Chapter 27.2
... White Dwarf Stars • For medium-sized stars, after helium fusion, the giant stage is over. • Outer gasses are lost, and a core is revealed, which heats and illuminates the expanding gasses, forming a planetary ...
... White Dwarf Stars • For medium-sized stars, after helium fusion, the giant stage is over. • Outer gasses are lost, and a core is revealed, which heats and illuminates the expanding gasses, forming a planetary ...
HOMEWORK #1
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
Scientists classify stars by
... hydrogen into helium by means of a process known as fusion. 3. It is this nuclear reaction that gives a star its energy. ...
... hydrogen into helium by means of a process known as fusion. 3. It is this nuclear reaction that gives a star its energy. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... • any object 15 to 75 times the mass of Jupiter • the object would not have been able to sustain fusion like a regular star - called "failed stars" • all are parts of a binary system. (two stars orbit around one another) • possible that brown dwarfs represent a lot of the mass in the universe ...
... • any object 15 to 75 times the mass of Jupiter • the object would not have been able to sustain fusion like a regular star - called "failed stars" • all are parts of a binary system. (two stars orbit around one another) • possible that brown dwarfs represent a lot of the mass in the universe ...
- hoganshomepage
... Spectroscope: Used to measure the chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
... Spectroscope: Used to measure the chemical composition of the stars. (also temperature and direction the star is moving in relation to the Earth.) How? Set up a spectroscope with different tubes; each gas has different spectras – light patterns. ...
Monday, October 27
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... Spiral Shaped like a spinning pinwheel Chart designation: "S" to stand for spiral galaxies ...
... Spiral Shaped like a spinning pinwheel Chart designation: "S" to stand for spiral galaxies ...
Codes of Life
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
... start to use helium as a fuel producing carbon. It also begins burning hydrogen in its atmosphere and will expand 100 times to become the red giant • When this happens to our Sun (in about 4 billion years) all inner planets and the Earth will be incinerated. ...
kolynos - Look and Learn
... only where necessary. After all, a motorist should be able to regulate his needs within a limit of ten miles ; these Aunt Sallys every few yards are silly. Country Planning should be put in the hands of an elected District Committee with one member from each parish, the members becoming part of the ...
... only where necessary. After all, a motorist should be able to regulate his needs within a limit of ten miles ; these Aunt Sallys every few yards are silly. Country Planning should be put in the hands of an elected District Committee with one member from each parish, the members becoming part of the ...
WHAT IS A STAR? - cloudfront.net
... If you remember feeling hot or pressured, this is similar to what happens to hydrogen atoms in the core of a star, where the temperature and pressure are very high. ...
... If you remember feeling hot or pressured, this is similar to what happens to hydrogen atoms in the core of a star, where the temperature and pressure are very high. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Way, is thought to have a supermassive black hole at its center. The black hole at the center of the Milky Way is sort of like the Sun at the center of our solar system - the galaxy orbits the black holes like the planets in solar systems orbit the stars. ...
... Way, is thought to have a supermassive black hole at its center. The black hole at the center of the Milky Way is sort of like the Sun at the center of our solar system - the galaxy orbits the black holes like the planets in solar systems orbit the stars. ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equilibrium): Gravity (inward) and Gas Pressure (outward) 24. Put the following structures in order from smallest to largest: Universe, star, galaxy, asteroid, planet, solar syste ...
... A. Gas/dust from a stellar nursery come together to form stars: Gravity B. Stars are made of gas, but keep a size/shape (equilibrium): Gravity (inward) and Gas Pressure (outward) 24. Put the following structures in order from smallest to largest: Universe, star, galaxy, asteroid, planet, solar syste ...
- ALMA Observatory
... Have you ever pulled a loose thread on your sweater, only to find that it has no end? Astronomers have observed a similar phenomenon in space! Two stars orbit around each other, in what is called a binary ...
... Have you ever pulled a loose thread on your sweater, only to find that it has no end? Astronomers have observed a similar phenomenon in space! Two stars orbit around each other, in what is called a binary ...
Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
... are the brightest, have an absolute magnitude of -10 Also used to show brightness of astronomical objects ...
... are the brightest, have an absolute magnitude of -10 Also used to show brightness of astronomical objects ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
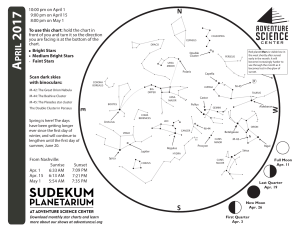
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.