Explain. How is Copernicus`s description of the system of planets
... • As Earth rotates, the moon's gravity pulls water toward the point on Earth's surface closest to the moon. ...
... • As Earth rotates, the moon's gravity pulls water toward the point on Earth's surface closest to the moon. ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. spectroscope d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbi ...
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. spectroscope d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbi ...
`earthlike` and second the probability that they have suitable climate
... The existence of planetary systems around other stars has been thought likely since at least the 18th century However they are very difficult to see directly with telescopes and the light reflected from such planets orbiting another star has never been observed. The reason it is so hard is that the ...
... The existence of planetary systems around other stars has been thought likely since at least the 18th century However they are very difficult to see directly with telescopes and the light reflected from such planets orbiting another star has never been observed. The reason it is so hard is that the ...
David`s Mapping the Heavens[1]
... Read the text book pg 220/221. Complete the following table. In each column outline what theory each astronomer came up with. Shapley ...
... Read the text book pg 220/221. Complete the following table. In each column outline what theory each astronomer came up with. Shapley ...
Part 2 - MGNet
... • Gas in accretion disk is heated by friction to Millions of degrees – Disk emits ultra-violet and X-ray ...
... • Gas in accretion disk is heated by friction to Millions of degrees – Disk emits ultra-violet and X-ray ...
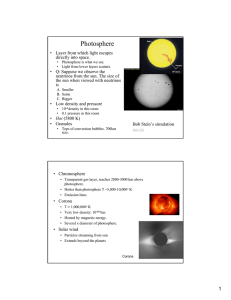
Photosphere
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram H-R plotted luminosity vs. surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram H-R plotted luminosity vs. surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. ...
Star Cycle Balloons - Communicating Astronomy With The Public
... Indicator: Describe observations accurately and carefully. Explain findings of an investigation both orally and written. ...
... Indicator: Describe observations accurately and carefully. Explain findings of an investigation both orally and written. ...
Ch 20 Notes Stars
... • Immediately after, the universe was extremely hot and made up of pure energy • There was a period of rapid expansion that caused the energy to cool, and allowed electrons, neutrons and protons to form • Hydrogen nuclei started to form but it was still too hot to ...
... • Immediately after, the universe was extremely hot and made up of pure energy • There was a period of rapid expansion that caused the energy to cool, and allowed electrons, neutrons and protons to form • Hydrogen nuclei started to form but it was still too hot to ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
... 24. The largest known stars. 25. Most low mass, red stars in our neighborhood. 26. Sirius B, the hot white dwarf only 1/1000th as luminous as the sun. 27. The vast majority of bright blue naked eye stars. 28. Most naked eye stars that appear red or orange in color. 29. The most massive young stars. ...
Circumpolar constellations
... Is there a direction you could look any clear night, no matter what time of year, and always see the same stars? Yes! Circumpolar constellations do not rise or set, but appear to move in a series of circles around Polaris, the pole star. In the northern hemisphere, between 30 and 40 degrees North la ...
... Is there a direction you could look any clear night, no matter what time of year, and always see the same stars? Yes! Circumpolar constellations do not rise or set, but appear to move in a series of circles around Polaris, the pole star. In the northern hemisphere, between 30 and 40 degrees North la ...
Solution - Caltech Astronomy
... the 96.38% of light visible in the secondary is due to the larger star, and that during the primary we expect 0.225 of this (plus the 3.62% contribution of the smaller star), which is far in excess of the 3.02% observed. Another way to estimate the temperature ratio is to note that the primary minim ...
... the 96.38% of light visible in the secondary is due to the larger star, and that during the primary we expect 0.225 of this (plus the 3.62% contribution of the smaller star), which is far in excess of the 3.02% observed. Another way to estimate the temperature ratio is to note that the primary minim ...
Life Cycle of Stars Activity
... Indicator: Describe observations accurately and carefully. Explain findings of an investigation both orally and written. ...
... Indicator: Describe observations accurately and carefully. Explain findings of an investigation both orally and written. ...
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
... • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
... • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 13
... 5. The picture below shows two cross sections of the same chunk of the universe, at time intervals separated by 2 billion years. We are on the Milky Way Galaxy, and have measured the distances to a number of other galaxies at both times. Our results (in millions of light years) are shown on the fig ...
