ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
The Sun and Other Stars - Tuslaw Local School District
... 2 or more stars called star systems • Binary stars - star systems w/ 2 stars • Triple stars - 3 stars ...
... 2 or more stars called star systems • Binary stars - star systems w/ 2 stars • Triple stars - 3 stars ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
Star Types
... sun, an O star, a white dwarf, or a red giant? Which of these star is the hottest? What are Sun-like stars (0.4 Msun < M < 8 Msun) in common? What about red dwarfs (0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun) ? Where do stars spend most of their time? ...
... sun, an O star, a white dwarf, or a red giant? Which of these star is the hottest? What are Sun-like stars (0.4 Msun < M < 8 Msun) in common? What about red dwarfs (0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun) ? Where do stars spend most of their time? ...
ASTRONOMY 1102 1
... example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not memorize rst, understand rst, and then commit to memory only a few basic de nitions and laws. Review homework. The basic properties of stars and the H{R diagram ARE NECESSARY BACK ...
... example of what the test will look like and a couple of examples of questions and problems. Review class notes: do not memorize rst, understand rst, and then commit to memory only a few basic de nitions and laws. Review homework. The basic properties of stars and the H{R diagram ARE NECESSARY BACK ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
... Many stars are found in multiple-star systems. Alpha Centauri is in a multiple star system. It is made up of three stars called a triple star system. Over half of the stars in the sky have at least one companion star. Most of these stars are double-star systems in which two stars revolve around e ...
RMH_Stellar_Evolution_Ast2001_09_29_09
... Indirect: -- must know distance Luminosity – depends on surface area (size) and temperature (Stefan-Boltzman Law) Mass -- with luminosity + physics , mass – luminosity relation ...
... Indirect: -- must know distance Luminosity – depends on surface area (size) and temperature (Stefan-Boltzman Law) Mass -- with luminosity + physics , mass – luminosity relation ...
SISTERS OF THE SUN
... • Each of them is __________ times brighter than our Sun. • The brightest one is __________ times brighter than our Sun. • They’ve been used as a/n ____________________ test all over the world. • They are related to a Celtic holiday now known as ____________________. • Are connected to a mythical or ...
... • Each of them is __________ times brighter than our Sun. • The brightest one is __________ times brighter than our Sun. • They’ve been used as a/n ____________________ test all over the world. • They are related to a Celtic holiday now known as ____________________. • Are connected to a mythical or ...
Unit 3 - Section 9.1 2011 Distances in Space0
... It makes intuitive sense that the farther a star is from Earth, the longer it takes light from the star to reach Earth. The star Polaris is 400 ly from Earth. In other words, it takes light from Polaris 400 years to reach Earth. The light that we see when we look at Polaris is 400 years old. We are ...
... It makes intuitive sense that the farther a star is from Earth, the longer it takes light from the star to reach Earth. The star Polaris is 400 ly from Earth. In other words, it takes light from Polaris 400 years to reach Earth. The light that we see when we look at Polaris is 400 years old. We are ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
... fusion and gravity are in balance – Duration ~ 10 billion years (much longer than all other stages combined) – Temperature ~ 15 million K at core, 6000 K at surface – Size ~ Sun ...
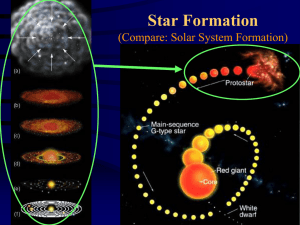
main sequence star
... sequence star. • Stars remain main sequence stars for 90% of their life. It is the longest stage in stellar evolution. • In the core, nuclear fusion is taking place. The first fusion to take place is hydrogen atoms fusing to become helium atoms. • The star stays about the same size because the gravi ...
... sequence star. • Stars remain main sequence stars for 90% of their life. It is the longest stage in stellar evolution. • In the core, nuclear fusion is taking place. The first fusion to take place is hydrogen atoms fusing to become helium atoms. • The star stays about the same size because the gravi ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.