Life: Definition, Origin, Criteria
... • Solar like Main Sequence star, stable for billions of years • Less than 1.5 times massive than the Sun; otherwise too much UV • More than 0.3 times the mass of the Sun; large warm region near the star for liquid water • Limited to no more than 10 billion stars ...
... • Solar like Main Sequence star, stable for billions of years • Less than 1.5 times massive than the Sun; otherwise too much UV • More than 0.3 times the mass of the Sun; large warm region near the star for liquid water • Limited to no more than 10 billion stars ...
OTA System Report For June 4, 2009 8:30 AM
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
... Previous 24 hours: 1) All hardware nominal, but FGS Thermal E442 – Aft F/G Panel is hitting YLW Hi 2) The 4 previous Acquisitions that were pending ETR telemetry were successful 3) There were 5 successful Acquisitions, and 1 TRANS Mode Observation with FGS 2 to support the AMA move. 4) 1 GSACQ was a ...
Lecture 14 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... It heats very rapidly. In just a few seconds it reaches >100,000,000K. Carbon and Oxygen ignite and burn by fusion to even heavier elements. The whole star explodes in a frenzy of nuclear burning. ...
... It heats very rapidly. In just a few seconds it reaches >100,000,000K. Carbon and Oxygen ignite and burn by fusion to even heavier elements. The whole star explodes in a frenzy of nuclear burning. ...
Document
... 3. Using Stellarium to help you find the names of the zodiacal constellations and their brightest stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try ...
... 3. Using Stellarium to help you find the names of the zodiacal constellations and their brightest stars, fill in the chart on the reverse side. The circle is the ecliptic going through the twelve constellations indicated by big arrows. Label each big arrow with the name of the constellation and try ...
Astronomy 360 - indstate.edu
... arcseconds) and indicate how far north or south of the celestial equator (defined by projecting the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere) the object lies. Lines of longitude have their equivalent in lines of right ascension (RA), but whereas longitude is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds ...
... arcseconds) and indicate how far north or south of the celestial equator (defined by projecting the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere) the object lies. Lines of longitude have their equivalent in lines of right ascension (RA), but whereas longitude is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds ...
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... • Formation time is the collapse time of the cluster, which is very short. ...
... • Formation time is the collapse time of the cluster, which is very short. ...
EARTH SCIENCE HOMEWORK 11-7 Sun`s surface
... 4. The intense __________ fields associated with sunspots might cause ___________, which are huge arching columns of ______. (pg. 730, P4) 5. Gases near a _________ sometimes brighten suddenly, shooting outward at high speed. These violent eruptions are called _______ ___________. (2 words) (pg. 730 ...
... 4. The intense __________ fields associated with sunspots might cause ___________, which are huge arching columns of ______. (pg. 730, P4) 5. Gases near a _________ sometimes brighten suddenly, shooting outward at high speed. These violent eruptions are called _______ ___________. (2 words) (pg. 730 ...
Observing the Universe 1
... 1. In which direction do the following appear to move during the day or night when viewed from the Earth, east to west, west to east, north to south or south to north. (a) Sun ...
... 1. In which direction do the following appear to move during the day or night when viewed from the Earth, east to west, west to east, north to south or south to north. (a) Sun ...
Galaxies - C. Levesque
... sequence where it is stable and consistent. • A cooler smaller star like our sun can last for about 8 billion years • Fast burning blue stars only last for a million years ...
... sequence where it is stable and consistent. • A cooler smaller star like our sun can last for about 8 billion years • Fast burning blue stars only last for a million years ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... ‘Smoking Gun’ for Stellar Explosion Mystery Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as i ...
... ‘Smoking Gun’ for Stellar Explosion Mystery Some stars end their lives in cataclysmic explosions: spectacular supernovae, which briefly become the most brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as i ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
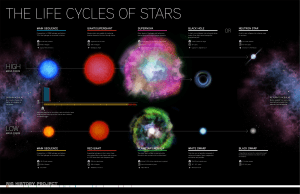
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
... When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, and then black dwarfs. For stars larger than our sun, after main sequence and giant s ...
The First Star at Night
... Canopus is the second brightest star in the night sky, so given that it is always above our horizon from here in Tasmania, one might expect that without Sirius in the sky, Canopus would always be the first star visible. However, it is rather more complicated than that. Even though we can always see ...
... Canopus is the second brightest star in the night sky, so given that it is always above our horizon from here in Tasmania, one might expect that without Sirius in the sky, Canopus would always be the first star visible. However, it is rather more complicated than that. Even though we can always see ...
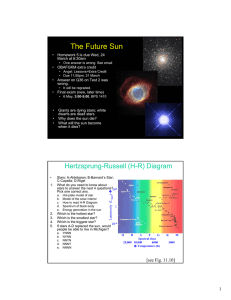
6. Star Colors and the Hertzsprung
... In many cases, the stars themselves can be used as standard candles, once the HR-diagram is calibrated. But need to know it is a main sequence star. ...
... In many cases, the stars themselves can be used as standard candles, once the HR-diagram is calibrated. But need to know it is a main sequence star. ...
Pretest
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 1
... e. Write down an explicit expression for the total gravitational potential energy of this toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: ...
... e. Write down an explicit expression for the total gravitational potential energy of this toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: ...
The Night Sky
... Assuming you can stand the cold evenings, the winter sky displays very prominent constellations, especially the hourglass shaped constellation Orion which can be seen in the southeast around 10 p.m. Orion can be used as a signpost to find other constellations and bright stars. Following Orion’s belt ...
... Assuming you can stand the cold evenings, the winter sky displays very prominent constellations, especially the hourglass shaped constellation Orion which can be seen in the southeast around 10 p.m. Orion can be used as a signpost to find other constellations and bright stars. Following Orion’s belt ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.