PowerPoint Presentation - Research in observational
... On the (red) giant branch: the first dredge-up • The expanding envelope is cool enough for molecules to form so that the opacity goes up and envelope convection sets in. • As the convective layer grows and extends from H-burning shell to surface, it brings to the surface the by products of H burnin ...
... On the (red) giant branch: the first dredge-up • The expanding envelope is cool enough for molecules to form so that the opacity goes up and envelope convection sets in. • As the convective layer grows and extends from H-burning shell to surface, it brings to the surface the by products of H burnin ...
File - We All Love Science
... – Stars smaller than 0.1 are very rare. Why? – These low mass stars are very dim and are called “Brown Dwarf” stars due to their dim red light ...
... – Stars smaller than 0.1 are very rare. Why? – These low mass stars are very dim and are called “Brown Dwarf” stars due to their dim red light ...
Stellar temperatures and spectral types
... small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you would calculate given their distance and the inverse ...
... small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you would calculate given their distance and the inverse ...
Space Interactive Internet Scavenger Hunt
... increase in size, the energy produced in the shell is spread out over a larger area, producing lower temperatures and an orange-red color output. The sun is expected to become a red giant in about five billion years, at which point Earth may be swallowed up by the expanding star. Long before then, h ...
... increase in size, the energy produced in the shell is spread out over a larger area, producing lower temperatures and an orange-red color output. The sun is expected to become a red giant in about five billion years, at which point Earth may be swallowed up by the expanding star. Long before then, h ...
Sky Diary - Society for Popular Astronomy
... so really detailed observation will be very difficult by the end of October. The apparent proximity of both Saturn and Jupiter to the Sun means that they too are lost to detailed night time observation but, Saturn in particular, may be found and observed in daylight as long as sensible precautions a ...
... so really detailed observation will be very difficult by the end of October. The apparent proximity of both Saturn and Jupiter to the Sun means that they too are lost to detailed night time observation but, Saturn in particular, may be found and observed in daylight as long as sensible precautions a ...
10 New Constellations
... Also known as Alpha Persei, Mirfak is located around 500 light years from Earth and is the brightest star in the constellation, it's a white supergiant with a diameter around 30 times larger than the sun. Algol Also known as Beta Persei, Algol is actually a three star system located around 90 light ...
... Also known as Alpha Persei, Mirfak is located around 500 light years from Earth and is the brightest star in the constellation, it's a white supergiant with a diameter around 30 times larger than the sun. Algol Also known as Beta Persei, Algol is actually a three star system located around 90 light ...
The Death of High Mass Stars
... The hot, tiny core is now called a White Dwarf and is surrounding by a Planetary Nebula (emission line nebula) The white dwarf has ~1/2 the star’s original mass since the other half is expelled in the planetary nebula. They are small (about the size of the Earth) and extremely dense (106 g/cm3). ...
... The hot, tiny core is now called a White Dwarf and is surrounding by a Planetary Nebula (emission line nebula) The white dwarf has ~1/2 the star’s original mass since the other half is expelled in the planetary nebula. They are small (about the size of the Earth) and extremely dense (106 g/cm3). ...
celestial sphere.
... (4) The Sun appears to move west to east relative to stars (1 year cycle) Today the Sun is “in” Sagittarius, next month in Capricornus, etc. Sun’s path on the celestial sphere = ecliptic ...
... (4) The Sun appears to move west to east relative to stars (1 year cycle) Today the Sun is “in” Sagittarius, next month in Capricornus, etc. Sun’s path on the celestial sphere = ecliptic ...
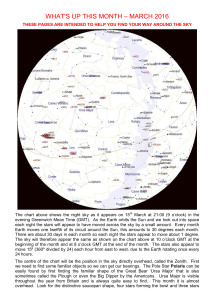
what`s up this month – march 2016
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
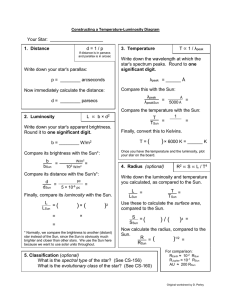
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
... have low, and even negative B-V. Cooler red stars have B-V values somewhat over 1. Create an H-R diagram of your data, as explained in the Introduction section. Use regular graph paper. Complete the following: ...
... have low, and even negative B-V. Cooler red stars have B-V values somewhat over 1. Create an H-R diagram of your data, as explained in the Introduction section. Use regular graph paper. Complete the following: ...
ASTR 1101-001 Spring 2008 - Louisiana State University
... Transient Events (in time) also occur ...
... Transient Events (in time) also occur ...
Answers - ddns.net
... 1. Planets do not move around their parent star while the star remains motionless; instead a star and its planet move around a common center of mass. Suppose that a star has mass M and a planet has mass m, and that the star is much more massive than the planet (mathematically represented as M À m). ...
... 1. Planets do not move around their parent star while the star remains motionless; instead a star and its planet move around a common center of mass. Suppose that a star has mass M and a planet has mass m, and that the star is much more massive than the planet (mathematically represented as M À m). ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation Canis Major, the Big Dog, and is commonly called the Dog Star. In ancient Greek times the dawn rising of Sirius marked the hottest part of summer. This is the origin of the phrase "dog ...
... visual magnitude of –1.42, it is twice as bright as any other star in our sky. Sirius resides in the constellation Canis Major, the Big Dog, and is commonly called the Dog Star. In ancient Greek times the dawn rising of Sirius marked the hottest part of summer. This is the origin of the phrase "dog ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.