Chapter 26
... • The outer layers expand and cool. • In this late stage of its life cycle, an average star like our Sun is called a giant. ...
... • The outer layers expand and cool. • In this late stage of its life cycle, an average star like our Sun is called a giant. ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... •Galaxy: large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space. The Milky Way measures about 100,000 light-years across, and is thought to contain 200 billion stars. •Universe: the totality of known or supposed objects and phenomena thro ...
... •Galaxy: large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space. The Milky Way measures about 100,000 light-years across, and is thought to contain 200 billion stars. •Universe: the totality of known or supposed objects and phenomena thro ...
FREE Sample Here
... is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. b) It is difficult to determine which is brighter; one might guess that α Pegasi should be brighter than Scorpii. Both constellations are bright constellations, and α is the brightest star in Pegasus, while would be one of the moderatel ...
... is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. b) It is difficult to determine which is brighter; one might guess that α Pegasi should be brighter than Scorpii. Both constellations are bright constellations, and α is the brightest star in Pegasus, while would be one of the moderatel ...
astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... As we dart away from our home galaxy at many times the speed of light to get to the next cluster of galaxies in the constellations of Virgo and Coma Berenices, we travel some 50 million light years As we reach the galaxies of Virgo and Coma Berenices, we realize that our Local Group is bound to this ...
... As we dart away from our home galaxy at many times the speed of light to get to the next cluster of galaxies in the constellations of Virgo and Coma Berenices, we travel some 50 million light years As we reach the galaxies of Virgo and Coma Berenices, we realize that our Local Group is bound to this ...
FREE Sample Here
... is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. b) It is difficult to determine which is brighter; one might guess that α Pegasi should be brighter than Scorpii. Both constellations are bright constellations, and α is the brightest star in Pegasus, while would be one of the moderatel ...
... is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. b) It is difficult to determine which is brighter; one might guess that α Pegasi should be brighter than Scorpii. Both constellations are bright constellations, and α is the brightest star in Pegasus, while would be one of the moderatel ...
Mark Rubin
... • For this reason, pop III stars dominate only during the very first stages of structure formation, with an average contribution to the total star formation rate that reaches a constant value of ~10 -3 at redshift 11-13. ...
... • For this reason, pop III stars dominate only during the very first stages of structure formation, with an average contribution to the total star formation rate that reaches a constant value of ~10 -3 at redshift 11-13. ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... high-resolution, low signal-to-noise spectra (e.g. Latham et al. 2009), or photometric observations that are of higher precision and spatial resolution than the discovery observations (e.g. a neighboring eclipsing binary may be blended with the target on the survey images, but not blended when obser ...
... high-resolution, low signal-to-noise spectra (e.g. Latham et al. 2009), or photometric observations that are of higher precision and spatial resolution than the discovery observations (e.g. a neighboring eclipsing binary may be blended with the target on the survey images, but not blended when obser ...
Characteristics of Stars
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
... they imagined that groups of stars formed pictures of people or animals. Today, we call these imaginary patterns of stars constellations. Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and ...
HW7-3
... (260) RQ 3: What is a brown dwarf? A brown dwarf is a “failed star.” They are balls of gas without fusion. The upper end of brown dwarfs is well defined: 8% M☉ = 80 Jupiters. There is a not-so-welldefined line between small brown dwarfs and large planets. (260) RQ 6: Why do expanding stars become co ...
... (260) RQ 3: What is a brown dwarf? A brown dwarf is a “failed star.” They are balls of gas without fusion. The upper end of brown dwarfs is well defined: 8% M☉ = 80 Jupiters. There is a not-so-welldefined line between small brown dwarfs and large planets. (260) RQ 6: Why do expanding stars become co ...
Lecture (Powerpoint)
... happen in many places throughout the cloud at the same time This is why stars tend to be clustered Amount of stars depends on size of gas cloud producing stars ...
... happen in many places throughout the cloud at the same time This is why stars tend to be clustered Amount of stars depends on size of gas cloud producing stars ...
Celestial Sphere, Celestial equator, N
... are declination and right ascension (RA). The earth’s daily rotation makes the stars appear to rotate around us. Because we only see half the celestial sphere at any one place, this simple rotation of the stars looks more complicated and actually makes it appear that stars rise and set. The set of s ...
... are declination and right ascension (RA). The earth’s daily rotation makes the stars appear to rotate around us. Because we only see half the celestial sphere at any one place, this simple rotation of the stars looks more complicated and actually makes it appear that stars rise and set. The set of s ...
