AST121 Introduction to Astronomy
... • A graph of stars’ luminosity (or absolute magnitude since they are related) vs. temperature (or spectral type since they are related) • short for Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... • A graph of stars’ luminosity (or absolute magnitude since they are related) vs. temperature (or spectral type since they are related) • short for Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
Stars - Montville.net
... • Nuclear fusion is what causes a star to “burn” • Hydrogen is converted into helium during nuclear ...
... • Nuclear fusion is what causes a star to “burn” • Hydrogen is converted into helium during nuclear ...
Parallax - High Point University
... • A graph of stars’ luminosity (or absolute magnitude since they are related) vs. temperature (or spectral type since they are related) • short for Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
... • A graph of stars’ luminosity (or absolute magnitude since they are related) vs. temperature (or spectral type since they are related) • short for Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ...
Topic 3 – Waves and the Universe
... o 3. The Phoenix lander discovered frozen water in the Martian soil in 2008 (still no direct evidence of life on Mars at present, though) Beyond the Solar System: Scientists have discovered planets orbiting other stars (in a similar way that planets orbit the Sun in our Solar System), but they are t ...
... o 3. The Phoenix lander discovered frozen water in the Martian soil in 2008 (still no direct evidence of life on Mars at present, though) Beyond the Solar System: Scientists have discovered planets orbiting other stars (in a similar way that planets orbit the Sun in our Solar System), but they are t ...
Topic 3 notes - WordPress.com
... o 3. The Phoenix lander discovered frozen water in the Martian soil in 2008 (still no direct evidence of life on Mars at present, though) Beyond the Solar System: Scientists have discovered planets orbiting other stars (in a similar way that planets orbit the Sun in our Solar System), but they are t ...
... o 3. The Phoenix lander discovered frozen water in the Martian soil in 2008 (still no direct evidence of life on Mars at present, though) Beyond the Solar System: Scientists have discovered planets orbiting other stars (in a similar way that planets orbit the Sun in our Solar System), but they are t ...
Evolution of Close Binary Systems
... • Before going on to the evolution of massive stars and supernovae II, we’ll think about the evolution of close binary systems. • There are many multiple star systems in the Galaxy, but for the vast majority, the separation of the stars is large enough that one star doesn’t affect the evolution of t ...
... • Before going on to the evolution of massive stars and supernovae II, we’ll think about the evolution of close binary systems. • There are many multiple star systems in the Galaxy, but for the vast majority, the separation of the stars is large enough that one star doesn’t affect the evolution of t ...
Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 1. Describe the three types of plate boundaries and characteristic features associated with them. 2. Know the 3 types of faults, what causes them, and what occurs along them. 3. Describe the agents of ...
... 1. Describe the three types of plate boundaries and characteristic features associated with them. 2. Know the 3 types of faults, what causes them, and what occurs along them. 3. Describe the agents of ...
Observing the Solar System
... Why do the planets stay in orbit? • INERTIA and GRAVITY • Inertia is a tendency of a moving object to continue in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has. • The force of gravity attracts all objects towards each other. No one i ...
... Why do the planets stay in orbit? • INERTIA and GRAVITY • Inertia is a tendency of a moving object to continue in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place. The more mass an object has, the more inertia it has. • The force of gravity attracts all objects towards each other. No one i ...
6. 1 Star Distances 6. 2 Apparent Brightness, Intrinsic Brightness
... stars. When two stars orbit a common center of mass, astronomers find their masses by observing the period and sizes of their orbits. ...
... stars. When two stars orbit a common center of mass, astronomers find their masses by observing the period and sizes of their orbits. ...
Problem 4: magnitude of the star?
... __E___9. A patch of sky shows a dark region nearly devoid of stars when viewed in visible light. However, an infrared image shows a small area within the region that is more than ten times as bright as the Sun. You are most likely observing A. A nova B. A pulsar C. A black hole D. A planetary nebula ...
... __E___9. A patch of sky shows a dark region nearly devoid of stars when viewed in visible light. However, an infrared image shows a small area within the region that is more than ten times as bright as the Sun. You are most likely observing A. A nova B. A pulsar C. A black hole D. A planetary nebula ...
