Chapter 24
... • Stellar parallax • Used for measuring distance to a star • Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth • Measured as an angle • Near stars have the largest parallax • Largest parallax is less than one second of arc ...
... • Stellar parallax • Used for measuring distance to a star • Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth • Measured as an angle • Near stars have the largest parallax • Largest parallax is less than one second of arc ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... The existence of a superwind is suggested by two independent variables. The high density observed within the observed shells in stellar ejecta, and relative paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. ...
... The existence of a superwind is suggested by two independent variables. The high density observed within the observed shells in stellar ejecta, and relative paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. ...
L10 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... The existence of a superwind is suggested by two independent variables. The high density observed within the observed shells in stellar ejecta, and relative paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. ...
... The existence of a superwind is suggested by two independent variables. The high density observed within the observed shells in stellar ejecta, and relative paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
... 13. (2 pts.) In the TV show Star Trek, the fastest the Enterprise can travel is warp 9 (1516 times the speed of light). How long would it take to travel from one end of the galaxy to the other moving at warp 9? What about from our solar system to the Galactic center? (Express your answers in the mos ...
Brightness and Distance
... steradian (a unit of solid angle). It is important to note that luminous intensity takes into account the response of the human visual system. In other words, our eyes are not equally sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light. Since the response of the human eye to brightness is close to logarit ...
... steradian (a unit of solid angle). It is important to note that luminous intensity takes into account the response of the human visual system. In other words, our eyes are not equally sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light. Since the response of the human eye to brightness is close to logarit ...
The Relationship Between a Star`s Color, Temperature, and
... • At 100 K (cold enough to freeze you solid in just seconds), a black body would emit only 5.67 W/m2. • At 10x hotter, 1000 K, the same black body would emit 104 times as much light energy, or 56,700 W/m2. ...
... • At 100 K (cold enough to freeze you solid in just seconds), a black body would emit only 5.67 W/m2. • At 10x hotter, 1000 K, the same black body would emit 104 times as much light energy, or 56,700 W/m2. ...
Properties of Stars: The H
... We can also determine the abundances of many elements in stars by using the `atomic fingerprints’ seen in spectral absorption lines. This is a tricky business! We already know that the strength and even presence of absorption lines is strongly temperature dependent. To use absorption line strengths ...
... We can also determine the abundances of many elements in stars by using the `atomic fingerprints’ seen in spectral absorption lines. This is a tricky business! We already know that the strength and even presence of absorption lines is strongly temperature dependent. To use absorption line strengths ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... Length of the Day and Sun’s path through the sky vary. One year = returns to the same spot More dramatic further north (Stonehenge) • Which stars are overhead changes with seasons. Gives passage of year ...
... Length of the Day and Sun’s path through the sky vary. One year = returns to the same spot More dramatic further north (Stonehenge) • Which stars are overhead changes with seasons. Gives passage of year ...
Stellar Evolution
... Observing Stellar Evolution in Star Clusters The following series of H–R diagrams shows how stars of the same age, but different masses, appear as the cluster as a whole ages. After 107 years, some of the most massive stars have already left the main sequence, while many of the least massive ha ...
... Observing Stellar Evolution in Star Clusters The following series of H–R diagrams shows how stars of the same age, but different masses, appear as the cluster as a whole ages. After 107 years, some of the most massive stars have already left the main sequence, while many of the least massive ha ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... • There are five constellations that are very close to the North Star. This means that they are visible in the northern sky all year long. These include: Ursa Major, the Great Bear; Ursa Minor, the Small Bear; Draco, the Dragon; Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia; and Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia. • ...
... • There are five constellations that are very close to the North Star. This means that they are visible in the northern sky all year long. These include: Ursa Major, the Great Bear; Ursa Minor, the Small Bear; Draco, the Dragon; Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia; and Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia. • ...
Stefan-Boltzmann Law Problems
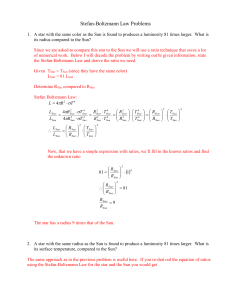
... This question is the most involved of th3ese practice problems because you are not given enough information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio o ...
... This question is the most involved of th3ese practice problems because you are not given enough information in the question to find the answer directly. The Stefan-Boltzmann Law is a relationship between luminosity, temperature and radius. In this problem we are asked to determine the radii ratio o ...
Type Ia supernovae and the ESSENCE supernova survey
... stars were smaller than less massive ones. If a white dwarf star had a mass approaching 1.4 Msun its ...
... stars were smaller than less massive ones. If a white dwarf star had a mass approaching 1.4 Msun its ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... (AAVSO) and the Chandra X-Ray mission have collaborated with variable star observations and educational materials in their mutual quest to understand stellar processes and evolution. The H-R Diagram student activity is an example of how evidence is used to construct a model to explain complex concep ...
... (AAVSO) and the Chandra X-Ray mission have collaborated with variable star observations and educational materials in their mutual quest to understand stellar processes and evolution. The H-R Diagram student activity is an example of how evidence is used to construct a model to explain complex concep ...
November 2013 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... Following Lee's “What's Up” Ron Hoekwater gave a short presentation on his visit to “Hard Luck Mine Castle”. He did some observing there, and the sky was very dark. Hard Luck is located NE of Scotty's Castle in Death Valley, in Nevada. Because of it's distance, (331 miles/~5 hours 35 min), this woul ...
... Following Lee's “What's Up” Ron Hoekwater gave a short presentation on his visit to “Hard Luck Mine Castle”. He did some observing there, and the sky was very dark. Hard Luck is located NE of Scotty's Castle in Death Valley, in Nevada. Because of it's distance, (331 miles/~5 hours 35 min), this woul ...
White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes
... Proton-proton chain (M 1.1 MSun) This is the main source of a star’s energy for spectral classes cooler than F0 It dominates at core temperatures between 3106 and about 2107 K CNO cycle (M 1.5 MSun) Same result as the PP chain, but carbon acts as a catalyst; i.e., it facilitates the fusion of ...
... Proton-proton chain (M 1.1 MSun) This is the main source of a star’s energy for spectral classes cooler than F0 It dominates at core temperatures between 3106 and about 2107 K CNO cycle (M 1.5 MSun) Same result as the PP chain, but carbon acts as a catalyst; i.e., it facilitates the fusion of ...
Stellar Evolution
... Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun Star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core Leads to a very different fate Path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line Stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the star dies in ...
... Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun Star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core Leads to a very different fate Path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line Stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off Eventually the star dies in ...
March 2010 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... constellation of Ophiuchus. While Barnard had excellent observing skills, a telescope was required to observe this star. Despite its closeness to us its magnitude is only 9.57. It is an old object, estimated at 7 to 12 billion years old, about twice the age of our sun. Since it was formed much longe ...
... constellation of Ophiuchus. While Barnard had excellent observing skills, a telescope was required to observe this star. Despite its closeness to us its magnitude is only 9.57. It is an old object, estimated at 7 to 12 billion years old, about twice the age of our sun. Since it was formed much longe ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.