Stars and Galaxies - La Salle Elementary Public Schools No 122
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Earth and Stars
... a fixed background, such as the very distant stars) with observations made from the ends of a known baseline, the distance to the object can be calculated. •A conveniently long baseline for measuring the parallax of stars (stellar parallax) is the diameter of the Earth's orbit, where observations ar ...
... a fixed background, such as the very distant stars) with observations made from the ends of a known baseline, the distance to the object can be calculated. •A conveniently long baseline for measuring the parallax of stars (stellar parallax) is the diameter of the Earth's orbit, where observations ar ...
Slides from Lecture06
... how strong the gravitational field is around that star. (Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation; §4-7) • By studying the motion of planets around our Sun, astronomers have determined that the Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kilograms. • We cannot measure the mass of individual, isolated ...
... how strong the gravitational field is around that star. (Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation; §4-7) • By studying the motion of planets around our Sun, astronomers have determined that the Sun has a mass of 2 x 1030 kilograms. • We cannot measure the mass of individual, isolated ...
Unit 3 - Section 8.9 2011 Celestrial Objects from Earth
... of planets in the sky is from west to east, but sometimes, outer planets seem to slow to a stop, reverse direction for a time, and then resume their original direction. Copernican Revolution In 1540, Copernicus proposed that the Sun, not the Earth, was the center of the Solar System. Such a model is ...
... of planets in the sky is from west to east, but sometimes, outer planets seem to slow to a stop, reverse direction for a time, and then resume their original direction. Copernican Revolution In 1540, Copernicus proposed that the Sun, not the Earth, was the center of the Solar System. Such a model is ...
Origins Of The Universe
... Red giant – star runs out of hydrogen and eventually swells then cools, finishing ‘life’ as a white dwarf Red super giant – very large stars run out of hydrogen and swell and then explode in a supernova, finishing ‘life’ as a neutron star or black hole ...
... Red giant – star runs out of hydrogen and eventually swells then cools, finishing ‘life’ as a white dwarf Red super giant – very large stars run out of hydrogen and swell and then explode in a supernova, finishing ‘life’ as a neutron star or black hole ...
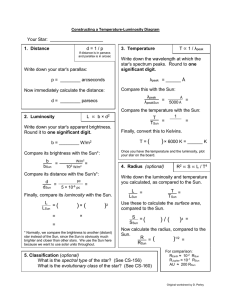
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
The Southern Fall PDF - Treasures of the Southern Sky
... in the near future. This may even have already happened, and if it has, we will know within the next 7500 years, when the light reaches us. Although a supernova event in Carina would produce a daytime star, it would not affect our planet. The story would be different if Eta Carinae had been born in ...
... in the near future. This may even have already happened, and if it has, we will know within the next 7500 years, when the light reaches us. Although a supernova event in Carina would produce a daytime star, it would not affect our planet. The story would be different if Eta Carinae had been born in ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
The Warrumbungle Observer The Warrumbungle Observer
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
... constellation Capricorn which looks like the letter ‘D’ in the eastern evening sky. Careful observations of Jupiter’s position each night will show Jupiter moving compared to the other stars in Capricorn and appearing to be moving up the left side of ‘the letter D’ Four of Jupiter’s moons are easily ...
The Solar System
... (Where do stars come from?) - Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula, which contracts due to gravity when it gets large enough. As temperatures increase, nuclear fusion begins and light is given off. Now it’s a star. - Most of its life is spent as a main sequence star -- an ave ...
... (Where do stars come from?) - Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula, which contracts due to gravity when it gets large enough. As temperatures increase, nuclear fusion begins and light is given off. Now it’s a star. - Most of its life is spent as a main sequence star -- an ave ...
88K PDF file
... 3. Chapter 12, Question 5: Albiero, a star in the constellation Cygnus, is a binary system whose components are easily separated in a small amateur telescope. Viewers describe the brighter star as “golden” and the fainter one as “sapphire blue” (a) What does this tell you about the relative tempera ...
... 3. Chapter 12, Question 5: Albiero, a star in the constellation Cygnus, is a binary system whose components are easily separated in a small amateur telescope. Viewers describe the brighter star as “golden” and the fainter one as “sapphire blue” (a) What does this tell you about the relative tempera ...
THE UNIVERSE Celestial Bodies - Joy Senior Secondary School
... A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the planet's energy. Some other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points due to their immense ...
... A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the planet's energy. Some other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points due to their immense ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.