Gemini South telescope makes the case for multiple Earth
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
... companions to the primary “host” star, to within a distance that is less than that of Mercury from our Sun. Faint “M-class” stars such as TRAPPIST-1 are of great interest to astronomers: their diminutive size allows easier detection of small, terrestrial planets. In the TRAPPIST-1 system, two of the ...
sample exam 1
... chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 9. In the 1996 movie Independence Day, an alien ship with “a quarter [of] the mass of the Moon” comes from outside the solar system and enters orbit around Earth. ...
... chosen, so I know which ones to grade. Please answer each question in sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 9. In the 1996 movie Independence Day, an alien ship with “a quarter [of] the mass of the Moon” comes from outside the solar system and enters orbit around Earth. ...
Option: Astrophysics Objects in the Universe: Asteroid: a small rocky
... 3. Terrestrial planets are dense, rocky and small; Jovian planets are gaseous and large Jovian Planets ...
... 3. Terrestrial planets are dense, rocky and small; Jovian planets are gaseous and large Jovian Planets ...
Evolution of Stars and Galaxies
... Typical absolute magnitude with yellow light. Takes 8 min. to get here Unusual: Sun is not part of a multiple star system or cluster (only 1 star near us!) ...
... Typical absolute magnitude with yellow light. Takes 8 min. to get here Unusual: Sun is not part of a multiple star system or cluster (only 1 star near us!) ...
Star Constellations - rosedalegrade9astronomy
... Astronomy is the study of the universe and the objects in it. The Universe is all the matter and energy that exists everywhere. The universe includes: o All stars and constellations, galaxies ...
... Astronomy is the study of the universe and the objects in it. The Universe is all the matter and energy that exists everywhere. The universe includes: o All stars and constellations, galaxies ...
Spectral Variations of Several RV Tauri Type Stars Patrick Durant
... results which include the run of temperature and luminosity variations vs. the star’s photometric behavior. Changes in other physical parameters as a function of phase are also ...
... results which include the run of temperature and luminosity variations vs. the star’s photometric behavior. Changes in other physical parameters as a function of phase are also ...
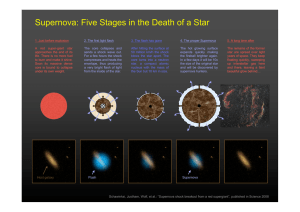
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
... After hitting the surface at 50 million km/h the shock blows the star apart. The core turns into a neutron star, a compact atomic nucleus with the mass of the Sun but 10 km in size. ...
... After hitting the surface at 50 million km/h the shock blows the star apart. The core turns into a neutron star, a compact atomic nucleus with the mass of the Sun but 10 km in size. ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... Magnitude system for brightness • Smaller numbers imply brighter stars. • “Apparent magnitude” is a measure of apparent brightness. Antares has mag. 1; Polaris has mag. 2; naked eye limit is about 6. Sirius has mag. –1.5. • “Absolute magnitude” is a measure of true brightness. It’s what the apparen ...
... Magnitude system for brightness • Smaller numbers imply brighter stars. • “Apparent magnitude” is a measure of apparent brightness. Antares has mag. 1; Polaris has mag. 2; naked eye limit is about 6. Sirius has mag. –1.5. • “Absolute magnitude” is a measure of true brightness. It’s what the apparen ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
... • Luminosity – brightness, or energy output of a star per second • Temperature- in stars, the temperature determines the luminosity and the rate of nuclear reactions (fusion) ...
September Evening Skies
... Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled on the map. The double star (Dbl) at the bend of the handle of the Big Dipper is easily detected. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. ...
... Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled on the map. The double star (Dbl) at the bend of the handle of the Big Dipper is easily detected. Much more difficult is the double star near Vega in Lyra. ...
Stars - RSM Home
... in the Milky Way. Who has seen it through a telescope? In what Constellation is it located? ...
... in the Milky Way. Who has seen it through a telescope? In what Constellation is it located? ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.