File
... per second, how long would it take to reach Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to Earth other than our Sun? Proxima Centauri is 4.01 ´ 1013 kilometers from Earth. Hint: there are ...
... per second, how long would it take to reach Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to Earth other than our Sun? Proxima Centauri is 4.01 ´ 1013 kilometers from Earth. Hint: there are ...
Constellations
... How stars would appear if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
... How stars would appear if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
PPT Format - HubbleSOURCE
... so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
... so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
Slide 1
... After the Sun's core hydrogen is depleted by nuclear fusion the core will consist primarily of 1) carbon. 2) deuterium. 3) helium. 4) oxygen. ...
... After the Sun's core hydrogen is depleted by nuclear fusion the core will consist primarily of 1) carbon. 2) deuterium. 3) helium. 4) oxygen. ...
Slide 1
... • An AU stands for ________________ The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
... • An AU stands for ________________ The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... 4. How do we know that many stars lived and died before our Sun was born? 5. Why do some giant stars pulsate in and out? 6. Why do stars in some binary systems evolve in unusual ways? ...
... 4. How do we know that many stars lived and died before our Sun was born? 5. Why do some giant stars pulsate in and out? 6. Why do stars in some binary systems evolve in unusual ways? ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... The Sun/Main Sequence Properties What are the properties of a main sequence star? How does a star’s mass affect the Luminosity, Temperature, Size, and lifespan of a star’s life? What process is responsible for producing energy in the Sun’s core? How is energy transported through the radiation zone? ...
... The Sun/Main Sequence Properties What are the properties of a main sequence star? How does a star’s mass affect the Luminosity, Temperature, Size, and lifespan of a star’s life? What process is responsible for producing energy in the Sun’s core? How is energy transported through the radiation zone? ...
Presentation for perspective graduate students 2006
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
... To determine stellar mases we rely on binary star systems. As seen from Earth, the two stars that make up this binary system are separated by less than 1/3 arcsecond. For simplicity, the diagram shows one star as remaining stationary; in reality, both stars move around their common center of mass ...
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
... This is the explosive death of a star, and often results in the star obtaining the brightness of 100 million suns for a short time. There are two general types of Supernova:Type I - These occur in binary star systems in which gas from one star falls on to a white dwarf, causing it to explode. Type I ...
... This is the explosive death of a star, and often results in the star obtaining the brightness of 100 million suns for a short time. There are two general types of Supernova:Type I - These occur in binary star systems in which gas from one star falls on to a white dwarf, causing it to explode. Type I ...
Stars - PAMS-Doyle
... • The nearest galaxy to ours is called the "Sagittarius Dwarf" and it is about 60 000 light years away from our own galaxy (the Milky Way). Assuming we can get a vehicle to reach the speed of light, it would take 60 000 years for a vehicle to travel to this galaxy. • Given current technology, it is ...
... • The nearest galaxy to ours is called the "Sagittarius Dwarf" and it is about 60 000 light years away from our own galaxy (the Milky Way). Assuming we can get a vehicle to reach the speed of light, it would take 60 000 years for a vehicle to travel to this galaxy. • Given current technology, it is ...
NAME - Net Start Class
... 19. The table above compares some facts about Venus with some facts about the planet Earth. How are the two planets MOST different? 20. It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light produced by the Sun to reach the Earth. Therefore, the Sun is located ...
... 19. The table above compares some facts about Venus with some facts about the planet Earth. How are the two planets MOST different? 20. It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light produced by the Sun to reach the Earth. Therefore, the Sun is located ...
ReviewQuestionsForClass
... How do size, temperature, and distance to a star affect its brightness? Which stars on the main sequence are the brightest? Hottest? Biggest? Bluest? Live the longest? What are the different astronomical objects? Comets, nebulae, main sequence stars, red giants, white dwarves, planetary nebulae, bin ...
... How do size, temperature, and distance to a star affect its brightness? Which stars on the main sequence are the brightest? Hottest? Biggest? Bluest? Live the longest? What are the different astronomical objects? Comets, nebulae, main sequence stars, red giants, white dwarves, planetary nebulae, bin ...
Stellar Evolution
... After the red giant phase, massive stars contract again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse elements into iron. When this occurs the star’s mass is so immense, it can no longer support it causing a sudden, violent, collapse. At this moment, the entire outer portion of the star is blown of ...
... After the red giant phase, massive stars contract again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse elements into iron. When this occurs the star’s mass is so immense, it can no longer support it causing a sudden, violent, collapse. At this moment, the entire outer portion of the star is blown of ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
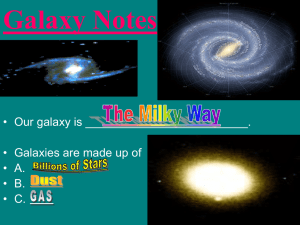
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
Assessment 1 - Stars - Teacher Key
... Iron, which acts as an energy sponge, forms within the star and the star is burning helium. 5 ...
... Iron, which acts as an energy sponge, forms within the star and the star is burning helium. 5 ...
FRIENDS OF THE PLANETARIUM NEWSLETTER April2002
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
... hottest. Stars are the same; with the hot 30,000 degree stars being a bluish white in colour and the cold stars like Betelgeuse being red. Our yellow sun lies in between with a surface temperature of around 6000 degrees. Despite its size of at least 160 million suns, its mass is only equivalent to s ...
Study Guide: Chapters 32-‐34 FROSH CHAPTER 32 1. What is
... 27. How can the elements in a star be identified? ...
... 27. How can the elements in a star be identified? ...
Temperature
... • Ionized gases at a star’s surface absorb specific frequencies of light. – Dark lines in a star’s spectrum ...
... • Ionized gases at a star’s surface absorb specific frequencies of light. – Dark lines in a star’s spectrum ...
Branches of Earth Science
... Light Year- Astronomers use light years to measure the distances ______________ stars o A light year is the distance that light ______________ in one year 9,460,730,472,580.8 km 5,878,630,000,000 miles Parallax- the apparent change in the ______________ of a star in the sky. o The change is due ...
... Light Year- Astronomers use light years to measure the distances ______________ stars o A light year is the distance that light ______________ in one year 9,460,730,472,580.8 km 5,878,630,000,000 miles Parallax- the apparent change in the ______________ of a star in the sky. o The change is due ...
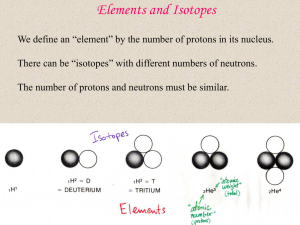
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... The temperature and pressure in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
... The temperature and pressure in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
Star Jeopardy "Review #1
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
... Type G2 star, middle of HR diagram-average size and luminosity, end of life will be white dwarf, only known star to support a planet with life. Why is our star (the sun) frequently referred to as an “average” star? Compare the important physical characteristics of the Sun with the most common types ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.