Physics 2028: Great Ideas in Science II: The Changing Earth Module
... between the stars =⇒ the interstellar medium. 2. The planets, asteroids, and comets are the byproducts of the formation of the Sun — most of the mass in the solar system lies in the Sun! 3. The Sun and the solar system formed about 4.6 billion (4.6×109 ) years ago. a) This age is deduced from the ab ...
... between the stars =⇒ the interstellar medium. 2. The planets, asteroids, and comets are the byproducts of the formation of the Sun — most of the mass in the solar system lies in the Sun! 3. The Sun and the solar system formed about 4.6 billion (4.6×109 ) years ago. a) This age is deduced from the ab ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... An international team of astronomers, studying the left-over remnants of stars like our own Sun, have found a remarkable object where the nuclear reactor that once powered it has only just shut down. This star, the hottest known white dwarf, H1504+65, seems to have been stripped of its entire outer ...
... An international team of astronomers, studying the left-over remnants of stars like our own Sun, have found a remarkable object where the nuclear reactor that once powered it has only just shut down. This star, the hottest known white dwarf, H1504+65, seems to have been stripped of its entire outer ...
Part A
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
... Different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum have different wavelengths and different energies. You can see only a small part of the energy in these wavelengths. ...
Lecture 4 January 31 - Center for Astrophysics and Space
... Sun shrank steadily, with T rising until, about 10 million years after it started to form, it reached its current size There is a VERY fast increase in nuclear energy production above 1,000,000K. At 15,000,000K in the core nuclear power generated finally balanced the luminosity from the surface. Tha ...
... Sun shrank steadily, with T rising until, about 10 million years after it started to form, it reached its current size There is a VERY fast increase in nuclear energy production above 1,000,000K. At 15,000,000K in the core nuclear power generated finally balanced the luminosity from the surface. Tha ...
Comets, Meteors, and Meteoroids
... meteoroids are smaller than a grain of sand. The flash of light is called a meteor. Meteors usually last just a second or two. Sometimes, there are meteor showers. In a meteor shower, lots of shooting stars seem to fall from one area of the sky. These meteor showers happen when the Earth travels thr ...
... meteoroids are smaller than a grain of sand. The flash of light is called a meteor. Meteors usually last just a second or two. Sometimes, there are meteor showers. In a meteor shower, lots of shooting stars seem to fall from one area of the sky. These meteor showers happen when the Earth travels thr ...
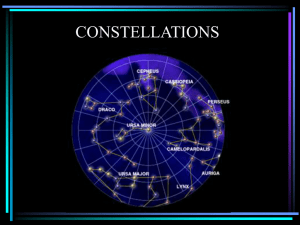
Constellations Overview
... There is a group of stars that appear in the sky all night long and all year long. It seems that these stars do not rise and set, but circle the Earth’s north pole each night. These stars are called circumpolar. ...
... There is a group of stars that appear in the sky all night long and all year long. It seems that these stars do not rise and set, but circle the Earth’s north pole each night. These stars are called circumpolar. ...
Opakování z minulého cvičení
... Comets are thought to originate in a spherical shell or halo, beyond the orbits of the planets and about halfway to the nearest star (tens of thousands of astronomical units from the Sun). Comets may have been stored in this Oort cloud since the formation of the Solar System; a rival theory suggests ...
... Comets are thought to originate in a spherical shell or halo, beyond the orbits of the planets and about halfway to the nearest star (tens of thousands of astronomical units from the Sun). Comets may have been stored in this Oort cloud since the formation of the Solar System; a rival theory suggests ...
Lecture 42
... stars, of which the star T-Tauri (now known to be a binary pair) is the type example. During this phase, a visible star begins to emerge from its cocoon of gas and dust, but it remains surrounded by its circumstellar disk. The luminosity is due entirely to continued accretion and gravitational colla ...
... stars, of which the star T-Tauri (now known to be a binary pair) is the type example. During this phase, a visible star begins to emerge from its cocoon of gas and dust, but it remains surrounded by its circumstellar disk. The luminosity is due entirely to continued accretion and gravitational colla ...
Presentation
... Death of a Star No more nuclear fusion no force to counteract force of gravity collapse Depending on mass, 3 possible outcomes: 1) White and Black Dwarf ...
... Death of a Star No more nuclear fusion no force to counteract force of gravity collapse Depending on mass, 3 possible outcomes: 1) White and Black Dwarf ...
Four Homework Assignments
... 10. Using the generic scaling relations for approximate T and ρ as a function of mass (M ) and radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is ...
... 10. Using the generic scaling relations for approximate T and ρ as a function of mass (M ) and radius (R), assuming Kramers opacity, and using the ideal gas law, derive a very approximate R(M ) for main-sequence stars from ∼1.5 M to 4.0 M . [Hint: You will need to know whether hydrogen burning is ...
After Dark M S
... supernovas, with one supernova exploding in the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, at the end of May and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of ...
... supernovas, with one supernova exploding in the Whirlpool Galaxy, M51, at the end of May and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of ...
Eyes to the Sky
... Every year or so one reaches naked-eye visibility. Even rarer are bright "Great Comets" like Hale-Bopp. ...
... Every year or so one reaches naked-eye visibility. Even rarer are bright "Great Comets" like Hale-Bopp. ...
Bluffing your way in Astronomy: Taurus
... our Sun’s surface with one square metre of Aldebaran, the bit of Sun would be a blindingly-bright yellow, while the bit of Aldebaran would be a noticeably dimmer orange. However since Aldebaran has a surface area about 1600 the size of the Sun’s, there is a lot more of it to shine light into space, ...
... our Sun’s surface with one square metre of Aldebaran, the bit of Sun would be a blindingly-bright yellow, while the bit of Aldebaran would be a noticeably dimmer orange. However since Aldebaran has a surface area about 1600 the size of the Sun’s, there is a lot more of it to shine light into space, ...
doc - Eu-Hou
... Ysard, N. Bavouzet & M. Vincendon in France. It is based on 2 images obtained from professional archives (Digital Sky Survey, photographic plates on a 48-inch (~1.2m) Schmidt telescope) and by Marc Serreau (a French amateur astronomer with a C8 (8-inch ~ 20cm) telescope. The quality of the images is ...
... Ysard, N. Bavouzet & M. Vincendon in France. It is based on 2 images obtained from professional archives (Digital Sky Survey, photographic plates on a 48-inch (~1.2m) Schmidt telescope) and by Marc Serreau (a French amateur astronomer with a C8 (8-inch ~ 20cm) telescope. The quality of the images is ...
Basic Properties of Stars
... Some stars are not on the main sequence. Some are very cool, but also very bright. Since cool objects don’t emit much light, these stars must be huge. They are red giants. Some stars are faint, but very hot. These must therefore be very small – they are white dwarf stars. ...
... Some stars are not on the main sequence. Some are very cool, but also very bright. Since cool objects don’t emit much light, these stars must be huge. They are red giants. Some stars are faint, but very hot. These must therefore be very small – they are white dwarf stars. ...
The Sun - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy CASA
... Mont Blanc neutrino detector saw a marginal signal 4.7 hours earlier. Real??? ...
... Mont Blanc neutrino detector saw a marginal signal 4.7 hours earlier. Real??? ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.