Size of the Earth
... Therefore, you can use your measurement of the elevation angle of the North Star in your second location as if you had measured it from Dorksville. But, you need to follow through with the rest of the analysis as if this measurement was made in Dorksville. This means that you must also use the dista ...
... Therefore, you can use your measurement of the elevation angle of the North Star in your second location as if you had measured it from Dorksville. But, you need to follow through with the rest of the analysis as if this measurement was made in Dorksville. This means that you must also use the dista ...
Measuring the Earth`s Diameter
... Therefore, you can use your measurement of the elevation angle of the North Star in your second location as if you had measured it from Dorksville. But, you need to follow through with the rest of the analysis as if this measurement was made in Dorksville. This means that you must also use the dista ...
... Therefore, you can use your measurement of the elevation angle of the North Star in your second location as if you had measured it from Dorksville. But, you need to follow through with the rest of the analysis as if this measurement was made in Dorksville. This means that you must also use the dista ...
Astronomy (stars, galaxies and the Universe)
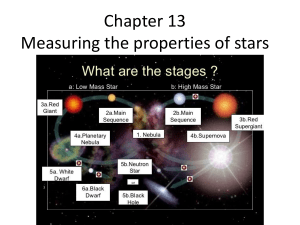
... All stars are created from the gases in a nebula When the contracting gas and dust from a nebula become so dense and hot that nuclear fusion begins, the protostar begins to shine When a star begins to run out of fuel, its core shrinks and its outer portion expands The evolutionary path of a star dep ...
... All stars are created from the gases in a nebula When the contracting gas and dust from a nebula become so dense and hot that nuclear fusion begins, the protostar begins to shine When a star begins to run out of fuel, its core shrinks and its outer portion expands The evolutionary path of a star dep ...
Solutions
... t¯ = 1.0 × 1015 s = 32 million years The geologic record makes it clear that the Solar system has been around for billions of years, so gravitational potential energy from the contraction of the Sun to its current size is insufficient to power the Sun. 3. Right now the Sun is a main-sequence star. L ...
... t¯ = 1.0 × 1015 s = 32 million years The geologic record makes it clear that the Solar system has been around for billions of years, so gravitational potential energy from the contraction of the Sun to its current size is insufficient to power the Sun. 3. Right now the Sun is a main-sequence star. L ...
Week 11 Concept Summary
... (c) Halo: The halo contains only older stars, almost all inside the globular clusters also found there. There is no gas and dust, and what stars are there have very low concentrations of heavy elements. They also orbit randomly in the gallaxy. 2. Interstellar Medium: This is the gas and dust that fl ...
... (c) Halo: The halo contains only older stars, almost all inside the globular clusters also found there. There is no gas and dust, and what stars are there have very low concentrations of heavy elements. They also orbit randomly in the gallaxy. 2. Interstellar Medium: This is the gas and dust that fl ...
color-stellar mass diagram
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
... luminosity, mass, color, morphology, stellar population of galaxies are strongly related. analysis of such properties in the cosmic time started first with the study of the luminosity function but later included galaxy counts as function of the various parameters however, almost all these properties ...
White Dwarfs - University of Maryland Astronomy
... Can’t see it—need to measure mass. Use orbital properties of companion; or, Measure speed and distance of orbiting gas. ...
... Can’t see it—need to measure mass. Use orbital properties of companion; or, Measure speed and distance of orbiting gas. ...
Here - Amateur Observers` Society of New York
... Observing Guide and The Observer's Handbook to plan your observations. When two or more celestial objects appear close together in the sky it is called a conjunction. These are regular occurrences that are listed in The Beginner’s Observing Guide, The Observer's Handbook and in popular astronomy mag ...
... Observing Guide and The Observer's Handbook to plan your observations. When two or more celestial objects appear close together in the sky it is called a conjunction. These are regular occurrences that are listed in The Beginner’s Observing Guide, The Observer's Handbook and in popular astronomy mag ...
