astro2_lec1 - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... distances to dozens of nebulae. Even the nearest, in Andromeda, was millions of light ...
... distances to dozens of nebulae. Even the nearest, in Andromeda, was millions of light ...
Distance to the SMC
... Walter Baade, using the newly built Palomar 200 inch telescope, discovered that stars can be classified into two general age categories. Population I stars are relatively young and formed after the interstellar medium was enriched with metals from the explosions of supernova and the deaths of other ...
... Walter Baade, using the newly built Palomar 200 inch telescope, discovered that stars can be classified into two general age categories. Population I stars are relatively young and formed after the interstellar medium was enriched with metals from the explosions of supernova and the deaths of other ...
Color and Temperature of Stars
... Universe. Nevertheless, our world and everything it contains—even life ...
... Universe. Nevertheless, our world and everything it contains—even life ...
Impossible planets.
... in October 1995 to announce they’d found something their colleagues had been seeking for decades -- a planet orbiting a sunlike star. The trouble was, nobody had ordered, or even imagined, a planet quite like the object circling 51 Pegasi, a star lying 50 light-years from Earth in the constellation ...
... in October 1995 to announce they’d found something their colleagues had been seeking for decades -- a planet orbiting a sunlike star. The trouble was, nobody had ordered, or even imagined, a planet quite like the object circling 51 Pegasi, a star lying 50 light-years from Earth in the constellation ...
The Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302)
... doughnut-shaped ring of dust, which appears as a dark band pinching the nebula in the center. The thick dust belt constricts the star’s outflow, creating the classic hourglass or butterfly shape displayed by some planetary nebulae. The “wings” of this cosmic butterfly are rough and lumpy, unlike the ...
... doughnut-shaped ring of dust, which appears as a dark band pinching the nebula in the center. The thick dust belt constricts the star’s outflow, creating the classic hourglass or butterfly shape displayed by some planetary nebulae. The “wings” of this cosmic butterfly are rough and lumpy, unlike the ...
Lecture Eight (Powerpoint format) - Flash
... three years on the Hubble Space Telescope. The image covers roughly 1000 AU. The outflow appears to be highly sporadic, but it remains unclear how it is being powered or even which binary member is powering it. ...
... three years on the Hubble Space Telescope. The image covers roughly 1000 AU. The outflow appears to be highly sporadic, but it remains unclear how it is being powered or even which binary member is powering it. ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Document
... Possible solutions to the Fermi paradox 2. Low probability of intelligent life • Life seems to appear quite easily in favorable conditions • But maybe it needs very special conditions for intelligence to emerge (= to become an asset in natural selection) • On Earth, it took more than 2 billion years ...
... Possible solutions to the Fermi paradox 2. Low probability of intelligent life • Life seems to appear quite easily in favorable conditions • But maybe it needs very special conditions for intelligence to emerge (= to become an asset in natural selection) • On Earth, it took more than 2 billion years ...
Notes 6 - University of Northern Iowa
... Another fun feature of an AGB star is the start of very strong winds. These stars are very high up on the HR diagram so they are pretty luminous to begin with. This can put them over the Eddington Luminosity briefly. The stellar winds are helped along when there are particles that easily absorb ener ...
... Another fun feature of an AGB star is the start of very strong winds. These stars are very high up on the HR diagram so they are pretty luminous to begin with. This can put them over the Eddington Luminosity briefly. The stellar winds are helped along when there are particles that easily absorb ener ...
Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Exercises 2
... 6. If the Sun suddenly collapsed to a black hole, a) at what distance from the solar centre would the event horizon lie? b) What would the period of the Earth’s revolution around the Sun be? 7. For every mass m which is swallowed by a black hole (via an accretion disk, say), an amount of energy νmc ...
... 6. If the Sun suddenly collapsed to a black hole, a) at what distance from the solar centre would the event horizon lie? b) What would the period of the Earth’s revolution around the Sun be? 7. For every mass m which is swallowed by a black hole (via an accretion disk, say), an amount of energy νmc ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM
... The age of a cluster is given by the main sequence turn-off point—the highest point on the main sequence that is still populated by stars. On the left is a wellknown schematic diagram combining the HR diagrams of star clusters of different ages: NGC2362 is the youngest and M67 the oldest. The pink n ...
... The age of a cluster is given by the main sequence turn-off point—the highest point on the main sequence that is still populated by stars. On the left is a wellknown schematic diagram combining the HR diagrams of star clusters of different ages: NGC2362 is the youngest and M67 the oldest. The pink n ...
Stellar Evolution
... reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature maintained by hydrogen fusion Star leaves the main sequence, becomes a red giant! ASTR 1120: Fall 2005 ...
... reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature maintained by hydrogen fusion Star leaves the main sequence, becomes a red giant! ASTR 1120: Fall 2005 ...
Chapter 2 Discovering the Universe for Yourself What does the
... • Earth s axis points in the same direction (to Polaris) all year round, so its orientation relative to the Sun changes as Earth orbits the Sun. • Summer occurs in your hemisphere when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. • AXIS TILT is the key to the se ...
... • Earth s axis points in the same direction (to Polaris) all year round, so its orientation relative to the Sun changes as Earth orbits the Sun. • Summer occurs in your hemisphere when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. • AXIS TILT is the key to the se ...
Blowin` in the wind: both `negative` and `positive` feedback in an
... 320 km/s) is consistent with the systemic redshift of the host galaxy (Brusa et al. 2010), and it is interpreted as due to the star formation in the host galaxy. We map the spatial extent of the Hα narrow component by fitting in each spaxels of the datacube the single Gaussian derived from the integr ...
... 320 km/s) is consistent with the systemic redshift of the host galaxy (Brusa et al. 2010), and it is interpreted as due to the star formation in the host galaxy. We map the spatial extent of the Hα narrow component by fitting in each spaxels of the datacube the single Gaussian derived from the integr ...
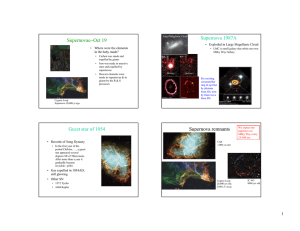
Supernovae Oct 19 − Supernova 1987A
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
iStage2_EN_iSky smart measurements of the heaven
... determine the size of the Earth. In most countries, the treatment of this subject in the school curriculum is rather theoretical. Students are not given any examples of how to apply the methods of calculation or any opportunities to compare classic methods with the use of ...
... determine the size of the Earth. In most countries, the treatment of this subject in the school curriculum is rather theoretical. Students are not given any examples of how to apply the methods of calculation or any opportunities to compare classic methods with the use of ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.