Page 48
... 2. Solar system – A large solar system is a large planetary system that consists of a combination of many smaller planetary systems and objects. 3. Planet – A planet is any of the celestial bodies (other than comets or satellites) that revolve around the sun in the solar system. Page ...
... 2. Solar system – A large solar system is a large planetary system that consists of a combination of many smaller planetary systems and objects. 3. Planet – A planet is any of the celestial bodies (other than comets or satellites) that revolve around the sun in the solar system. Page ...
Stars
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
Chapter 12
... when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
... when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit-
... After the Variable stage of a Medium to Low Mass Star, the outer shell forms a Planetary Nebula around a hot, smaller and less luminous star called a White Dwarf. White Dwarfs are about the size of our Earth but still have a mass near the original Main Sequence star. Eventually the White Dwarf will ...
... After the Variable stage of a Medium to Low Mass Star, the outer shell forms a Planetary Nebula around a hot, smaller and less luminous star called a White Dwarf. White Dwarfs are about the size of our Earth but still have a mass near the original Main Sequence star. Eventually the White Dwarf will ...
Astronomy 115 Homework Set #1 – Due: Thursday, Feb
... 1. What is the average density of the Sun? How does this compare with the average density of Jupiter? 2. How many hydrogen atoms are converted to helium each second in order to power the Sun’s luminosity? To arrive at the solution, answer the following: (a) What is the mass of 4 hydrogen atoms? (b) ...
... 1. What is the average density of the Sun? How does this compare with the average density of Jupiter? 2. How many hydrogen atoms are converted to helium each second in order to power the Sun’s luminosity? To arrive at the solution, answer the following: (a) What is the mass of 4 hydrogen atoms? (b) ...
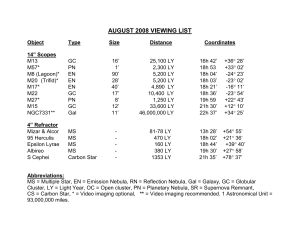
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Stars
... • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
... • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
Make one copy for each student on plain paper. Life Cycle of Star
... Make one copy for each student on plain paper. ...
... Make one copy for each student on plain paper. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
... – Smaller stars will live on for billions of years because they burn their fuel much more slowly ...
Constellation Information
... Gemini. Cancers chief attraction is the huge star cluster labeled M44. Its bright enough to see with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-pow ...
... Gemini. Cancers chief attraction is the huge star cluster labeled M44. Its bright enough to see with the naked eye as a dim, fuzzy patch if you have a clear, moonless evening at an observing site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-pow ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... thermonuclear reactions take place at its core, why doesn’t the star collapse? Answer: A white dwarf consists of carbon and oxygen. Nuclear reactions involving these nuclei require a temperature of 600 million K (pg 387). This is a lot hotter than the 10 million K for hydrogen fusion because the car ...
... thermonuclear reactions take place at its core, why doesn’t the star collapse? Answer: A white dwarf consists of carbon and oxygen. Nuclear reactions involving these nuclei require a temperature of 600 million K (pg 387). This is a lot hotter than the 10 million K for hydrogen fusion because the car ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... 13. White dwarfs are about the size of __Earth (planets)__ . 14. Neutron stars are about ___12__ miles in diameter. 15. Our Sun is a G2___ class star. 16. The MOST massive of stars live (the longest or the shortest) lives. 17. Supernovas are produced by the explosion of _super massive__ stars. The r ...
... 13. White dwarfs are about the size of __Earth (planets)__ . 14. Neutron stars are about ___12__ miles in diameter. 15. Our Sun is a G2___ class star. 16. The MOST massive of stars live (the longest or the shortest) lives. 17. Supernovas are produced by the explosion of _super massive__ stars. The r ...
Irregular Galaxies
... • It is 100,000 light years wide…In other words, it would take light 100,000 years to travel across it. Even so, the Milky Way is only one tiny piece of many, many galaxies. • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. ...
... • It is 100,000 light years wide…In other words, it would take light 100,000 years to travel across it. Even so, the Milky Way is only one tiny piece of many, many galaxies. • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. ...
30-2 Directed Reading
... c. a hot, extremely dense core of matter leftover from an old star d. a cool, extremely dense core of matter leftover from a red giant _____ 23. Where are white dwarfs located on the H-R diagram? a. in the lower left b. in the lower right c. in the upper left d. in the upper right _____ 24. An explo ...
... c. a hot, extremely dense core of matter leftover from an old star d. a cool, extremely dense core of matter leftover from a red giant _____ 23. Where are white dwarfs located on the H-R diagram? a. in the lower left b. in the lower right c. in the upper left d. in the upper right _____ 24. An explo ...
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: students may think that all of the stars in a constellation are near each ...
... science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: students may think that all of the stars in a constellation are near each ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 7. What is Nuclear Fusion? 8. How does nuclear fusion produce energy? 9. Nuclear fusion can only occur in the center of the solar system. Why is that? 10. What would happen to the orbit of a planet if it suddenly started orbiting faster? 11. As a new star is born, what type of atoms first begin to f ...
... 7. What is Nuclear Fusion? 8. How does nuclear fusion produce energy? 9. Nuclear fusion can only occur in the center of the solar system. Why is that? 10. What would happen to the orbit of a planet if it suddenly started orbiting faster? 11. As a new star is born, what type of atoms first begin to f ...
Star Types
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
... The H-R diagram “The stars are distant and unobtrusive, but bright and enduring as our fairest and most ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... The Central Problem in astronomy is distance. What we see is basically a twodimensional picture of the sky. To interpret many pieces of information available to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But B ...
... The Central Problem in astronomy is distance. What we see is basically a twodimensional picture of the sky. To interpret many pieces of information available to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But B ...
Stars
... Alpha Centauri Our nearest neighbor is actually a trinary (triple) star system consisting of two medium size stars orbiting closely around each other and a third, distant red dwarf orbiting the middle two. This red dwarf, called Proxima Centauri, is actually our nearest neighbor currently. It has a ...
... Alpha Centauri Our nearest neighbor is actually a trinary (triple) star system consisting of two medium size stars orbiting closely around each other and a third, distant red dwarf orbiting the middle two. This red dwarf, called Proxima Centauri, is actually our nearest neighbor currently. It has a ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
... A star has a high luminosity (100 solar luminosities) and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What type of star is it? ...
BrainPOP - The Science Spot
... 1. Stars change during their lifetime, which can be _______________ of years long. They start out as diffuse clouds of _______ and _________ drifting through space. __________ pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a __ ...
... 1. Stars change during their lifetime, which can be _______________ of years long. They start out as diffuse clouds of _______ and _________ drifting through space. __________ pulls the clouds together causing clumps to form. If the clump is large enough, the __________ caused by gravity inside a __ ...
1 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... 26. From the earth's north pole (a) the entire celestial sphere is visible at some time during the year, (b) only half the celestial sphere is visible during a year, (c) only stars within 23.5° of the celestial equator can ever be seen, (d) only stars within 66.5° of the north pole can ever be seen. ...
... 26. From the earth's north pole (a) the entire celestial sphere is visible at some time during the year, (b) only half the celestial sphere is visible during a year, (c) only stars within 23.5° of the celestial equator can ever be seen, (d) only stars within 66.5° of the north pole can ever be seen. ...
Friday, August 29
... • Length of the shadow of a meter stick was 0.605m • Trigonometry: 58.8 degrees (sig figs!) ...
... • Length of the shadow of a meter stick was 0.605m • Trigonometry: 58.8 degrees (sig figs!) ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.