Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Neutron star – The superdense remains of a massive star that collapsed with enough force to push all of its electrons into the nuclei they orbit, resulting in a mass of ...
... Neutron star – The superdense remains of a massive star that collapsed with enough force to push all of its electrons into the nuclei they orbit, resulting in a mass of ...
Binocular Universe: Bikini Bottom
... circled by a close-set pair of stars. The more massive of those two is a blue star, but little is known about its companion apart from it taking only 8.7 days to orbit. The two are separated from each other by only one-third Mercury's distance from the Sun. Our last stop within Capricornus is the c ...
... circled by a close-set pair of stars. The more massive of those two is a blue star, but little is known about its companion apart from it taking only 8.7 days to orbit. The two are separated from each other by only one-third Mercury's distance from the Sun. Our last stop within Capricornus is the c ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... 14. What is a galaxy?____________________________________________________________ 15. What is the Big Bang Theory? _______________________________________________________ 16. What is the most common type of star in the Milky Way galaxy? ______________________________________________ 17. How is dista ...
... 14. What is a galaxy?____________________________________________________________ 15. What is the Big Bang Theory? _______________________________________________________ 16. What is the most common type of star in the Milky Way galaxy? ______________________________________________ 17. How is dista ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... • The star radiates light in all directions so that its emission is spread over a sphere • To find the intensity, I, of light from a star at the Earth (the intensity is the emission per unit area), divide the star’s luminosity by the area of a sphere, with the star at the centre and radius equal to ...
... • The star radiates light in all directions so that its emission is spread over a sphere • To find the intensity, I, of light from a star at the Earth (the intensity is the emission per unit area), divide the star’s luminosity by the area of a sphere, with the star at the centre and radius equal to ...
Overview Notes - School District of La Crosse
... 1. astronomer can’t do controlled experiments a. how would a black hole be constructed b. How is it possible to repeat the experiment? c. can’t examine things from different angles d. Astronomers can- collect light and other forms of EMR and try to interpret what the light means 1. Once the object h ...
... 1. astronomer can’t do controlled experiments a. how would a black hole be constructed b. How is it possible to repeat the experiment? c. can’t examine things from different angles d. Astronomers can- collect light and other forms of EMR and try to interpret what the light means 1. Once the object h ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as a Luminous Blue Variable like Eta Carinae, as an extremely large star that are now often regarded as the ...
... 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as a Luminous Blue Variable like Eta Carinae, as an extremely large star that are now often regarded as the ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
Exploration of the Universe
... model? Who first proposed the heliocentric model? Who discovered that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses? 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10 ...
... model? Who first proposed the heliocentric model? Who discovered that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses? 6. Describe two features of the Sun. 7. Define asteroids, comets, meteors and meteorites. 8. Name three types of electromagnetic radiation. 9. What two factors affect the brightness of a star? 10 ...
HOMEWORK 5 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 9 4.A A red giant star will
... the Earth’s orbit will not change. Since the Sun is so far away, it appears to the Earth to be a point source. The black hole will also appear to be a point source so the orbit will not change. CHAPTER 11 1.C The halo is home to old, metal-poor stars. Globular clusters contain some of the oldest sta ...
... the Earth’s orbit will not change. Since the Sun is so far away, it appears to the Earth to be a point source. The black hole will also appear to be a point source so the orbit will not change. CHAPTER 11 1.C The halo is home to old, metal-poor stars. Globular clusters contain some of the oldest sta ...
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
Module 7 Developmental task - Number
... The solar system Eight planets rotate the Sun in our solar system – our Earth being the third planet from the Sun. The planets vary in size – the smallest, Mercury, has a radius of only 2 439 km, whereas the largest planet, Jupiter, has a radius more than 70 000 km at its equator. ...
... The solar system Eight planets rotate the Sun in our solar system – our Earth being the third planet from the Sun. The planets vary in size – the smallest, Mercury, has a radius of only 2 439 km, whereas the largest planet, Jupiter, has a radius more than 70 000 km at its equator. ...
Question 1: The average distance from Earth to the sun is
... Question 1: Explosive events related to the acceleration of high-energy particles near the sun which can reach Earth and interfere with the Earth’s magnetosphere are known as … ...
... Question 1: Explosive events related to the acceleration of high-energy particles near the sun which can reach Earth and interfere with the Earth’s magnetosphere are known as … ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... Stars vary widely in their surface temperatures' The coolest stars have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how tempera ...
... Stars vary widely in their surface temperatures' The coolest stars have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how tempera ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
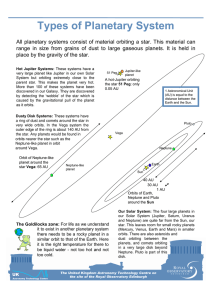
Types of Planetary System
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
... a ring of dust and comets around the star in very wide orbits. In the Vega system the outer edge of the ring is about 140 AU from the star. Any planets would be found in orbits nearer the star such as the Neptune-like planet in orbit around Vega. Orbit of Neptune-like planet around the star Vega: 65 ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Chapter 11 - USD Home Pages
... 35. a. What is the approximate mass of a main sequence star that is 10,000 times as luminous as the Sun? b. What is the approximate lumniosuty of a main-sequence star whose mass is one-tenth that of the Sun? Answer: a. Reading Fig 11-14: Find 104 L on the vertical scale; trace horizontally until yo ...
... 35. a. What is the approximate mass of a main sequence star that is 10,000 times as luminous as the Sun? b. What is the approximate lumniosuty of a main-sequence star whose mass is one-tenth that of the Sun? Answer: a. Reading Fig 11-14: Find 104 L on the vertical scale; trace horizontally until yo ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
December 2014 - Coconino Astronomical Society
... noticed by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus (c. 129 BCE) who observed that star positions had shifted in a systematic way from earlier Babylonian catalogues. Because the Earth's precession occurs in the opposite direction to the Earth's orbit, the Ecliptic and Celestial Equator move in opposite direc ...
... noticed by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus (c. 129 BCE) who observed that star positions had shifted in a systematic way from earlier Babylonian catalogues. Because the Earth's precession occurs in the opposite direction to the Earth's orbit, the Ecliptic and Celestial Equator move in opposite direc ...
Stars - etpt2020s11
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
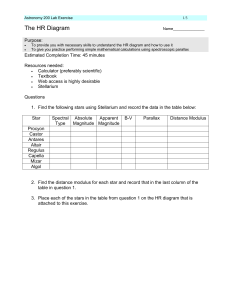
labex7
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
solar system review jeopardy
... The group of objects that orbit the sun between the inner and outer planets. ...
... The group of objects that orbit the sun between the inner and outer planets. ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.