January 2007 - Western Nevada Astronomical Society
... two successive meridian transits by the Sun. A sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds long, the length it takes a star to cross your meridian two times successively. A solar day is about 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day because while the Earth rotates on its axis it also moves along in ...
... two successive meridian transits by the Sun. A sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds long, the length it takes a star to cross your meridian two times successively. A solar day is about 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day because while the Earth rotates on its axis it also moves along in ...
Phys 1533 Descriptive Astronomy
... • Summer solstice - when the sun is at its northernmost point above the celestial equator. This is the northern hemisphere’s longest day of the year. • Winter solstice - when the sun is at its southernmost point below the celestial equator. This is the northern hemisphere’s shortest day of the year. ...
... • Summer solstice - when the sun is at its northernmost point above the celestial equator. This is the northern hemisphere’s longest day of the year. • Winter solstice - when the sun is at its southernmost point below the celestial equator. This is the northern hemisphere’s shortest day of the year. ...
SHELL H II REGIONS IN NGC 6334
... well known molecular outflow with an upper limit of 1,000 years for its age. It is conceivable that the molecular outflow and the ejection of BN and I happened in the same event. The energy in the outflow is about 4X1047 ergs, that can be provided by the formation of a close binary system or even a ...
... well known molecular outflow with an upper limit of 1,000 years for its age. It is conceivable that the molecular outflow and the ejection of BN and I happened in the same event. The energy in the outflow is about 4X1047 ergs, that can be provided by the formation of a close binary system or even a ...
Document
... red giant is increasing due to the great increase in luminosity being provided by the fusion occurring in a shell around the core. ...
... red giant is increasing due to the great increase in luminosity being provided by the fusion occurring in a shell around the core. ...
Death of Stars notes
... • The SOFIA finding demonstrates that supernovas not only produce dust, but that the dust can survive the explosion to become raw material for the formation of other stars—and planets. • This result supports the notion that most of the dust observed in distant young galaxies may have been made by su ...
... • The SOFIA finding demonstrates that supernovas not only produce dust, but that the dust can survive the explosion to become raw material for the formation of other stars—and planets. • This result supports the notion that most of the dust observed in distant young galaxies may have been made by su ...
CHAP
... - Cool stars appear _________ in color with a surface temperature of about 3,200 degrees Celsius. - Warm stars appear _____________ in color with a surface temperature of about 5,500 degrees Celsius. - The hottest stars are ____________ in color and have a surface temperature over 20,000 degrees Cel ...
... - Cool stars appear _________ in color with a surface temperature of about 3,200 degrees Celsius. - Warm stars appear _____________ in color with a surface temperature of about 5,500 degrees Celsius. - The hottest stars are ____________ in color and have a surface temperature over 20,000 degrees Cel ...
exoplanets
... •Tells little about the planet •Cannot be repeated Advantages •Can monitor many stars cheaply •Sensitive to small masses Score = 18 ...
... •Tells little about the planet •Cannot be repeated Advantages •Can monitor many stars cheaply •Sensitive to small masses Score = 18 ...
Eruptive Variables - Scientific Research Publishing
... As regards the conditions of equilibrium of a star, it is necessary to take account the radiation pressure. The formulae from the theory enable in to calculate what proportion of the weight of the stellar mass is borne by the radiation pressure, and what part being supported by the hot gases pressur ...
... As regards the conditions of equilibrium of a star, it is necessary to take account the radiation pressure. The formulae from the theory enable in to calculate what proportion of the weight of the stellar mass is borne by the radiation pressure, and what part being supported by the hot gases pressur ...
constellation - Bucks-Mont Astronomical Association
... visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the f ...
... visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this one. But its great luminosity and relative proximity makes it easy to overlook the f ...
Full Press Release - The Open University
... Figure 1: Artist impression of the AKARI satellite in orbit ...
... Figure 1: Artist impression of the AKARI satellite in orbit ...
Astrophysics notes
... A continuous spectrum upon which dark lines appear due to missing wavelengths. Produced by a cool, non-luminous gas in front of a continuous spectrum source. ...
... A continuous spectrum upon which dark lines appear due to missing wavelengths. Produced by a cool, non-luminous gas in front of a continuous spectrum source. ...
Main Sequence Lifetime
... • Core becomes extremely dense until it becomes electron degenerate (around 1000 kg per cubic ...
... • Core becomes extremely dense until it becomes electron degenerate (around 1000 kg per cubic ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Location of prime meridian is arbitrary = Greenwich observatory in UK 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies o ...
... Location of prime meridian is arbitrary = Greenwich observatory in UK 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies o ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Location of prime meridian is arbitrary = Greenwich observatory in UK 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies o ...
... Location of prime meridian is arbitrary = Greenwich observatory in UK 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies o ...
Sizing Up The Universe
... centered on the center of our galaxy (about 8,000 parsecs, or 25,000 light-years, from us). ...
... centered on the center of our galaxy (about 8,000 parsecs, or 25,000 light-years, from us). ...
Star in a Box - Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope
... This makes them change position on the Hertzprung-Russell diagram. ...
... This makes them change position on the Hertzprung-Russell diagram. ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
... • We identify a star cluster that is close enough to determine its distance by parallax • We plots its H-R diagram • Since we know the distances to the cluster stars • We can determine their luminosities ...
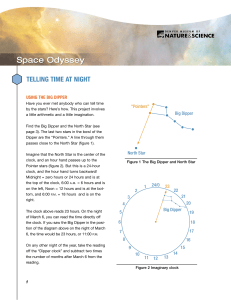
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.