A105 –Stars and Galaxies
... Estimate the period of the orbit (the time for one complete orbit, or the time between maximums (or minimums) in the velocity curve). What is the length of the “year” of 51 Peg’s planet? Next, estimate the mass of 51 Peg’s planet. The following graph relates the mass of the planet to the range of ve ...
... Estimate the period of the orbit (the time for one complete orbit, or the time between maximums (or minimums) in the velocity curve). What is the length of the “year” of 51 Peg’s planet? Next, estimate the mass of 51 Peg’s planet. The following graph relates the mass of the planet to the range of ve ...
Parallax, Event Horizon, HR diagrams equation
... Physics : distance to the stars and counting the stars "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
... Physics : distance to the stars and counting the stars "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... A planet needs the right star! Constraints on star systems: 1) Old enough to allow time for evolution (rules out high-mass stars - 1%) 2) Need to have stable orbits (might rule out binary/multiple star systems - 50%) 3) Size of “habitable zone”: region in which a planet of the right size could have ...
... A planet needs the right star! Constraints on star systems: 1) Old enough to allow time for evolution (rules out high-mass stars - 1%) 2) Need to have stable orbits (might rule out binary/multiple star systems - 50%) 3) Size of “habitable zone”: region in which a planet of the right size could have ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the development of nocturnal navigation. Today stargazing is mostly a hobby. But stargazing can prove very useful if ...
... constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the development of nocturnal navigation. Today stargazing is mostly a hobby. But stargazing can prove very useful if ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... White Dwarf • The remaining core becomes a white dwarf • White dwarfs are usually composed of carbon and oxygen (can not fuse carbon) • Oxygen-neon-magnesium white dwarfs can also form (hot enough to fuse carbon but not neon) • Helium white dwarfs can form ...
... White Dwarf • The remaining core becomes a white dwarf • White dwarfs are usually composed of carbon and oxygen (can not fuse carbon) • Oxygen-neon-magnesium white dwarfs can also form (hot enough to fuse carbon but not neon) • Helium white dwarfs can form ...
The Sun: Example of Radiation Laws
... The production of neutrinos and the nucleosynthesis and ejection of heavy nuclei in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernov ...
... The production of neutrinos and the nucleosynthesis and ejection of heavy nuclei in Type II supernovae was confirmed by SN 1987a in the Large Magellenic Cloud, a nearby galaxy, on February 23, 1987. Neutrino detectors in Ohio and Japan detected a total of about 20 neutrinos even though this supernov ...
School Supplies - Rowan County Schools
... Large & Small Magellanic Clouds Can only be seen by astronomers in the ________________ Hemisphere The two ______________ galaxies to the Milky Way (Less than 200,000 light years away) Visible to the naked eye Relatively small and _____________ in shape Only five percent of the _________ o ...
... Large & Small Magellanic Clouds Can only be seen by astronomers in the ________________ Hemisphere The two ______________ galaxies to the Milky Way (Less than 200,000 light years away) Visible to the naked eye Relatively small and _____________ in shape Only five percent of the _________ o ...
Stellar Evolution
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
... elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H–R diagram is essentially a straight line – it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a supernova. ...
Right Ascension
... The position of a star on the main sequence is determined by its mass. Heavier stars are more luminous and hotter, and so they appear further up to the left. ...
... The position of a star on the main sequence is determined by its mass. Heavier stars are more luminous and hotter, and so they appear further up to the left. ...
Seasons
... Spins of Dancers or Ice Skaters Those Funky Coin Vortexes in Stores Tops and Gyroscopes Riding a Bicycle ...
... Spins of Dancers or Ice Skaters Those Funky Coin Vortexes in Stores Tops and Gyroscopes Riding a Bicycle ...
The Solar System. The Inner Planets.
... of impact craters. They have volcanic activity in the past (example lunar maria). Mercury has a 88-day orbit and a 59-day rotation. Temperature is up to 425oC on the day side and down to 150oC on the night side. It has many craters, but also traces of geological activity. ...
... of impact craters. They have volcanic activity in the past (example lunar maria). Mercury has a 88-day orbit and a 59-day rotation. Temperature is up to 425oC on the day side and down to 150oC on the night side. It has many craters, but also traces of geological activity. ...
