Luminescence spectroscopy
... deactivation to ground state, or intersystem crossing (ISC). The process of intersystem crossing involves transfer of the electron from an excited singlet to a triplet state. This process can actually take place since the vibrational levels in the singlet and triplet states overlap. However, crossin ...
... deactivation to ground state, or intersystem crossing (ISC). The process of intersystem crossing involves transfer of the electron from an excited singlet to a triplet state. This process can actually take place since the vibrational levels in the singlet and triplet states overlap. However, crossin ...
GCSE ADDITIONAL CHEMISTRY (C2) REVISION BOOKLET
... j) False. It is slippery but the reason given is wrong. The layers of atoms are held together by weak intermolecular forces called van der Waals forces. 2 The correct answers are in bold. Ionic compounds have high melting points because the forces of attraction between the ions are strong. When they ...
... j) False. It is slippery but the reason given is wrong. The layers of atoms are held together by weak intermolecular forces called van der Waals forces. 2 The correct answers are in bold. Ionic compounds have high melting points because the forces of attraction between the ions are strong. When they ...
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
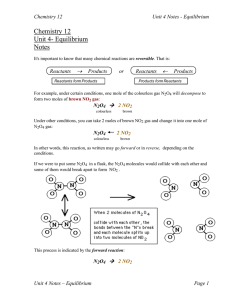
... In the example that we did to construct the graphs, we had started with pure N2O4 and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had start ...
... In the example that we did to construct the graphs, we had started with pure N2O4 and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had start ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... because of van der Waal interactions. 10. What uses do halogenated hydrocarbons have? ...
... because of van der Waal interactions. 10. What uses do halogenated hydrocarbons have? ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
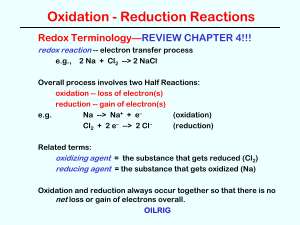
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
AP Chemistry
... MnO4-, and one containing H+, are mixed in a beaker and allowed to react. The initial concentrations of the species in the mixture are 0.60 M Fe2+, 0.10 M MnO4-, and 1.0 M H+. e. Which has the higher concentration, Mn2+ or MnO4-, when the reaction mixture has come to equilibrium? Explain. ...
... MnO4-, and one containing H+, are mixed in a beaker and allowed to react. The initial concentrations of the species in the mixture are 0.60 M Fe2+, 0.10 M MnO4-, and 1.0 M H+. e. Which has the higher concentration, Mn2+ or MnO4-, when the reaction mixture has come to equilibrium? Explain. ...
Balancing and Predicting Chemical Reactions:
... For each of the following reactants, use the activity series to determine whether the reaction would take place or not. If no reaction takes place, write NR in the blank. If a reaction does take place, write the formulas for the products of the reaction. (Hint: If an active metal replaces the hydrog ...
... For each of the following reactants, use the activity series to determine whether the reaction would take place or not. If no reaction takes place, write NR in the blank. If a reaction does take place, write the formulas for the products of the reaction. (Hint: If an active metal replaces the hydrog ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Allylic carbocation reacts with Br- to complete the electrophilic addition • Reaction can occur at C1 or C3 • Both carbons share positive charge • Mixture of 1,2- and 1,4-addition products results ...
... Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Allylic carbocation reacts with Br- to complete the electrophilic addition • Reaction can occur at C1 or C3 • Both carbons share positive charge • Mixture of 1,2- and 1,4-addition products results ...
Course No - Chemistry
... Thermodynamic functions: State and path functions and their differentials. Thermodynamic processes. Concept of heat and work. First Laws of thermodynamics: Heat capacity, heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure and their relationship. Joule's law, Joule-Thomson coefficient and inver ...
... Thermodynamic functions: State and path functions and their differentials. Thermodynamic processes. Concept of heat and work. First Laws of thermodynamics: Heat capacity, heat capacities at constant volume and constant pressure and their relationship. Joule's law, Joule-Thomson coefficient and inver ...
chemical kinetics - Berkeley City College
... The rate of reaction is a measure of the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. Rate can be measured at the beginning of the reaction, which is called the initial rate, at any point in time while the reaction is in progress, called instantaneous rate, or over an interval of time ...
... The rate of reaction is a measure of the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. Rate can be measured at the beginning of the reaction, which is called the initial rate, at any point in time while the reaction is in progress, called instantaneous rate, or over an interval of time ...
1.Hydrocarbons contain only hydrogen and carbon. Which of the
... The instantaneous rate of reaction is 1.8 × 10-3 M/s when [A] is equal to 0.63 M. What is the rate constant, k, of this reaction? (Points : 4) 1.4 × 10-3 M-1s-1 2.2 × 102 M-1s-1 4.5 × 10-3 M-1s-1 7.1 × 10-4 M-1s-1 20. The activation energy (Ea) on a reaction diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction is ge ...
... The instantaneous rate of reaction is 1.8 × 10-3 M/s when [A] is equal to 0.63 M. What is the rate constant, k, of this reaction? (Points : 4) 1.4 × 10-3 M-1s-1 2.2 × 102 M-1s-1 4.5 × 10-3 M-1s-1 7.1 × 10-4 M-1s-1 20. The activation energy (Ea) on a reaction diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction is ge ...
Bk3BP08EE
... The reaction of HBr with both trans- and cis-hex-3-ene results in the formation of the same product, 3-bromohexane, CH3CH2C*HBrCH2CH2CH3. Since carbon-3 is chiral, the product exhibits optical isomerism. In the reaction, H+ is first added to the carbon-4 to form a carbocation. The “+” charge is on c ...
... The reaction of HBr with both trans- and cis-hex-3-ene results in the formation of the same product, 3-bromohexane, CH3CH2C*HBrCH2CH2CH3. Since carbon-3 is chiral, the product exhibits optical isomerism. In the reaction, H+ is first added to the carbon-4 to form a carbocation. The “+” charge is on c ...