Nervous System
... Your nervous system controls all of your body’s actions and functions. It senses changes not only within your body but also outside of it in your environment Enables you to respond within fractions of a second. ...
... Your nervous system controls all of your body’s actions and functions. It senses changes not only within your body but also outside of it in your environment Enables you to respond within fractions of a second. ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The Brain The four major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain. It is the last center to receive sensory input and carry out integration before commanding voluntary motor responses. It ...
... The Brain The four major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The Cerebrum The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain. It is the last center to receive sensory input and carry out integration before commanding voluntary motor responses. It ...
Slide 1
... northern Italy, where his father was working as a district medical officer. He studied medicine at the University of Pavia, where he attended as an 'intern student' the Institute of Psychiatry directed by Cesare Lombroso (1835-1909). Golgi also worked in the laboratory of experimental pathology dire ...
... northern Italy, where his father was working as a district medical officer. He studied medicine at the University of Pavia, where he attended as an 'intern student' the Institute of Psychiatry directed by Cesare Lombroso (1835-1909). Golgi also worked in the laboratory of experimental pathology dire ...
PSYC 100 Chap. 2 - Traditional method: Observing electrical activity
... - Links in the networks are fluid- here new synapses will replace old synapses - Ironically, elimination of old synapses play a larger role in scalpting the neural networks compared to the creation of new synapses - Reason: nervous system always create new synapses more than needed, thus gradually r ...
... - Links in the networks are fluid- here new synapses will replace old synapses - Ironically, elimination of old synapses play a larger role in scalpting the neural networks compared to the creation of new synapses - Reason: nervous system always create new synapses more than needed, thus gradually r ...
Cognitive Activity in Artificial Neural Networks
... a. Churchland brings up the difficulty in replicating even the most seemingly-simple of human actions. For example, producing the sound for the letter ‘a’ is easy for a human to do, but requires a lot of programming time for a digital computer to do. What accounts for this level of difficulty is the ...
... a. Churchland brings up the difficulty in replicating even the most seemingly-simple of human actions. For example, producing the sound for the letter ‘a’ is easy for a human to do, but requires a lot of programming time for a digital computer to do. What accounts for this level of difficulty is the ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 01
... • Clinicopathologic method is used in the field of behavioral neurology: “Study of how client’s behaviors/abilities are related to or supported by the neurological system” • Examples from the fields of speech-language pathology and audiology, that we’ll encounter in this class Dysarthria (speech mo ...
... • Clinicopathologic method is used in the field of behavioral neurology: “Study of how client’s behaviors/abilities are related to or supported by the neurological system” • Examples from the fields of speech-language pathology and audiology, that we’ll encounter in this class Dysarthria (speech mo ...
Focus on Vocabulary Chapter 02
... misconceptions to get rid of (“one of the hardiest weeds in the garden of psychology”). Research into the association areas of the brain has shown that they do not have specific functions; rather, they are involved in many different operations such as interpreting, integrating, and acting on sensory ...
... misconceptions to get rid of (“one of the hardiest weeds in the garden of psychology”). Research into the association areas of the brain has shown that they do not have specific functions; rather, they are involved in many different operations such as interpreting, integrating, and acting on sensory ...
Slide 1
... • Exhausted area before routing resource • Synchronous, Low neuron count • No autonomous learning • FPGA routing resources occupy ...
... • Exhausted area before routing resource • Synchronous, Low neuron count • No autonomous learning • FPGA routing resources occupy ...
PSB 4002 - Developmental Psychobiology Laboratory
... • Each of these neurons receives connections from other neurons at sites called synapses. There are roughly one million billion of these connections in just in your ...
... • Each of these neurons receives connections from other neurons at sites called synapses. There are roughly one million billion of these connections in just in your ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
... Memory systems start to decline Prefrontal cortex continues to mature New synapses in language and perception centers Myelination continues ...
quiz for chapter 1 - The Happiness Hypothesis
... xd. they show we are good a making up convincing explanations for our behavior, even when we don’t know what causes our behavior. 4. (p. 12). When reviewing New vs. Old divisions in the brain, Haidt (2006) refers to Damasio’s work regarding damage to parts of the orbitofrontal cortex, and the result ...
