Meandering Road from Dynamics to Thermodynamics and Vice Versa
... The science of mechanics may trace back to Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) and Archimedes (c. 287-212 B.C.), while thermal science may trace back to the steam engines by Savery in 1697 and Newcomen in 1712 or to the works of Rankine, Clausius, and Lord Kelvin in the 1850s. Both are old sciences where, from ...
... The science of mechanics may trace back to Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) and Archimedes (c. 287-212 B.C.), while thermal science may trace back to the steam engines by Savery in 1697 and Newcomen in 1712 or to the works of Rankine, Clausius, and Lord Kelvin in the 1850s. Both are old sciences where, from ...
Meandering Road From Dynamics To Thermodynamics And Vice
... that has the ability to cause changes. Energy is a property possessed by a system, but heat is not a property possessed by any system. In daily life, “heat” and “thermal energy” are often synonymously used. In thermodynamics, “heat transfer” and “energy transfer by heat” are interchangeably used. To ...
... that has the ability to cause changes. Energy is a property possessed by a system, but heat is not a property possessed by any system. In daily life, “heat” and “thermal energy” are often synonymously used. In thermodynamics, “heat transfer” and “energy transfer by heat” are interchangeably used. To ...
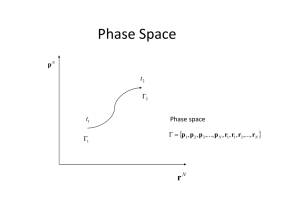
Phase Space Phase Space
... Within the statistical description, the motion of one single system with given initial conditions is not considered; thus, p(t), q(t) are not sought. Instead, the motion of a whole set of phase points, representing the collection of possible states of the given system. Such a set of phase points is ...
... Within the statistical description, the motion of one single system with given initial conditions is not considered; thus, p(t), q(t) are not sought. Instead, the motion of a whole set of phase points, representing the collection of possible states of the given system. Such a set of phase points is ...
I. IONIZATION OF CESIUM AT SURFACES II. THE ENERGY
... The fixed biases used in the operation of the circuit were generally supplied by batteries, and the value of the potential was accurately known. ...
... The fixed biases used in the operation of the circuit were generally supplied by batteries, and the value of the potential was accurately known. ...
5 Energetics/thermochemistry
... Because of these random motions at all temperatures above absolute zero (0 K or −273 °C), the particles in matter have kinetic energy. The average kinetic energy of these individual particles causes what we perceive through sense perception as warmth. Whenever a substance becomes warmer, the average ...
... Because of these random motions at all temperatures above absolute zero (0 K or −273 °C), the particles in matter have kinetic energy. The average kinetic energy of these individual particles causes what we perceive through sense perception as warmth. Whenever a substance becomes warmer, the average ...
Chemistry 882: Spectroscopy and Kinetics
... exam, unless the exam question explicitly asks you to derive them. You will also be permitted to bring in two pages to each exam with any information which you think is important. I expect to see all of your work for problems on homework and exams. You may receive partial credit when you do have wri ...
... exam, unless the exam question explicitly asks you to derive them. You will also be permitted to bring in two pages to each exam with any information which you think is important. I expect to see all of your work for problems on homework and exams. You may receive partial credit when you do have wri ...
Hybridization Theory Review Review
... noble core electrons – a set of electrons that are isoelectronic with a noble element. Because these inner-core electrons are not involved in bond making or breaking they are normally abbreviated as a noble element (in brackets) for convenience. pi (π) bond – overlap of adjacent, parallel p orbitals ...
... noble core electrons – a set of electrons that are isoelectronic with a noble element. Because these inner-core electrons are not involved in bond making or breaking they are normally abbreviated as a noble element (in brackets) for convenience. pi (π) bond – overlap of adjacent, parallel p orbitals ...
Integrated Science Resource Level
... Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matt ...
... Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy. Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for the cycling of matt ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.