September 2016
... Lizard), past the pentagon shape of Cepheus and on through the ‘W’ shape of Cassiopeia (the Queen). At the top, centre of the chart above is the fairly faint constellation of Ursa Minor (the Little Bear) also called the Little Dipper by the Americans. Although Ursa Minor may be a little difficult to ...
... Lizard), past the pentagon shape of Cepheus and on through the ‘W’ shape of Cassiopeia (the Queen). At the top, centre of the chart above is the fairly faint constellation of Ursa Minor (the Little Bear) also called the Little Dipper by the Americans. Although Ursa Minor may be a little difficult to ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... Manual for .STC-files in Celestia Important! The HIP number and “Name of object” field are both optional, but at least a HIP number or a Star name is required for Celestia to be able to create and place that object! HIP number (optional) = Celestia uses "Hipparcos numbers", short HIP, to keep track ...
... Manual for .STC-files in Celestia Important! The HIP number and “Name of object” field are both optional, but at least a HIP number or a Star name is required for Celestia to be able to create and place that object! HIP number (optional) = Celestia uses "Hipparcos numbers", short HIP, to keep track ...
Version A - Otterbein University
... example, say we are seeing Taurus in the south at midnight on December 1. At what other combination of date and time do we see Taurus in the south? a. January 1 at 2 am b. November 1 at 10pm c. February 1 at 6pm d. December 15 at 11pm e. None of the above 31. The sidereal day (a full rotation of the ...
... example, say we are seeing Taurus in the south at midnight on December 1. At what other combination of date and time do we see Taurus in the south? a. January 1 at 2 am b. November 1 at 10pm c. February 1 at 6pm d. December 15 at 11pm e. None of the above 31. The sidereal day (a full rotation of the ...
Version B - Otterbein University
... a. You would have the same view since the Earth barely moves around the Sun in two hours. b. Aries would be in the South because the stars shift by one constellation. c. Pisces would be in the South because the stars shift a constellation per hour. d. Gemini would be highest in the South because the ...
... a. You would have the same view since the Earth barely moves around the Sun in two hours. b. Aries would be in the South because the stars shift by one constellation. c. Pisces would be in the South because the stars shift a constellation per hour. d. Gemini would be highest in the South because the ...
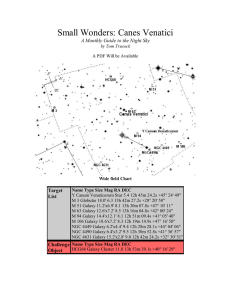
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... Many brown dwarfs in constellation Orion. Infrared image of a Jupiter-size planet orbiting a brown dwarf. Brown dwarfs are substellar objects with insufficient mass to sustain nuclear fusion in their cores. They have higher surface temperatures than planets and masses between 10to 80 times that of J ...
... Many brown dwarfs in constellation Orion. Infrared image of a Jupiter-size planet orbiting a brown dwarf. Brown dwarfs are substellar objects with insufficient mass to sustain nuclear fusion in their cores. They have higher surface temperatures than planets and masses between 10to 80 times that of J ...
The star is born
... reflection nebula (nebula=cloud) Very dense cloud of dust can hide stars behind it and is called “dark nebula.” Warm dust ( a few 100 degrees) can be observed glowing in the IR Gas produces interstellar absorption lines in stars, but not many elements in proper state of ionization to produce absorpt ...
... reflection nebula (nebula=cloud) Very dense cloud of dust can hide stars behind it and is called “dark nebula.” Warm dust ( a few 100 degrees) can be observed glowing in the IR Gas produces interstellar absorption lines in stars, but not many elements in proper state of ionization to produce absorpt ...
HW Set II– page 1 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions
... 4-50 When a large star becomes a supernova, its core may be compressed so tightly that it becomes a neutron star, with a radius of about 20 km (about the size of the San Francisco area). If a neutron star rotates once every second, (a) what is the speed of a particle on the star's equator and (b) wh ...
... 4-50 When a large star becomes a supernova, its core may be compressed so tightly that it becomes a neutron star, with a radius of about 20 km (about the size of the San Francisco area). If a neutron star rotates once every second, (a) what is the speed of a particle on the star's equator and (b) wh ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.