Name
... What is the relationship between the gravitational pull on an object and its period of revolution? (Example, if a planet is experiencing more gravitational pull acting on it from the Sun, will it have a slower or faster period of revolution?) Give an example of this in our solar system. ____________ ...
... What is the relationship between the gravitational pull on an object and its period of revolution? (Example, if a planet is experiencing more gravitational pull acting on it from the Sun, will it have a slower or faster period of revolution?) Give an example of this in our solar system. ____________ ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... So, what does support it? Electron degeneracy pressure (EDP), our old friend. The core of a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease ...
... So, what does support it? Electron degeneracy pressure (EDP), our old friend. The core of a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease ...
Day-7
... Method is robust but you must be patient: Require at least 3 transits, preferably 4 with same brightness change, duration and temporal separation (the first two establish a possible period, the third confirms it) ...
... Method is robust but you must be patient: Require at least 3 transits, preferably 4 with same brightness change, duration and temporal separation (the first two establish a possible period, the third confirms it) ...
Stellar Evolution
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
... again allowing the core to become hot enough to fuse heavier and heavier elements until they reach iron. When this occurs the star doesn’t have enough energy to further fuse iron so gravity quickly crushes the star, causing the protons and electrons to combine and become neutrons. At this moment, th ...
Astronomy Miscellaneous Items Test
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
... Answer the following questions. Answer in complete sentences, but answer succinctly. Remember: You must pass with 80% to receive credit for this section. This test is worth 3 points 1. What calendar do we use now, on a day-to-day basis? 2. The keeping of time accurately is very important to astronom ...
Parallax, Apparent Magnitude and Absolute Magnitude
... We can use similar triangles to deduce the distance of a star from its parallax shift. Figure 3 shows the parallax angle p (defined as one half of the shift in angular position six months apart), in the right angled triangle with base equal to the Earth-Sun distance and height equal to the distance, ...
... We can use similar triangles to deduce the distance of a star from its parallax shift. Figure 3 shows the parallax angle p (defined as one half of the shift in angular position six months apart), in the right angled triangle with base equal to the Earth-Sun distance and height equal to the distance, ...
Stars - Trimble County Schools
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
Lecture10
... Parallax is a tool to measure distances The Inverse-Square Law relates luminosity and brightness Low luminosity stars are more common than more luminous ones Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • M ...
... Parallax is a tool to measure distances The Inverse-Square Law relates luminosity and brightness Low luminosity stars are more common than more luminous ones Colors and spectral types measure a star’s temperature The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram is a graph plotting luminosity vs temperature • M ...
Here
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... belongs to the solar system. belongs to the Milky Way. is located as distances of less than 100 pc from us. is located in galaxies other than the Milky Way. does not belong to a particular galaxy at all. ...
... belongs to the solar system. belongs to the Milky Way. is located as distances of less than 100 pc from us. is located in galaxies other than the Milky Way. does not belong to a particular galaxy at all. ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... Note: The eye has a different response to light than mechanical devices. Thus: mV = visual apparent magnitude mB = bolometric apparent magnitude (magnitude including all wavelengths) Relationship between apparent magnitude and apparent brightness What this says is that if I have two stars with magni ...
... Note: The eye has a different response to light than mechanical devices. Thus: mV = visual apparent magnitude mB = bolometric apparent magnitude (magnitude including all wavelengths) Relationship between apparent magnitude and apparent brightness What this says is that if I have two stars with magni ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 1
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
... A. They go through first red giant, helium burning in the core, and double shell burning phases. B. Then they go through a sequence of situations where the core is contracting and heating up when no fusion is going on inside it and then stops contracting when the next type of fusion begins. Meanwhil ...
Student 4
... a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of star in our galaxy but because they are dull, individual red dwarfs cannot easily be observed. From Earth, not one is visible to the naked eye. P ...
... a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of star in our galaxy but because they are dull, individual red dwarfs cannot easily be observed. From Earth, not one is visible to the naked eye. P ...
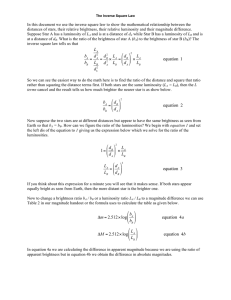
Inverse Square Law
... Earth so that bA = bB. How can we figure the ratio of the luminosities? We begin with equation 1 and set the left dis of the equation to 1 giving us the expression below which we solve for the ratio of the luminosities. ...
... Earth so that bA = bB. How can we figure the ratio of the luminosities? We begin with equation 1 and set the left dis of the equation to 1 giving us the expression below which we solve for the ratio of the luminosities. ...
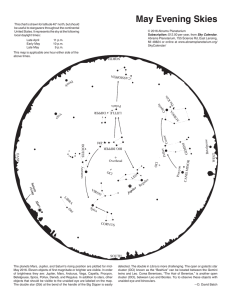
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.