The Life Cycle of a Star
... the star has ignited, it becomes a main sequence star. Main Sequence stars fuse hydrogen to form helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy. It takes about 10 billion years to consume all the hydrogen in a Main Sequence star. ...
... the star has ignited, it becomes a main sequence star. Main Sequence stars fuse hydrogen to form helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy. It takes about 10 billion years to consume all the hydrogen in a Main Sequence star. ...
Document
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
Here
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
... Constellations • People have long made up stories about groups of stars that appear close together on the sky. • Such groupings are called constellations. The sky was “officially” divided up into 88 constellations in 1930 so that a star is associated with only one constellation. ...
Stars
... through the heavens as the Earth stands still. This conclusion would be very wrong, however. It has taken astronomers thousands of years to realize that stars are different distances from us and that the scale of our universe is truly enormous. Stars that lie in the same constellation only appear to ...
... through the heavens as the Earth stands still. This conclusion would be very wrong, however. It has taken astronomers thousands of years to realize that stars are different distances from us and that the scale of our universe is truly enormous. Stars that lie in the same constellation only appear to ...
presentation source
... cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest members. GENS4001 1999-X1 ...
... cloud. Pressure builds till nuclear fusion ignites in centre, becoming a star. • Associated with disks (planetary systems), outflows and jets. • Disperse their cocoon to become visible. • Typically form in clusters, dominated by light from 1-2 brightest members. GENS4001 1999-X1 ...
Finding Constellations From Orion
... when stars illuminate it. Following the direction it’s pointing takes you to a faint constellation known as Lepus (LEE-pus), the Hare. This may be what the Great Dog is chasing. Drawing a line from the small group of stars making up Orion’s head through Betelgeuse takes us to another faint constella ...
... when stars illuminate it. Following the direction it’s pointing takes you to a faint constellation known as Lepus (LEE-pus), the Hare. This may be what the Great Dog is chasing. Drawing a line from the small group of stars making up Orion’s head through Betelgeuse takes us to another faint constella ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2003
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
... Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2007 • Initial pleasantries, who I am, who you are • This should be the most interesting course you take in college • National Solar Observatory ...
Astronomy Universe2
... • The H-R diagram represents a pattern that was discovered that allows stars to be compared by brightness and color. • The majority of stars are found in a band stretching diagonally across the diagram called the “Main Sequence”. • Stars start out in the Main Sequence and as the core cools, they mov ...
... • The H-R diagram represents a pattern that was discovered that allows stars to be compared by brightness and color. • The majority of stars are found in a band stretching diagonally across the diagram called the “Main Sequence”. • Stars start out in the Main Sequence and as the core cools, they mov ...
PHYS 1470 3.0 W16/17 Highlights of Astronomy Assignment #1
... a) If Betelgeuze’s Hour Angle, HA, is +3h 11m 00s what is the Local Sidereal Time, LST? b) If the Local Sidereal Time is 4h 10m 00s what is the Hour Angle of Betelgeuze? c) From which direction did Betelgeuze rise? In which direction will Betelgeuze set? d) Search the web to find Betelgeuze’s declin ...
... a) If Betelgeuze’s Hour Angle, HA, is +3h 11m 00s what is the Local Sidereal Time, LST? b) If the Local Sidereal Time is 4h 10m 00s what is the Hour Angle of Betelgeuze? c) From which direction did Betelgeuze rise? In which direction will Betelgeuze set? d) Search the web to find Betelgeuze’s declin ...
Stars - Moodle
... star Polaris • We know Polaris as the North Star • It is located directly above the North Pole so as the Earth spins the stars appear to move ...
... star Polaris • We know Polaris as the North Star • It is located directly above the North Pole so as the Earth spins the stars appear to move ...
Stars with mass less than 0.5 solar masses
... These are little stars, very hot initially, which cool slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime the fusion of hydrogen in the external layers. This c ...
... These are little stars, very hot initially, which cool slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime the fusion of hydrogen in the external layers. This c ...
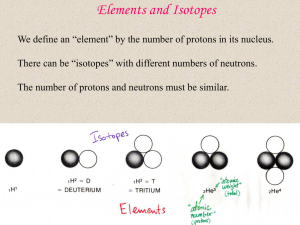
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... The temperature and pressure in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
... The temperature and pressure in the core are extreme enough for fusion (and the Sun’s gravity keeps them that way). Most energy is produced in the inner 20%. Convection carries the energy in the outer 30%. Most of the mass is in the inner 50% because the density is much higher. ...
HR Diagram (Temperature Versus Absolute Magnitude)
... • This distance is one Astronomical Unit (AU) • Astronomical units can be used to measure distances within our solar systems ...
... • This distance is one Astronomical Unit (AU) • Astronomical units can be used to measure distances within our solar systems ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... How do astronomers use parallax to measure the distances to stars? Why does parallax vary inversely with distance? Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relatio ...
... How do astronomers use parallax to measure the distances to stars? Why does parallax vary inversely with distance? Describe and explain the relationship between a star’s apparent brightness (or flux), its absolute brightness (or luminosity), and its distance from us. Describe and explain the relatio ...
Science Centre Talk
... Timescale ~1s Velocities ~1/4 c Cooling by photodisintegration γ+56Fe↔134He+4n and electron capture p++e-→n+νe ...
... Timescale ~1s Velocities ~1/4 c Cooling by photodisintegration γ+56Fe↔134He+4n and electron capture p++e-→n+νe ...
The Northern sky - Visit Isle of Man
... spectacular sights to see. In particular about an hour or more after sunset in locations such as Nairbyl, the Sound or Fort Island ...
... spectacular sights to see. In particular about an hour or more after sunset in locations such as Nairbyl, the Sound or Fort Island ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.