Extraterrestrial Life
... • CHZ depends on all this.... And it’s smaller than HZ (which moves with time). At present HZ is 0.95 to 1.5 AU. • ‡ Np = 0.1 or 1 or 3 (optimistic view) ...
... • CHZ depends on all this.... And it’s smaller than HZ (which moves with time). At present HZ is 0.95 to 1.5 AU. • ‡ Np = 0.1 or 1 or 3 (optimistic view) ...
Origins of the Universe
... 2x as fast are 2x as far away from Earth (the Hubble Law) • The only explanation for this is that everything is moving away from us • This means the universe is ...
... 2x as fast are 2x as far away from Earth (the Hubble Law) • The only explanation for this is that everything is moving away from us • This means the universe is ...
Variable star information
... can be observed using a small telescope. In addition, these variables have all been observed using the Optical Monitoring Camera, or OMC, onboard the INTEGRAL mission. In the provided Observing list, the stars are referred to using an abbreviation depending on the type of variable they are. A short ...
... can be observed using a small telescope. In addition, these variables have all been observed using the Optical Monitoring Camera, or OMC, onboard the INTEGRAL mission. In the provided Observing list, the stars are referred to using an abbreviation depending on the type of variable they are. A short ...
Ancient Astronomy
... In 1572 observed a Super Nova – no parallax found (over night) Can’t be a star – heavens unalterable – must be near Earth In 1577 observed a comet – no parallax found Observed other stars – no parallax found Concluded Copernicus was wrong - Earth did not move Danish King built him the “Sky Castle” S ...
... In 1572 observed a Super Nova – no parallax found (over night) Can’t be a star – heavens unalterable – must be near Earth In 1577 observed a comet – no parallax found Observed other stars – no parallax found Concluded Copernicus was wrong - Earth did not move Danish King built him the “Sky Castle” S ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B pre-main
... The optical to near-infrared (300−2500 nm) spectrum of the candidate massive young stellar object (YSO) B275, embedded in the star-forming region M 17, has been observed with X-shooter on the ESO Very Large Telescope. The spectrum includes both photospheric absorption lines and emission features (H ...
... The optical to near-infrared (300−2500 nm) spectrum of the candidate massive young stellar object (YSO) B275, embedded in the star-forming region M 17, has been observed with X-shooter on the ESO Very Large Telescope. The spectrum includes both photospheric absorption lines and emission features (H ...
Phases of the Moon - Cold Lake Middle School
... is tilted on its axis, different constellations are visible during different times of year and from different parts of the earth. - Constellations which are visible year-round from the Northern Hemisphere are called circumpolar constellations because they appear to circle the North Pole throughout t ...
... is tilted on its axis, different constellations are visible during different times of year and from different parts of the earth. - Constellations which are visible year-round from the Northern Hemisphere are called circumpolar constellations because they appear to circle the North Pole throughout t ...
The solar system rotates around the sun due to the sun`s
... When we look into the universe and see that all galaxies have a red shift. What does this tell us about the universe? A ...
... When we look into the universe and see that all galaxies have a red shift. What does this tell us about the universe? A ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... other spiral galaxies to help us predict its structure. 2 million light yrs. away ...
... other spiral galaxies to help us predict its structure. 2 million light yrs. away ...
Lab 4
... Photometry is the determination and use of the color spectrum of astronomical objects to determine the objects’ properties. Two properties you will investigate later are distance and age. The objects you will use are stars in various clusters in the Milky Way galaxy and beyond. This is known as the ...
... Photometry is the determination and use of the color spectrum of astronomical objects to determine the objects’ properties. Two properties you will investigate later are distance and age. The objects you will use are stars in various clusters in the Milky Way galaxy and beyond. This is known as the ...
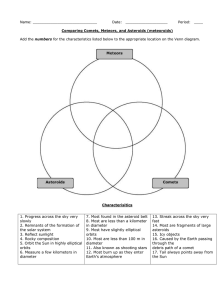
Microsoft Word - students_diffe
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
... 8. Most are less than a kilometer in diameter 9. Most have slightly elliptical orbits 10. Most are less than 100 m in diameter 11. Also known as shooting stars 12. Most burn up as they enter Earth’s atmosphere ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.