Questions for Study
... 6.2 Heat of Reaction Heat is a difficult term to understand. The word heat makes a good verb but a poor noun. Heat is energy in transit from a hotter object to a colder one. Objects do not possess heat. They possess energy that can be transferred as heat. Once the energy arrives at its destination, ...
... 6.2 Heat of Reaction Heat is a difficult term to understand. The word heat makes a good verb but a poor noun. Heat is energy in transit from a hotter object to a colder one. Objects do not possess heat. They possess energy that can be transferred as heat. Once the energy arrives at its destination, ...
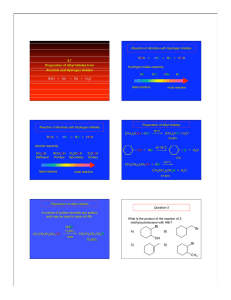
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... B) attack of the bromide on the carbocation C) simultaneous formation of the C-Br bond and the breaking of the C-OH bond D) carbocation formation ...
... B) attack of the bromide on the carbocation C) simultaneous formation of the C-Br bond and the breaking of the C-OH bond D) carbocation formation ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion - Towson University
... Reactions of Arenediazonium Salts Allow Formation of “Impossibly” Substituted Aromatic Rings. Typical synthetid sequence consists of: (1) nitration, (2) reduction, (3) diazotization, and (4) nucleophilic ...
... Reactions of Arenediazonium Salts Allow Formation of “Impossibly” Substituted Aromatic Rings. Typical synthetid sequence consists of: (1) nitration, (2) reduction, (3) diazotization, and (4) nucleophilic ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nitriles
... The mechanism for all of the above reactions (except the last [Friedel-Crafts]) is pretty much the same – a nucleophile adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group, creating a tetrahedral intermediate. The electrons on oxygen then pop down, expelling the good leaving group (Cl-). This type of reaction ...
... The mechanism for all of the above reactions (except the last [Friedel-Crafts]) is pretty much the same – a nucleophile adds to the electrophilic carbonyl group, creating a tetrahedral intermediate. The electrons on oxygen then pop down, expelling the good leaving group (Cl-). This type of reaction ...
Chapter 10_Organohalides
... reaction pathway with Cl2 or Br2 and light (h) • Not very useful to the lack of control over the reaction and can lead ...
... reaction pathway with Cl2 or Br2 and light (h) • Not very useful to the lack of control over the reaction and can lead ...
Collision Theory
... now insert each of these modules into Equation (R3.A-20). B.1 Model 1 In this model, we say only those hard collisions that have kinetic energy EA or greater will react. Let E ≡ εt. That is, below this energy, EA, the molecules do not have sufficient energy to react so the reaction cross section is ...
... now insert each of these modules into Equation (R3.A-20). B.1 Model 1 In this model, we say only those hard collisions that have kinetic energy EA or greater will react. Let E ≡ εt. That is, below this energy, EA, the molecules do not have sufficient energy to react so the reaction cross section is ...
CHM_221_201620 - Oakton Community College
... 1. Apply the three models of bonding–Lewis, valence bond and molecular orbital theory–as well as their extensions–hybridization and resonance–to describe covalent bonding in organic species. 2. Draw and interconvert drawings of neutral and charged organic species using condensed formulae, bond-line ...
... 1. Apply the three models of bonding–Lewis, valence bond and molecular orbital theory–as well as their extensions–hybridization and resonance–to describe covalent bonding in organic species. 2. Draw and interconvert drawings of neutral and charged organic species using condensed formulae, bond-line ...
CHM_223_201620 - Oakton Community College
... 1. Apply the three models of bonding–Lewis, valence bond and molecular orbital theory–as well as their extensions–hybridization and resonance–to describe covalent bonding in organic species. 2. Draw and interconvert drawings of neutral and charged organic species using condensed formulae, bond-line ...
... 1. Apply the three models of bonding–Lewis, valence bond and molecular orbital theory–as well as their extensions–hybridization and resonance–to describe covalent bonding in organic species. 2. Draw and interconvert drawings of neutral and charged organic species using condensed formulae, bond-line ...