Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
n - TU Chemnitz
... spontaneously in formic aldehyde and HN3, we tried to figure out, whether α-azido alcohols can be generated in an analogeous way to the cyanohydrin synthesis from aldehydes and hydrazoic acid instead of aldehydes and cyanohydric acid (Figure 2). OH ...
... spontaneously in formic aldehyde and HN3, we tried to figure out, whether α-azido alcohols can be generated in an analogeous way to the cyanohydrin synthesis from aldehydes and hydrazoic acid instead of aldehydes and cyanohydric acid (Figure 2). OH ...
Web Supplement 7.2
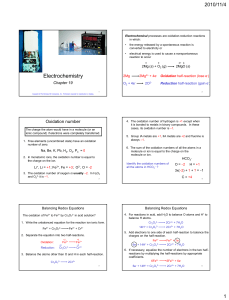
... for balancing nonredox equations. Equation 7.1 is a good example; you can easily see that the molar masses have been conserved between the products and reactions, so that the reaction is balanced with respect to molar mass. Note that for redox reactions, you must also ensure that the net charge is t ...
... for balancing nonredox equations. Equation 7.1 is a good example; you can easily see that the molar masses have been conserved between the products and reactions, so that the reaction is balanced with respect to molar mass. Note that for redox reactions, you must also ensure that the net charge is t ...
Word Document
... provided about the nature and structure of the atom. Include how the experimental results led to the conclusions obtained. 2. Explain the cause of spectral lines and why they are different for each element. 1. What Period 2 element has exactly three p orbital electrons in its shell? ...
... provided about the nature and structure of the atom. Include how the experimental results led to the conclusions obtained. 2. Explain the cause of spectral lines and why they are different for each element. 1. What Period 2 element has exactly three p orbital electrons in its shell? ...
Quantum Mechanics Gibbs free energy
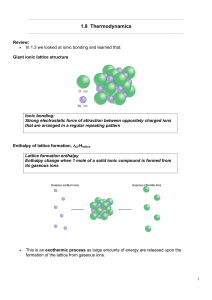
... the same initial state to the same final state.[2] Gibbs energy (also referred to as ∆G) is also the chemical potential that is minimized when a system reaches equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature. Its derivative with respect to the reaction coordinate of the system vanishes at the equil ...
... the same initial state to the same final state.[2] Gibbs energy (also referred to as ∆G) is also the chemical potential that is minimized when a system reaches equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature. Its derivative with respect to the reaction coordinate of the system vanishes at the equil ...