REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? _GRAVITY__ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the BIG BANG theory. The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _AWAY____ Dia ...
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? _GRAVITY__ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the BIG BANG theory. The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _AWAY____ Dia ...
Astronomical Ideas – Math Review practice problems 1. The radius
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
Only Thirty Questions To Go (150,000 points) 1.) If the distance
... A – air and light pollution in urban areas make it harder to see the faintest stars. B – electric lights and television allow us to work and play indoors at night. C – you can’t easily see the stars driving around at night in your car. D – All of the above. 15.) Kepler’s First Law includes… B – plan ...
... A – air and light pollution in urban areas make it harder to see the faintest stars. B – electric lights and television allow us to work and play indoors at night. C – you can’t easily see the stars driving around at night in your car. D – All of the above. 15.) Kepler’s First Law includes… B – plan ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o The inner planets are all smaller and made of solid, rocklike material. o The outer planets are all cold since they are far away from the Sun. o Pluto is a dwarf planet. o Scientists study space with telescopes. o A(n) asteroid is a large chunk of rock or metal in space. o A(n) comet is mostly ice ...
... o The inner planets are all smaller and made of solid, rocklike material. o The outer planets are all cold since they are far away from the Sun. o Pluto is a dwarf planet. o Scientists study space with telescopes. o A(n) asteroid is a large chunk of rock or metal in space. o A(n) comet is mostly ice ...
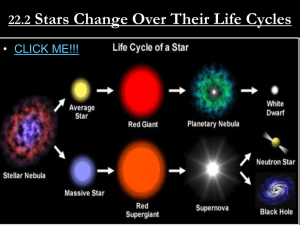
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
... • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
Northern Hemisphere – December 2012
... Mercury reaches greatest western elongation (its furthest from the Sun in the sky) on the 4th, being around 20 degrees from the Sun, and on that day rises two hours before the Sun, near to Venus. It remains at magnitude -0.5 during the month, beginning December 48 percent illuminated and with an ang ...
... Mercury reaches greatest western elongation (its furthest from the Sun in the sky) on the 4th, being around 20 degrees from the Sun, and on that day rises two hours before the Sun, near to Venus. It remains at magnitude -0.5 during the month, beginning December 48 percent illuminated and with an ang ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... magnitude and its distance from Earth then calculate its absolute magnitude. ...
... magnitude and its distance from Earth then calculate its absolute magnitude. ...
Main Sequence Stars
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
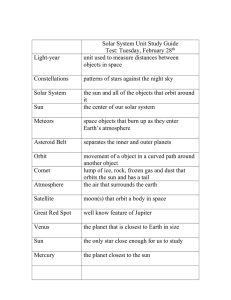
Solar System Unit Study Guide
... massive star that has collapsed and pulls everything in, even light the largest planet the smallest planet, now known as a dwarf planet Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto ...
... massive star that has collapsed and pulls everything in, even light the largest planet the smallest planet, now known as a dwarf planet Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto ...
Constellations
... Asterism: Smaller groups of stars that form patterns within a constellation, from the Greek word aster, meaning star ...
... Asterism: Smaller groups of stars that form patterns within a constellation, from the Greek word aster, meaning star ...
The Night Sky
... A large numerous collections of stars, gas giants and planets that make up a visual universe. They are held together by each planets and stars gravity. Other Galaxies: Sunflower galaxy- A galaxy in a spiral form discovered in 1779 Whirlpool galaxy- A whirlpool like galaxy. thought to be about 14 mil ...
... A large numerous collections of stars, gas giants and planets that make up a visual universe. They are held together by each planets and stars gravity. Other Galaxies: Sunflower galaxy- A galaxy in a spiral form discovered in 1779 Whirlpool galaxy- A whirlpool like galaxy. thought to be about 14 mil ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
... 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. ...
Midterm II Jeopardy
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
... $200 - This planet occasionally has dust storms which obscure its ENTIRE surface. (Mars) $400 - You can only see these planets close to the horizon (45 degrees or less). (Venus & Mercury) $600 - This is how we observed the rings around Uranus. (Occultation) $800 - These two planets most closely rese ...
Coursework 7 File
... 1. The atoms in a gas of temperature T have kinetic energies Eke = 32 kT on average. Assuming that this is the typical energy associated with collisions between hydrogen nuclei at the centre of the Sun, leading to fusion reactions, calculate the distance of closest approach between two hydrogen nucl ...
... 1. The atoms in a gas of temperature T have kinetic energies Eke = 32 kT on average. Assuming that this is the typical energy associated with collisions between hydrogen nuclei at the centre of the Sun, leading to fusion reactions, calculate the distance of closest approach between two hydrogen nucl ...
chap17_f04_probs
... relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, therefore R = 2. The star ...
... relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividing each side of the expression by 16 gives, R2 = 4, therefore R = 2. The star ...
Star
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
... -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
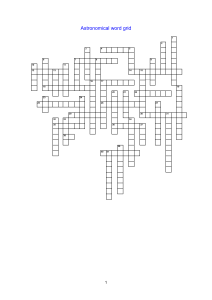
Astronomy word grid
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.