Introduction to drugs and the brain
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
WebQuest * Human Senses
... Explore the brain by function and answer the following questions. 1. Vision. a. In terms of vision, nerve impulses travel along the retina through the to the brains visual processing centers in the ...
... Explore the brain by function and answer the following questions. 1. Vision. a. In terms of vision, nerve impulses travel along the retina through the to the brains visual processing centers in the ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Brain and Behavior
... Individual neurons are the signaling elements of the nervous system, arranged in functional groups Supported by empirical observations of Ramon y Cajal, Wernicke, Jackson, Sherrington. ...
... Individual neurons are the signaling elements of the nervous system, arranged in functional groups Supported by empirical observations of Ramon y Cajal, Wernicke, Jackson, Sherrington. ...
Document
... • Easier to understand adult organization once the simple developing system is understood • The various dimensions and divisions of the CNS are defined in the neural tube • Development of the neural tube cavity becomes the ventricles of the brain and canal of the cord • Development of the neural tub ...
... • Easier to understand adult organization once the simple developing system is understood • The various dimensions and divisions of the CNS are defined in the neural tube • Development of the neural tube cavity becomes the ventricles of the brain and canal of the cord • Development of the neural tub ...
Surface-uniform sampling, possibilities and limitations
... subdivided into 50 to 100 regions, some of which have known functions. The regions all have 6 layers of neurons, but they neither have sharp borders nor are their position detectable on the surface. Among individuals, regions vary in extent (by 10 to 25%) and in position (by 5 to 10mm) as does the o ...
... subdivided into 50 to 100 regions, some of which have known functions. The regions all have 6 layers of neurons, but they neither have sharp borders nor are their position detectable on the surface. Among individuals, regions vary in extent (by 10 to 25%) and in position (by 5 to 10mm) as does the o ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
... - Also thought to contain "reward centers" because animals will feverishly engage in behavior that results in electrical stimulation of this area. - e.g., rat press bar in cage. ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
Print › psych chapter 2 | Quizlet | Quizlet
... A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next. ...
... A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next. ...
the brain - WordPress.com
... cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. This structure is associated with regulation ...
... cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex This structure is associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. This structure is associated with regulation ...
Assignment 1 Key
... 4. From the theories of Charles Darwin and related research since his time, modern researchers believe which of the following regarding human emotions? a. emotions are inherited rather than learned b. human emotions are similar to emotions expressed by other animals c. emotions are common to all hum ...
... 4. From the theories of Charles Darwin and related research since his time, modern researchers believe which of the following regarding human emotions? a. emotions are inherited rather than learned b. human emotions are similar to emotions expressed by other animals c. emotions are common to all hum ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... of human brains because a reptile’s (who appear early on the evolutionary scale) entire brain resembles our brain stem. ...
... of human brains because a reptile’s (who appear early on the evolutionary scale) entire brain resembles our brain stem. ...
Ch 3 Biopsychology & the Foundations of Neuroscience
... O 19. ________________ each hemisphere of the brain to take control of different functions. O 20. Spatial orientation appears to be a function Right Hemisphere , while speech of the brain's _____________ Left Hemisphere processing is located in ______________. ...
... O 19. ________________ each hemisphere of the brain to take control of different functions. O 20. Spatial orientation appears to be a function Right Hemisphere , while speech of the brain's _____________ Left Hemisphere processing is located in ______________. ...
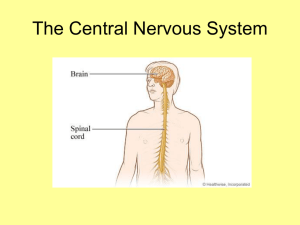
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those parts should be located. Therefore it plays a role in posture, balance, and coordination. ...
... eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information from the cerebral cortex as to where those parts should be located. Therefore it plays a role in posture, balance, and coordination. ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... Occipital Lobe- Receives and processes information from the eyes. Temporal Lobe- Processes auditory information from the ears. Basal Ganglia- Helps to coordinate fine motions, such as fingertip movements. Limbic System- Important for emotional behavior and controlling movements of visceral ...
... Occipital Lobe- Receives and processes information from the eyes. Temporal Lobe- Processes auditory information from the ears. Basal Ganglia- Helps to coordinate fine motions, such as fingertip movements. Limbic System- Important for emotional behavior and controlling movements of visceral ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... • He survived this ordeal but it was reported that his behaviour changed after the event. He became anti-social and ill-mannered. ...
... • He survived this ordeal but it was reported that his behaviour changed after the event. He became anti-social and ill-mannered. ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 2:Hindbrain The
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.