times over the course of their lifetimes as each sourc e of fuel is used up. The star expands and then pressure in the core “ignites” the next element in the succession of fusion from Hydrogen to Iron. Stars that end up with mass less than 1.5 times ou ...
An Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology
... changed, 22 leap seconds have had to be added, about one every 18 months, but there were none between 1998 and 2005 showing the slowdown is not particularly regular. Leap seconds are somewhat of a nuisance for systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) Network and there is pressure to do aw ...
... changed, 22 leap seconds have had to be added, about one every 18 months, but there were none between 1998 and 2005 showing the slowdown is not particularly regular. Leap seconds are somewhat of a nuisance for systems such as the Global Positioning System (GPS) Network and there is pressure to do aw ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
... Aldebaran (K5 III) and Pollux (K0 III) are orange giants that will cool into red giants like the sun. 23.8 (OMIT THIS SECTION) Q12. Q13. Q14. Q15. Q16. Conclusion Describe what you learned about the path a star takes after it moves off the main sequence. The path is complex and depends on the star’s ...
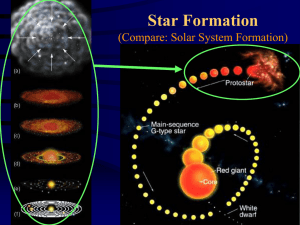
Star Life Cycles
... Stars can be bigger than the Sun! Giant and Supergiant stars are larger. Betelgeuse is 600 times greater in ...
... Stars can be bigger than the Sun! Giant and Supergiant stars are larger. Betelgeuse is 600 times greater in ...
Lecture 5
... Mass-Luminosity Relation for MainSequence Stars • Main sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for main-sequence stars • The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its lu ...
... Mass-Luminosity Relation for MainSequence Stars • Main sequence stars are stars like the Sun but with different masses • The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation between mass and luminosity for main-sequence stars • The greater the mass of a main-sequence star, the greater its lu ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
... fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... Vega is an AOV star, of effective temperature T = 9520 K, and absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol = 0.3. Given that the Sun has effective temperature 5800 K and Mbol = 4.72, estimate the radius of Vega in units of the solar radius, stating ...
... Vega is an AOV star, of effective temperature T = 9520 K, and absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol = 0.3. Given that the Sun has effective temperature 5800 K and Mbol = 4.72, estimate the radius of Vega in units of the solar radius, stating ...
Hertzsprung2 - courses.psu.edu
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
... What is the luminosity (relative to the sun) of a star 3 times more massive than the sun? ...
parallax in arc seconds
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
... member of a triple star system called the Alpha Centauri System. Proxima Centauri has the largest known stellar parallax at 0.76”. ...
6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... a. New stars form from the material of old stars. b. A star does not change its’ size or temperature during its’ life. c. The shortest stage in a star’s life cycle is the main sequence. ...
... a. New stars form from the material of old stars. b. A star does not change its’ size or temperature during its’ life. c. The shortest stage in a star’s life cycle is the main sequence. ...
Chapter 2: The Sky
... Celestial Sphere • When we look at the sky, we see stars but have no actual clue as to how far away they are. Therefore it is as if they were all on a sphere out a long distance from us. This conceptual device is known as the celestial sphere. • Distances between objects then are measured in angle ...
... Celestial Sphere • When we look at the sky, we see stars but have no actual clue as to how far away they are. Therefore it is as if they were all on a sphere out a long distance from us. This conceptual device is known as the celestial sphere. • Distances between objects then are measured in angle ...
File
... From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then write the entire sentence in your notebook. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
... From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence and then write the entire sentence in your notebook. spectrograph constellation light-year ...
chapter10
... The Final Breaths of Sun-Like Stars: Planetary Nebulae Remnants of stars with ~ 1 – a few Msun Radii: R ~ 0.2 - 3 light years Expanding at ~10 – 20 km/s ( Doppler shifts) Less than 10,000 years old ...
... The Final Breaths of Sun-Like Stars: Planetary Nebulae Remnants of stars with ~ 1 – a few Msun Radii: R ~ 0.2 - 3 light years Expanding at ~10 – 20 km/s ( Doppler shifts) Less than 10,000 years old ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... _______ 33. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? a. elliptical b. irregular c. spherical d. spiral _______ 34. Why are scientists able to use spectra to determine the composition of stars? a. Because all stars have the same composition as Earth. b. Because every chemical element has a characteristi ...
