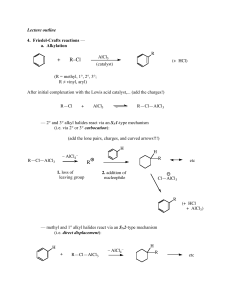
Combi chemistry
... History of combi-chem -> Although combinatorial chemistry has only really been taken up by industry since the 1990s, its roots can be seen as far back as the 1960s when are searcher at Rockefeller University, Bruce Merrifield, started investigating the solid-state synthesis of peptides -> Bruce Mer ...
... History of combi-chem -> Although combinatorial chemistry has only really been taken up by industry since the 1990s, its roots can be seen as far back as the 1960s when are searcher at Rockefeller University, Bruce Merrifield, started investigating the solid-state synthesis of peptides -> Bruce Mer ...
Advanced Chemistry
... 7) When the concentration of B in the reaction below is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) The order of the reaction with respect to substa ...
... 7) When the concentration of B in the reaction below is doubled, all other factors being held constant, it is found that the rate of the reaction remains unchanged. 2 A(g) + B(g) 2 C(g) The most probable explanation for this observation is that (A) The order of the reaction with respect to substa ...
chapter 5 - chemical reactions
... 1. All reactants and products of a reaction must be known before attempting to write an equation. 2. Identify the reactants and products and write their chemical symbols or formulas CORRECTLY. 3. Indicate the state of substances: (g) for gas, (l) for liquid, (s) for solid, and (aq) for aqueous solut ...
... 1. All reactants and products of a reaction must be known before attempting to write an equation. 2. Identify the reactants and products and write their chemical symbols or formulas CORRECTLY. 3. Indicate the state of substances: (g) for gas, (l) for liquid, (s) for solid, and (aq) for aqueous solut ...
Viscosity activation energy
... is sufficiently short (even the Equator looks like a straight line to the horizon limits). When viscosity is studied in wider interval, the declination from a straight line is becoming evident. The situation is more complicated with relaxation experiments because, in this case, it is much more diffi ...
... is sufficiently short (even the Equator looks like a straight line to the horizon limits). When viscosity is studied in wider interval, the declination from a straight line is becoming evident. The situation is more complicated with relaxation experiments because, in this case, it is much more diffi ...
template
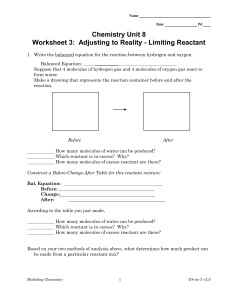
... 3. When 0.50 mole of aluminum reacts with 0.72 mole of iodine to form aluminum iodide, how many moles of the excess reactant will remain? ____________ How many moles of aluminum iodide will be formed? _____________ Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:___________ ...
... 3. When 0.50 mole of aluminum reacts with 0.72 mole of iodine to form aluminum iodide, how many moles of the excess reactant will remain? ____________ How many moles of aluminum iodide will be formed? _____________ Bal. Equation: Before: __________________________________________ Change:___________ ...
Final Review Answers
... b. A student dissolved 52.0g of sodium fluoride in 125g of water (solubility of NaF is 12g/100g H 2O at 25oC). Is the solution saturated or unsaturated? 15 g; saturated Chapters 17-18 Rates of Reaction and Equilibrium Define the following terms: (look up on own) a. activation energy c. chemical equi ...
... b. A student dissolved 52.0g of sodium fluoride in 125g of water (solubility of NaF is 12g/100g H 2O at 25oC). Is the solution saturated or unsaturated? 15 g; saturated Chapters 17-18 Rates of Reaction and Equilibrium Define the following terms: (look up on own) a. activation energy c. chemical equi ...
Remodeling of the natural product fumagillol
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
... Further optimization using La(OTf)3 and Zn(OTf)2 catalysts was next pursued. The transformations were robust and did not require inert atmosphere, nor special precautions for anhydrous solvent. Other nonpolar solvents provided similar regioselectivity, though toluene proved to be optimal, in which c ...
An enquiry into theoretical bioinorganic chemistry: How heuristic is
... a perfect structural and time resolution of their catalytic chemical reactions to obtain results that explain experimental studies but also to provide complementary information not accessible in experiment. Exactly this is at least in principle possible by a quantum mechanical description based on t ...
... a perfect structural and time resolution of their catalytic chemical reactions to obtain results that explain experimental studies but also to provide complementary information not accessible in experiment. Exactly this is at least in principle possible by a quantum mechanical description based on t ...
Introduction
... aware that some reactions require a more rigorous approach to balancing their equations. As long as the reactions proceed to completion (so that at least one of the reactants is completely consumed), we can easily calculate the amount of products formed. Some reactions do not proceed to completion. ...
... aware that some reactions require a more rigorous approach to balancing their equations. As long as the reactions proceed to completion (so that at least one of the reactants is completely consumed), we can easily calculate the amount of products formed. Some reactions do not proceed to completion. ...