Application of the Purdue Ontology for Pharmaceutical Engineering
... which describes materials; the Purdue Ontology for Degradant Structures (PODS) which describes the chemical structure of materials with respect to molecular fragments; the Purdue Ontology for Reaction Expression (PORE) which describes the interactions between materials including chemical reactions; ...
... which describes materials; the Purdue Ontology for Degradant Structures (PODS) which describes the chemical structure of materials with respect to molecular fragments; the Purdue Ontology for Reaction Expression (PORE) which describes the interactions between materials including chemical reactions; ...
AS 2, Module 2
... 11 The reaction between methane and chlorine involves free radicals created by the action of light. Free radicals can also be created by the use of high temperatures which is known as pyrolysis. The following reactions occur when ethane is pyrolysed at 700 °C. P C2H6 → 2CH3 Q CH3 1 C2H6 → C2H ...
... 11 The reaction between methane and chlorine involves free radicals created by the action of light. Free radicals can also be created by the use of high temperatures which is known as pyrolysis. The following reactions occur when ethane is pyrolysed at 700 °C. P C2H6 → 2CH3 Q CH3 1 C2H6 → C2H ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 30. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 31. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
... ____ 30. Which observation does NOT indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? a. formation of a precipitate c. evolution of heat and light b. production of a gas d. change in total mass of substances ____ 31. A solid produced by a chemical reaction in solution that separates from the solution ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... have formed the products. List as many reaction types as may apply. Assume that all the productions for the reaction are listed. a. a compound and an element b. two compounds c. one compound ...
... have formed the products. List as many reaction types as may apply. Assume that all the productions for the reaction are listed. a. a compound and an element b. two compounds c. one compound ...
Chem 150 Unit 4 - Chemical Properties I Chemical Reactions
... The chemical properties of molecules describe processes that involve the making and breaking the stronger covalent bonds that hold molecules together. As a consequence, the compositions of the the molecules participating in a chemical process change. These processes are called chemical reactions and ...
... The chemical properties of molecules describe processes that involve the making and breaking the stronger covalent bonds that hold molecules together. As a consequence, the compositions of the the molecules participating in a chemical process change. These processes are called chemical reactions and ...
Chemical Reactions (Part One)
... The ripening of all fruit and vegetables involves similar chemical reactions. The speed of ripening is affected by the temperature and by the presence of a chemical called ethene, C2H4. Food scientists can tell producers and supermarkets the best conditions for slowing down or speeding up the ripeni ...
... The ripening of all fruit and vegetables involves similar chemical reactions. The speed of ripening is affected by the temperature and by the presence of a chemical called ethene, C2H4. Food scientists can tell producers and supermarkets the best conditions for slowing down or speeding up the ripeni ...
Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
... potassium dichromate written above the arrow like this: K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 2. The reactants are the alcohol and “[O]” symbolising the oxidation agent 3. Heat is always needed ...
... potassium dichromate written above the arrow like this: K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 2. The reactants are the alcohol and “[O]” symbolising the oxidation agent 3. Heat is always needed ...
Download the paper in pdf format
... side reactions involving the products are eliminated. The strategy based on the rotavapor technique does not contradict wellestablished, conventional chemical kinetic theory and the thermodynamic theory of chemical equilibrium. As shown in Scheme 2, the optimum situation is that the two products (so ...
... side reactions involving the products are eliminated. The strategy based on the rotavapor technique does not contradict wellestablished, conventional chemical kinetic theory and the thermodynamic theory of chemical equilibrium. As shown in Scheme 2, the optimum situation is that the two products (so ...
Ch 5 HEAT IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemical reactions and the
... Enthalpy is a state function, and depends on temperature, state , and composition of the substance, so we must include states in chemical equations used with enthalpy and enthalpy changes. Enthalpy is an extensive property it is proportional to the quantity of reactants. We can easily measure th ...
... Enthalpy is a state function, and depends on temperature, state , and composition of the substance, so we must include states in chemical equations used with enthalpy and enthalpy changes. Enthalpy is an extensive property it is proportional to the quantity of reactants. We can easily measure th ...
Synthesis Reaction
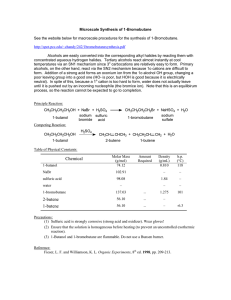
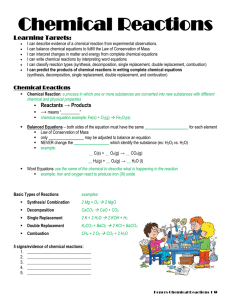
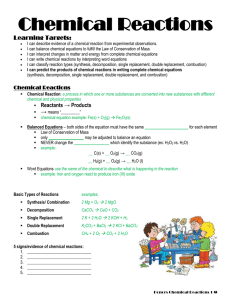
... I can describe evidence of a chemical reaction from experimental observations. I can balance chemical equations to fulfill the Law of Conservation of Mass I can interpret changes in matter and energy from complete chemical equations I can write chemical reactions by interpreting word equations I can ...
... I can describe evidence of a chemical reaction from experimental observations. I can balance chemical equations to fulfill the Law of Conservation of Mass I can interpret changes in matter and energy from complete chemical equations I can write chemical reactions by interpreting word equations I can ...