... _______ 33. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way? a. elliptical b. irregular c. spherical d. spiral _______ 34. Why are scientists able to use spectra to determine the composition of stars? a. Because all stars have the same composition as Earth. b. Because every chemical element has a characteristi ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightness is about 2x10-8W D) Distances can be calculated by measuring B and modeling L Practice Problem #3 i) Example: Distance to Alkaid (η UMa) (1) Luminosity = 700 LSun = 2.68x1029 W (2) Brightness = 2.337 ...
... C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightness is about 2x10-8W D) Distances can be calculated by measuring B and modeling L Practice Problem #3 i) Example: Distance to Alkaid (η UMa) (1) Luminosity = 700 LSun = 2.68x1029 W (2) Brightness = 2.337 ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a nearby black hole. a neutron star explodes. ...
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a nearby black hole. a neutron star explodes. ...
Brobo_solarsystem_faceoff
... Discovered the mysterious “Planet X” who’s exsistance had been proven but not observed F. His insite to the motion of the stars was rejected by the Catholic church for several decades. Basic Understanding of the Planets, Dwarf Planets, and Other Bodies 57. Why is Venus’ temperature paterns the way t ...
... Discovered the mysterious “Planet X” who’s exsistance had been proven but not observed F. His insite to the motion of the stars was rejected by the Catholic church for several decades. Basic Understanding of the Planets, Dwarf Planets, and Other Bodies 57. Why is Venus’ temperature paterns the way t ...
ES High mass star life cycle plus black holes
... Now we are going to have a little practice quiz. On Thursday we watched a video about the life cycle of a low mass star. What I would you to attempt is to draw the life cycle of a low mass star. All stars start as a nebula and this is also the ending point for many stars so this a true cycle. Protos ...
... Now we are going to have a little practice quiz. On Thursday we watched a video about the life cycle of a low mass star. What I would you to attempt is to draw the life cycle of a low mass star. All stars start as a nebula and this is also the ending point for many stars so this a true cycle. Protos ...
EM review
... Brightness measured in terms of radiated flux, F. This is the total amount of light energy emitted per surface area. Assuming that the star is spherical, F=L/4πr2, where L is the star’s luminosity. Also defined is the absolute magnitude of a star, M. This is the apparent magnitude a star would hav ...
... Brightness measured in terms of radiated flux, F. This is the total amount of light energy emitted per surface area. Assuming that the star is spherical, F=L/4πr2, where L is the star’s luminosity. Also defined is the absolute magnitude of a star, M. This is the apparent magnitude a star would hav ...
File
... –The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars and constellations to be visible at different times during the year. ...
... –The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars and constellations to be visible at different times during the year. ...
8th Grade - Astronomy
... A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the universe each with billions of stars. Astronomers classify galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Our own galaxy is called the Milk ...
... A huge group of stars, star clusters, star systems, dust and gas bound together by Galaxy gravity. There are billions of galaxies in the universe each with billions of stars. Astronomers classify galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Our own galaxy is called the Milk ...
AY 20 Fall 2010
... (2000), (2000) = position at noon GMT (Universal Time UT) on January 1, 2000 Current positions from = [m +nsintanδ]N δ = [ncos]N N=number of years since 2000 m ~ 3.07˝/yr and n ~ 20.04˝/yr ...
... (2000), (2000) = position at noon GMT (Universal Time UT) on January 1, 2000 Current positions from = [m +nsintanδ]N δ = [ncos]N N=number of years since 2000 m ~ 3.07˝/yr and n ~ 20.04˝/yr ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • The star runs out of fuel • The core shrinks and the outer parts expand • It turns red as it is cooling • This phase will last until the star exhausts its remaining fuel. • The pressure of the nuclear reaction is not strong enough to equalize the force of gravity so the star will collapse. ...
... • The star runs out of fuel • The core shrinks and the outer parts expand • It turns red as it is cooling • This phase will last until the star exhausts its remaining fuel. • The pressure of the nuclear reaction is not strong enough to equalize the force of gravity so the star will collapse. ...
"Stars" Power Point notes
... • Apparent magnitude is the apparent brightness of a star as measured on Earth. - Apparent magnitude depends on the star’s actual brightness and distance. - The smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star. (http://spaceweather.com/flybys ) ...
... • Apparent magnitude is the apparent brightness of a star as measured on Earth. - Apparent magnitude depends on the star’s actual brightness and distance. - The smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star. (http://spaceweather.com/flybys ) ...
Unit 2-1 Life Cycle of the Sun
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.