The Scales of Things
... Cepheid variable stars are pulsating stars, named after the brightest member of the class, Delta Cephei. Cepheids are brightest when they are hottest, close to the minimum size. Since all Cepheids are about the same temperature, the size of a Cepheid determines its luminosity. Thus there is a per ...
... Cepheid variable stars are pulsating stars, named after the brightest member of the class, Delta Cephei. Cepheids are brightest when they are hottest, close to the minimum size. Since all Cepheids are about the same temperature, the size of a Cepheid determines its luminosity. Thus there is a per ...
How far away are the Stars?
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age ...
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age ...
Unit 1
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
STAR MAKER Olaf Stapledon
... shrinking and condensing. The nether stars were no longer visible through it. Soon the earth below me was like a huge circular table-top, a broad disc of darkness surrounded by stars. I was apparently soaring away from my native planet at incredible speed. The sun, formerly visible to imagination in ...
... shrinking and condensing. The nether stars were no longer visible through it. Soon the earth below me was like a huge circular table-top, a broad disc of darkness surrounded by stars. I was apparently soaring away from my native planet at incredible speed. The sun, formerly visible to imagination in ...
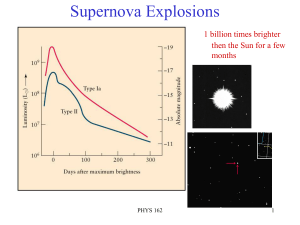
Supernovas 10/19
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
The solar system rotates around the sun due to the sun`s
... Scientists have performed lots research and the conclusions all support the theory ...
... Scientists have performed lots research and the conclusions all support the theory ...
8.2Apply Exponent Properties Involving Quotients
... of 1 in magnitude, the energy released is multiplied by a factor of about 31. How many times greater is the energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 7 than the energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 4? ...
... of 1 in magnitude, the energy released is multiplied by a factor of about 31. How many times greater is the energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 7 than the energy released by an earthquake of magnitude 4? ...
Agenda - Relativity Group
... skins inside the star. However, since fusion of iron uses up energy instead of releasing energy, an iron core cannot support the weight of the outer layers. The collapse of this core — which occurs in a fraction of a second — results in a supernova that nearly obliterates the star (perhaps leaving a ...
... skins inside the star. However, since fusion of iron uses up energy instead of releasing energy, an iron core cannot support the weight of the outer layers. The collapse of this core — which occurs in a fraction of a second — results in a supernova that nearly obliterates the star (perhaps leaving a ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2016 – HOMEWORK #3
... At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc second is 3 × 106 LV . a) Calculate the total mass, and the mass to light ratio, in the inn ...
... At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc second is 3 × 106 LV . a) Calculate the total mass, and the mass to light ratio, in the inn ...
File
... The positions of three galaxies, A, B and C, are marked on the graph. From which galaxy, A, B or C, would the wavelength of the light reaching the Earth seem to have changed the most? Galaxy ................................. Give a reason for your answer. ...
... The positions of three galaxies, A, B and C, are marked on the graph. From which galaxy, A, B or C, would the wavelength of the light reaching the Earth seem to have changed the most? Galaxy ................................. Give a reason for your answer. ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... What do star clusters and associations have to do with star formation? 10. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.18 Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or o ...
... What do star clusters and associations have to do with star formation? 10. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.18 Compare and contrast the observed properties of open star clusters and globular star clusters. 11. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.19 How can we tell whether a star cluster is young or o ...
Document
... • Patterns come from star positions ONLY • Today a constellation is a region in the sky that is named for an ancient constellation it contains. ...
... • Patterns come from star positions ONLY • Today a constellation is a region in the sky that is named for an ancient constellation it contains. ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #3
... At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc second is 3 × 106 LV . a) Calculate the total mass, and the mass to light ratio, in the inn ...
... At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc second is 3 × 106 LV . a) Calculate the total mass, and the mass to light ratio, in the inn ...
Challenging our Understanding of Stellar Structure and Evolution
... Galaxy and how does it evolve? To answer these and other fundamental questions requires masses to 1% accuracy. Why 1%? Our knowledge of stars consists of surface temperature, Te ; apparent magnitude; metallicity; distance, hence luminosity; and through Te (or long-baseline interferometry), radius; a ...
... Galaxy and how does it evolve? To answer these and other fundamental questions requires masses to 1% accuracy. Why 1%? Our knowledge of stars consists of surface temperature, Te ; apparent magnitude; metallicity; distance, hence luminosity; and through Te (or long-baseline interferometry), radius; a ...
Powerpoint Review
... about ten feet from you, which of these would be the brightest? The spotlight right? Now imagine the candle is ten feet from you and the spotlight is one mile away from you. Which one would be brighter? The candle would appear brighter. This helps to illustrate that there are three things that affec ...
... about ten feet from you, which of these would be the brightest? The spotlight right? Now imagine the candle is ten feet from you and the spotlight is one mile away from you. Which one would be brighter? The candle would appear brighter. This helps to illustrate that there are three things that affec ...
Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... – Pressure in the core is more than a billion times the atmospheric pressure on Earth with a temperature hotter than 15 million kelvins – Get their energy from nuclear fusion • Combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms into helium • When hydrogen nuclei collide, they fuse to form new nuclei called deute ...
... – Pressure in the core is more than a billion times the atmospheric pressure on Earth with a temperature hotter than 15 million kelvins – Get their energy from nuclear fusion • Combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms into helium • When hydrogen nuclei collide, they fuse to form new nuclei called deute ...
What is a white dwarf?
... • Supernovae are MUCH, MUCH more luminous (about 10 million times) • Nova: H to He fusion in a surface layer, white dwarf left intact • White dwarf Supernova: complete explosion of white dwarf, nothing left behind ...
... • Supernovae are MUCH, MUCH more luminous (about 10 million times) • Nova: H to He fusion in a surface layer, white dwarf left intact • White dwarf Supernova: complete explosion of white dwarf, nothing left behind ...
Guidestar: February, 2015 - Houston Astronomical Society
... Houston Astronomical Society is available on the web site. Associate Members, immediate family members of a Regular Member, have all membership rights, but do not receive publications. Sustaining members have the same rights as regular members with the additional dues treated as a donation to the So ...
... Houston Astronomical Society is available on the web site. Associate Members, immediate family members of a Regular Member, have all membership rights, but do not receive publications. Sustaining members have the same rights as regular members with the additional dues treated as a donation to the So ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.