... 5. The picture below shows two cross sections of the same chunk of the universe, at time intervals separated by 2 billion years. We are on the Milky Way Galaxy, and have measured the distances to a number of other galaxies at both times. Our results (in millions of light years) are shown on the fig ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... The stars – how far, how bright? Starlight – how bright? The discovery of stars brighter then first-magnitude extended the apparent magnitude scale upwards to 0 and then -1 and so on. The invention and development of telescopes allowed for the discovery of stars dimmer then +6, so the scale was ex ...
... The stars – how far, how bright? Starlight – how bright? The discovery of stars brighter then first-magnitude extended the apparent magnitude scale upwards to 0 and then -1 and so on. The invention and development of telescopes allowed for the discovery of stars dimmer then +6, so the scale was ex ...
mars, antares, the sting and more
... TO FIND THE SCORPION, LOOK JUST ABOVE THE HORIZON FOR STARS THAT FORM A FISHHOOK SHAPE. IT'S A LITTLE TOUGHER TO SEE THE DISTINCT OUTLINE OF THE CONSTELLATION SINCE THERE ARE TWO VISITING PLANETS AMONG THE NORMAL STARS OF THE SCORPION. BUT BE PATIENT, WE'LL GET TO THOSE SOON ENOUGH. JAMES: IT MAY BE ...
... TO FIND THE SCORPION, LOOK JUST ABOVE THE HORIZON FOR STARS THAT FORM A FISHHOOK SHAPE. IT'S A LITTLE TOUGHER TO SEE THE DISTINCT OUTLINE OF THE CONSTELLATION SINCE THERE ARE TWO VISITING PLANETS AMONG THE NORMAL STARS OF THE SCORPION. BUT BE PATIENT, WE'LL GET TO THOSE SOON ENOUGH. JAMES: IT MAY BE ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
14-1 Reading Questions: Neutron Stars
... 1. A neutron star, containing a little more than _________ solar mass, compressed to a radius of about __________, can be left as a remnant after a type ______ supernova explosion. A neutron star’s density is so high that physicists calculate that this material is stable only as a __________________ ...
... 1. A neutron star, containing a little more than _________ solar mass, compressed to a radius of about __________, can be left as a remnant after a type ______ supernova explosion. A neutron star’s density is so high that physicists calculate that this material is stable only as a __________________ ...
Comparing Earth, Sun and Jupiter
... stars and dust. This appears as a roughly linear feature on the sky The dust obscures most of the light from these stars. If there were no dust, the centre of the galaxy would be as bright as the full moon Looking in infrared light, which is less affected by dust, we can see the full structure o ...
... stars and dust. This appears as a roughly linear feature on the sky The dust obscures most of the light from these stars. If there were no dust, the centre of the galaxy would be as bright as the full moon Looking in infrared light, which is less affected by dust, we can see the full structure o ...
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
... “E” buttons to move the telescope until the central red box is centered on one of the galaxies (you can change how quickly the telescope moves - or slews - by clicking on the Slew Rate button). Next, click on Change View to change from the finder scope to the spectrometer. You will see an enlarged v ...
... “E” buttons to move the telescope until the central red box is centered on one of the galaxies (you can change how quickly the telescope moves - or slews - by clicking on the Slew Rate button). Next, click on Change View to change from the finder scope to the spectrometer. You will see an enlarged v ...
StarFlight - Center for the Presentation of Science
... conclusions were that most people interviewed knew some basic facts about the Solar System and the Constellations, but many people had incomplete understandings of the relationship between different objects in the universe. For example, a respondent who knew that the Earth revolves around the Sun, m ...
... conclusions were that most people interviewed knew some basic facts about the Solar System and the Constellations, but many people had incomplete understandings of the relationship between different objects in the universe. For example, a respondent who knew that the Earth revolves around the Sun, m ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... •Galaxy: large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space. The Milky Way measures about 100,000 light-years across, and is thought to contain 200 billion stars. •Universe: the totality of known or supposed objects and phenomena thro ...
... •Galaxy: large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space. The Milky Way measures about 100,000 light-years across, and is thought to contain 200 billion stars. •Universe: the totality of known or supposed objects and phenomena thro ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.


![David`s Mapping the Heavens[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008084229_1-877ead4b57cbb51d927fdcd6d06ce5c8-300x300.png)