Unit 1
... energy diagrams and energy considerations. Controlling reaction rates is important in many commercial and industrial processes. By applying collision theory to the rates of fast and slow reactions, teachers might look for complete and detailed explanations using the correct terminology. A balloon st ...
... energy diagrams and energy considerations. Controlling reaction rates is important in many commercial and industrial processes. By applying collision theory to the rates of fast and slow reactions, teachers might look for complete and detailed explanations using the correct terminology. A balloon st ...
Carbon Bond - Rutgers Chemistry
... exchange processes mediated by [Cp*(PMe3)IrH]+ also proceed by initial C-H oxidative addition. However, in the latter case, the Ir(V) intermediates that are initially formed undergo R-H reductive elimination much more rapidly than H-H reductive elimination. The reason for this is probably thermodyna ...
... exchange processes mediated by [Cp*(PMe3)IrH]+ also proceed by initial C-H oxidative addition. However, in the latter case, the Ir(V) intermediates that are initially formed undergo R-H reductive elimination much more rapidly than H-H reductive elimination. The reason for this is probably thermodyna ...
How do we predict chemical change?
... Not every combination of substances will lead to the formation of new compounds via a chemical reaction. How can we predict when a chemical process takes place? One approach could be to compare the relative stability of reactants and products. We might expect that chemical reactions will proceed in ...
... Not every combination of substances will lead to the formation of new compounds via a chemical reaction. How can we predict when a chemical process takes place? One approach could be to compare the relative stability of reactants and products. We might expect that chemical reactions will proceed in ...
Organic #2
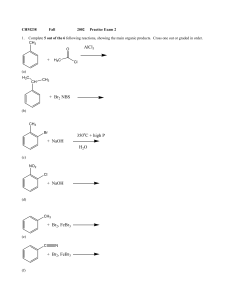
... Explain how you could distinguish between these two products. Name the reagents you would use and say what you would observe. What reagent would be use to convert butan-1-ol to 1-chlorobutane? Treatment of 1-chlorobutane with alcoholic potassium hydroxide produces a compound with the formula C4H8. ...
... Explain how you could distinguish between these two products. Name the reagents you would use and say what you would observe. What reagent would be use to convert butan-1-ol to 1-chlorobutane? Treatment of 1-chlorobutane with alcoholic potassium hydroxide produces a compound with the formula C4H8. ...
Organometallic Organometallic Chemistry
... A reductive elimination involves the elimination or expulsion of a molecule from a transition metal complex. In the process of this elimination, the metal center is reduced by two electrons. ...
... A reductive elimination involves the elimination or expulsion of a molecule from a transition metal complex. In the process of this elimination, the metal center is reduced by two electrons. ...
Functional Groups
... Properties of Alcohols Compared to alkenes alcohols have higher boiling points. This is explained by the OH group which allows hydrogen bonding. This functional group also makes alcohols polar which allows simple (small) alcohols to dissolve in water. Long chain alcohols act as nonpolar molecules ma ...
... Properties of Alcohols Compared to alkenes alcohols have higher boiling points. This is explained by the OH group which allows hydrogen bonding. This functional group also makes alcohols polar which allows simple (small) alcohols to dissolve in water. Long chain alcohols act as nonpolar molecules ma ...
Roll No.
... A translucent white waxy solid (A) on heating in an inert atmosphere is 5 converted to its allotropic forms (B). Allotrope (A) on reaction with very dilute aqueous KOH liberates a highly poisonous gas (C) having rotten fish smell with excess of chlorine. (A) Forms (D) which hydrolysis to compound (E ...
... A translucent white waxy solid (A) on heating in an inert atmosphere is 5 converted to its allotropic forms (B). Allotrope (A) on reaction with very dilute aqueous KOH liberates a highly poisonous gas (C) having rotten fish smell with excess of chlorine. (A) Forms (D) which hydrolysis to compound (E ...
IA Practical Report Properties of Alkanes and Alkenes
... b) What kind of reaction occurs when Br2 and cyclohexene are mixed? c) Draw the reaction of ethene and Br2 (aq). Draw the reaction that cyclohexene underwent. Why did the colour change during the reaction? 7. KMnO4 is known as an “oxidizing agent” because it adds oxygen to other compounds. In this l ...
... b) What kind of reaction occurs when Br2 and cyclohexene are mixed? c) Draw the reaction of ethene and Br2 (aq). Draw the reaction that cyclohexene underwent. Why did the colour change during the reaction? 7. KMnO4 is known as an “oxidizing agent” because it adds oxygen to other compounds. In this l ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... closely packed, thereby maximizing the dispersion forces present. Higher intermolecular forces lead to higher melting points. CH3C16H30COOH with one double bond has additional geometrical constraints due to the relative rigidity of that double bond, so the tails cannot pack as efficiently, and the m ...
... closely packed, thereby maximizing the dispersion forces present. Higher intermolecular forces lead to higher melting points. CH3C16H30COOH with one double bond has additional geometrical constraints due to the relative rigidity of that double bond, so the tails cannot pack as efficiently, and the m ...
organometallic reagents
... The strategic bonds are around the functional group. Of the three paths, a,b, and c, is best: The building blocks are almost equal in size (5 and 6 carbon fragments), providing the greatest simplification in structure. ...
... The strategic bonds are around the functional group. Of the three paths, a,b, and c, is best: The building blocks are almost equal in size (5 and 6 carbon fragments), providing the greatest simplification in structure. ...
Energetics - WordPress.com
... different bonds with different strengths are being broken and formed. The amount (or concentration) of reactants; the greater the amount that reacts , the greater the heat change. The states of the reactants and products – changing state involves an enthalpy change, and so will affect the total amou ...
... different bonds with different strengths are being broken and formed. The amount (or concentration) of reactants; the greater the amount that reacts , the greater the heat change. The states of the reactants and products – changing state involves an enthalpy change, and so will affect the total amou ...
Unit 2 Summary - A
... (iii) E/Z isomerism as an example of stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, (iv) cis-trans isomerism as a special case of EIZ isomerism in which two of the substituent grou ...
... (iii) E/Z isomerism as an example of stereoisomerism, in terms of restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group, (iv) cis-trans isomerism as a special case of EIZ isomerism in which two of the substituent grou ...
ALCOHOLS
... the human food chain is now being used to grow sugar to make biofuels. However, ethanol produced in this way is considered to be carbon neutral since all of the CO2 released during its combustion was removed during photosynthesis by the growing crop. It can not be considered to be 100% carbon neutra ...
... the human food chain is now being used to grow sugar to make biofuels. However, ethanol produced in this way is considered to be carbon neutral since all of the CO2 released during its combustion was removed during photosynthesis by the growing crop. It can not be considered to be 100% carbon neutra ...