Different levels of reversibility
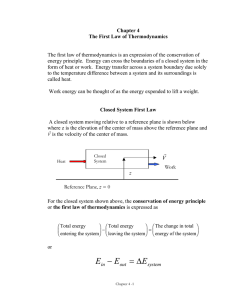
... The first law of thermodynamics gives an overall law of energy conservation. Stated simply, the energy of an isolated system remains constant. For any subsystem in the isolated system, the energy change equals the difference between the heat added and the work done. The internal energy of a system d ...
... The first law of thermodynamics gives an overall law of energy conservation. Stated simply, the energy of an isolated system remains constant. For any subsystem in the isolated system, the energy change equals the difference between the heat added and the work done. The internal energy of a system d ...
Quantum Energy Regression using Scattering Transforms
... Density Functional Theory calculations for every distinct atomic species present in a molecular database. The electron density model (1) only gives a crude approximation to ρx . It is a sum of independent atomic contributions and hence does not model any chemical effects like bond sharing. An exampl ...
... Density Functional Theory calculations for every distinct atomic species present in a molecular database. The electron density model (1) only gives a crude approximation to ρx . It is a sum of independent atomic contributions and hence does not model any chemical effects like bond sharing. An exampl ...
Characterization techniques for nanotechnology
... the tip specimen interaction are often monitored using an optical lever detection system, in which a laser is reflected off of the cantilever and onto a positionsensitive photodiode. During scanning, a particular operating parameter is maintained at a constant level, and images are generated through ...
... the tip specimen interaction are often monitored using an optical lever detection system, in which a laser is reflected off of the cantilever and onto a positionsensitive photodiode. During scanning, a particular operating parameter is maintained at a constant level, and images are generated through ...
p-type and n-type semiconductors
... neighboring silicon atoms. The solid, then, consists of basic units of five silicon atoms: the original atom plus the four other atoms with which it shares its valence electrons. The solid silicon crystal, then, is composed of a regular series of units of five silicon atoms. This regular, fixed arra ...
... neighboring silicon atoms. The solid, then, consists of basic units of five silicon atoms: the original atom plus the four other atoms with which it shares its valence electrons. The solid silicon crystal, then, is composed of a regular series of units of five silicon atoms. This regular, fixed arra ...
3. Liquid crystals
... Definition of orientational order parameter should be one in ordered phase and zero in isotropic phase only polar angle β relevant → use a function of cos(β) nematic phase: β and π-β are equally likely → use a function of cos 2(β) average of cos 2(β) for isotropic distribution is 1/3 ...
... Definition of orientational order parameter should be one in ordered phase and zero in isotropic phase only polar angle β relevant → use a function of cos(β) nematic phase: β and π-β are equally likely → use a function of cos 2(β) average of cos 2(β) for isotropic distribution is 1/3 ...
The Motionless Electromagnetic Generator: How It
... Outside the core, there freely appears an extra curl-free magnetic vector potential A. The MEG thus has two energy reservoirs: (i) the normal B-field energy and flux of any transformer resulting from the energy input to its primary coil(s), but now totally localized within the core material, and (ii ...
... Outside the core, there freely appears an extra curl-free magnetic vector potential A. The MEG thus has two energy reservoirs: (i) the normal B-field energy and flux of any transformer resulting from the energy input to its primary coil(s), but now totally localized within the core material, and (ii ...
How Atoms Bond: Ionic Bonds
... have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive protons are permanently in the atom’s nucleus, the negative electrons in an atom are not: electrons move around in the shells. A ...
... have equal numbers of positive protons and negative electrons , the electric charges cancel each other out. Net charge: zero. OK, now back to electrons. While the positive protons are permanently in the atom’s nucleus, the negative electrons in an atom are not: electrons move around in the shells. A ...
GHW#12-Chapter-6-Tro
... CH4 (g) C2H6 (g) CH3OH (l) CH3OH (g) CO (g) CO2 (g) HCl (g) H2O (l) H2O (g) NaCl (s) SO2 (g) ...
... CH4 (g) C2H6 (g) CH3OH (l) CH3OH (g) CO (g) CO2 (g) HCl (g) H2O (l) H2O (g) NaCl (s) SO2 (g) ...
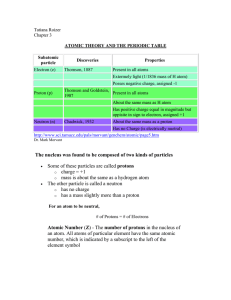
atomic theory and the periodic table
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
IEEE_2010_NOCT_Using_EWM.pdf
... fundamental of electromagnetic wave (EMW) propagation based on Maxwell’s equations. This approach enables the EMW energy in individual layers and at different regions of the PV module to be evaluated from the dielectric constants and thickness of each material. Once the light intensity in the cell i ...
... fundamental of electromagnetic wave (EMW) propagation based on Maxwell’s equations. This approach enables the EMW energy in individual layers and at different regions of the PV module to be evaluated from the dielectric constants and thickness of each material. Once the light intensity in the cell i ...
THERMODYNAMICS LECTURE NOTES
... considered very small volume, thus average density keeps on fluctuating with time. For such a situation the definite value of density cannot be given. Therefore, we may consider some limiting volume ΔVlimit such that the fluid around the point may be treated continuous and the average density at the ...
... considered very small volume, thus average density keeps on fluctuating with time. For such a situation the definite value of density cannot be given. Therefore, we may consider some limiting volume ΔVlimit such that the fluid around the point may be treated continuous and the average density at the ...
An Environmental Cell T.E.M Applied to the Study of
... Why not an entire new field? •Nano-sized carbon particles used in tires for about 100 years •Vaccines, which often consist of one or more proteins with nanoscale dimensions •Chemical catalysts, such as those turning cheap graphite into synthetic diamond. •Photosynthesis (natural nanotechnology) ...
... Why not an entire new field? •Nano-sized carbon particles used in tires for about 100 years •Vaccines, which often consist of one or more proteins with nanoscale dimensions •Chemical catalysts, such as those turning cheap graphite into synthetic diamond. •Photosynthesis (natural nanotechnology) ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.