Staff demonstrating hours for level-3 Inorganic Lab
... EXAMPLE trans-(Et3P)2PtHCl + C2H4 trans-(Et3P)2PtCl(C2H5) In this example the resulting ethyl complex is stable because the d 8 platinum Pt(2+) atom strongly prefers square-planar geometry. A related route is insertion of a carbene into a TM-H bond EXAMPLE CpMo(CO)3H + CH2N2 CpMo(CO)3(CH3) CH2N2 ...
... EXAMPLE trans-(Et3P)2PtHCl + C2H4 trans-(Et3P)2PtCl(C2H5) In this example the resulting ethyl complex is stable because the d 8 platinum Pt(2+) atom strongly prefers square-planar geometry. A related route is insertion of a carbene into a TM-H bond EXAMPLE CpMo(CO)3H + CH2N2 CpMo(CO)3(CH3) CH2N2 ...
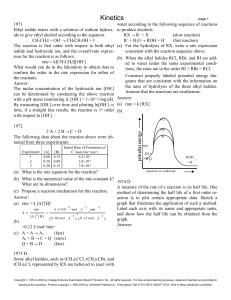
Kinetics
... (b) Slight increase in collision frequency occurs. More (d) 1. molecules have enough energy that many more collisions have the necessary activation energy. Raises reaction rate a great deal. ...
... (b) Slight increase in collision frequency occurs. More (d) 1. molecules have enough energy that many more collisions have the necessary activation energy. Raises reaction rate a great deal. ...
ap chemistry syllabus
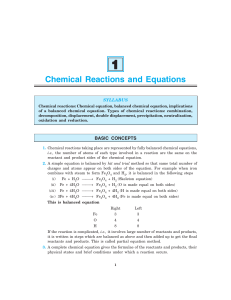
... chemical equation that identifies the ratios with which reactants react and products form. Enduring Understanding 3.B-Chemical reactions can be classified by considering what the reactants are, what the products are, or how they change from one into the other. Classes of chemical reactions include s ...
... chemical equation that identifies the ratios with which reactants react and products form. Enduring Understanding 3.B-Chemical reactions can be classified by considering what the reactants are, what the products are, or how they change from one into the other. Classes of chemical reactions include s ...
Date - Chaminade University`s syllabus repository
... Illustrate the mechanism of each of the functional group inter-conversions identifying intermediates and transition states where appropriate. Identify thermodynamically favorable conformations for acyclic and cyclic molecules Use principles of stereochemistry to explain stereoselective reactio ...
... Illustrate the mechanism of each of the functional group inter-conversions identifying intermediates and transition states where appropriate. Identify thermodynamically favorable conformations for acyclic and cyclic molecules Use principles of stereochemistry to explain stereoselective reactio ...
Course No - Chemistry
... integration, integration by substitution; indefinite and definite integral. Permutations and combinations. Chemical Kinetics: Order of reaction; derivation of rate equations for second (two reactants) and third order reactions. Determination of order of reaction by differential rate, integration, ha ...
... integration, integration by substitution; indefinite and definite integral. Permutations and combinations. Chemical Kinetics: Order of reaction; derivation of rate equations for second (two reactants) and third order reactions. Determination of order of reaction by differential rate, integration, ha ...
CARBANIONS Carbanions are units that contain a negative charge
... functions, and 3) in 1,4-additions such as Michael Reactions. Fluorinated carbanions are very common useful intermediates for the synthesis of new fluorinated materials. As already noted, the fluorine atom will act in a stabilizing manner to with draw electrons from the carbanion when the carbanion ...
... functions, and 3) in 1,4-additions such as Michael Reactions. Fluorinated carbanions are very common useful intermediates for the synthesis of new fluorinated materials. As already noted, the fluorine atom will act in a stabilizing manner to with draw electrons from the carbanion when the carbanion ...
Chemistry 30 – Organic Chemistry
... • If Br2(aq) is mixed with an alkene or alkyne, addition will occur and the brown colour will disappear in the aqueous layer • If Br2(aq) is mixed with an alkane or aromatic, substitution (slow) will occur and the aqueous layer will remain brown………….. ...
... • If Br2(aq) is mixed with an alkene or alkyne, addition will occur and the brown colour will disappear in the aqueous layer • If Br2(aq) is mixed with an alkane or aromatic, substitution (slow) will occur and the aqueous layer will remain brown………….. ...
Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the
... • There will be two possible Wittig routes to an alkene. • Analyze the structure retrosynthetically, i.e., work the synthesis out backwards. • Disconnect (break the bond of the target that can be formed by a known reaction) the doubly bonded carbons. One becomes the aldehyde or ketone, the other th ...
... • There will be two possible Wittig routes to an alkene. • Analyze the structure retrosynthetically, i.e., work the synthesis out backwards. • Disconnect (break the bond of the target that can be formed by a known reaction) the doubly bonded carbons. One becomes the aldehyde or ketone, the other th ...
1. Chemical Energetics March
... instrumental (measurement) error there will always be experimental error due to heat loss and this must be commented upon (errors can cancel one another out to give the impression that the experiment is better than it was) this is minimised if improved insulation is used ...
... instrumental (measurement) error there will always be experimental error due to heat loss and this must be commented upon (errors can cancel one another out to give the impression that the experiment is better than it was) this is minimised if improved insulation is used ...
Name: Chemistry Honors Date: Period: ____ Reduction/Oxidation
... What is electrochemistry and how can it be helpful to us? This is a question that could have a multitude of answers! As the name may suggest, electrochemistry deals with the chemistry of electrons: here electrons are and how they can move. Electrochemistry is the study of electron movement as it rel ...
... What is electrochemistry and how can it be helpful to us? This is a question that could have a multitude of answers! As the name may suggest, electrochemistry deals with the chemistry of electrons: here electrons are and how they can move. Electrochemistry is the study of electron movement as it rel ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... compensates for the change in heat, the concentrations of reactants and products will change. This change will minimize the effect of changing the heat of the system; however, because heat is not part of the Keq equation, the Keq value will change to reflect the new concentrations of the reactants a ...
... compensates for the change in heat, the concentrations of reactants and products will change. This change will minimize the effect of changing the heat of the system; however, because heat is not part of the Keq equation, the Keq value will change to reflect the new concentrations of the reactants a ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... D. 3.6 x 10-3 39. Assume that the following system has reached equilibrium in a closed container. Which of the following changes will produce a greater yield by shifting the equilibrium to the right? S8 (s) + 12 O2 (g) 8 SO3 (g) ΔH = -3166 kJ A. add a catalyst C. increase the temperature B. increas ...
... D. 3.6 x 10-3 39. Assume that the following system has reached equilibrium in a closed container. Which of the following changes will produce a greater yield by shifting the equilibrium to the right? S8 (s) + 12 O2 (g) 8 SO3 (g) ΔH = -3166 kJ A. add a catalyst C. increase the temperature B. increas ...