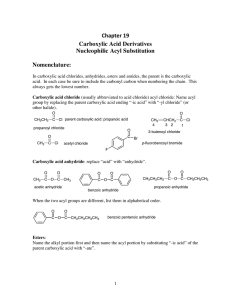
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl
... There is a very large range of reactivity between the most reactive (acid chlorides) and the least reactive (amides). In general, acid chlorides react about 1013 times faster in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions than amides. In order to understand the reactivity order, we need to look at the ...
... There is a very large range of reactivity between the most reactive (acid chlorides) and the least reactive (amides). In general, acid chlorides react about 1013 times faster in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions than amides. In order to understand the reactivity order, we need to look at the ...
Support Material
... (a) Ge doped with In (b) B doped with Si Ans. Hint : (a) Ge is group 14 element and In is group 13 element. Therefore, an electron de cit hole is created. Thus semi-conductor is p-type. (b) Since B is group 13 element and Si is group 14 element, there will be a free electron, thus, it is n-type semi ...
... (a) Ge doped with In (b) B doped with Si Ans. Hint : (a) Ge is group 14 element and In is group 13 element. Therefore, an electron de cit hole is created. Thus semi-conductor is p-type. (b) Since B is group 13 element and Si is group 14 element, there will be a free electron, thus, it is n-type semi ...
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Chemistry
... Module III – Thermodynamics First law of thermodynamics, mathematical form, intrinsic energy, enthalpy, reversible, process and maximum work, work of expansion of an ideal gas in reversible isothermal process. Heat capacity of gases at constant volume and constant pressure, derivation of CP – CV = R ...
... Module III – Thermodynamics First law of thermodynamics, mathematical form, intrinsic energy, enthalpy, reversible, process and maximum work, work of expansion of an ideal gas in reversible isothermal process. Heat capacity of gases at constant volume and constant pressure, derivation of CP – CV = R ...
Ether - Clayton State University
... attached to at least one other carbon. The minor product is 1-butene (10%) because only one of the C=C bond carbons is attached to at least one other carbon. The major product in these rxns will always be the one resulting in the highest number of carbon groups bonded to the C=C carbons. ...
... attached to at least one other carbon. The minor product is 1-butene (10%) because only one of the C=C bond carbons is attached to at least one other carbon. The major product in these rxns will always be the one resulting in the highest number of carbon groups bonded to the C=C carbons. ...