... xd. they show we are good a making up convincing explanations for our behavior, even when we don’t know what causes our behavior. 4. (p. 12). When reviewing New vs. Old divisions in the brain, Haidt (2006) refers to Damasio’s work regarding damage to parts of the orbitofrontal cortex, and the result ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... Kohonen nets teach us an important lesson about the ability of neurons to encode information, not only in weights, but also in spatial organisation. What are the consequences for network dynamics? Can these principles be extended beyond simple centre-surround constraints of self-excitation and neigh ...
... Kohonen nets teach us an important lesson about the ability of neurons to encode information, not only in weights, but also in spatial organisation. What are the consequences for network dynamics? Can these principles be extended beyond simple centre-surround constraints of self-excitation and neigh ...
The Evolution of Reentrance in the Vertebrate Brain
... in Macaque monkey visual cortex, interconnected by as many as 300 reentrant fiber projections. Whether or not this upward trend continues in man is not completely clear at this time. Brodmann's cytoarchitectonic maps of humans and monkeys (reproduced in Pandya et al, 1988) show similar areal divisio ...
... in Macaque monkey visual cortex, interconnected by as many as 300 reentrant fiber projections. Whether or not this upward trend continues in man is not completely clear at this time. Brodmann's cytoarchitectonic maps of humans and monkeys (reproduced in Pandya et al, 1988) show similar areal divisio ...
Analogies for Memory and Remembering
... the field) the easier it is to find the path. Also, the more complex the pattern of the path is, the greater your chances of finding your way onto a branch of the pattern and thereby discovering the entire pathway. This last part helps us explain why a memory that is saved in several parts of the b ...
... the field) the easier it is to find the path. Also, the more complex the pattern of the path is, the greater your chances of finding your way onto a branch of the pattern and thereby discovering the entire pathway. This last part helps us explain why a memory that is saved in several parts of the b ...
Abstract View OPTICAL RECORDING OF THE TRITONIA SWIMMING CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATOR. ;
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
... during fictive swimming. Candidate central pattern generator (CPG) interneurons were identified by their bursting patterns and positions in the brain. Previously identifed populations of interneurons were imaged, including the dorsal swim interneurons (DSI), C2, and ventral swim interneurons (VSI). ...
Document
... – Step 2: autopsy the brain and pin point a specific region associated with the behavior ...
... – Step 2: autopsy the brain and pin point a specific region associated with the behavior ...
From Vision to Movement
... Approaching the brain from a global view, one starts with the impression that vision is encoded in occipital cortex, movement in frontal cortex, and parietal cortex is involved in the transformation from vision to action. However, things are not that simple. For example, frontal cortex neurons often ...
... Approaching the brain from a global view, one starts with the impression that vision is encoded in occipital cortex, movement in frontal cortex, and parietal cortex is involved in the transformation from vision to action. However, things are not that simple. For example, frontal cortex neurons often ...
Optogenetics: Molecular and Optical Tools for Controlling Life with
... Halorhodopsins are light-driven inward chloride pumps from archaeal species that live in very high-salinity environments. When expressed in neurons, and illuminated, they pump chloride ions into the cells, thus hyperpolarizing them. The first halorhodopsin to be used in neurons was the halorhodopsin ...
... Halorhodopsins are light-driven inward chloride pumps from archaeal species that live in very high-salinity environments. When expressed in neurons, and illuminated, they pump chloride ions into the cells, thus hyperpolarizing them. The first halorhodopsin to be used in neurons was the halorhodopsin ...
Page 1 of 4 Further reading - New Scientist 20/07/2009 http://www
... neurons in the other levels. Friston created a computer simulation of the cortex with layers of "neurons" passing signals back and forth. Signals going from higher to lower levels represent the brain's internal predictions, while signals going the other way represent sensory input. As new informatio ...
... neurons in the other levels. Friston created a computer simulation of the cortex with layers of "neurons" passing signals back and forth. Signals going from higher to lower levels represent the brain's internal predictions, while signals going the other way represent sensory input. As new informatio ...
Structure of the Vertebrate Nervous System
... by causing gene mutations critical to their development or functioning. – Transcranial magnetic stimulation: the application of intense magnetic fields to temporarily inactivate neurons. ...
... by causing gene mutations critical to their development or functioning. – Transcranial magnetic stimulation: the application of intense magnetic fields to temporarily inactivate neurons. ...
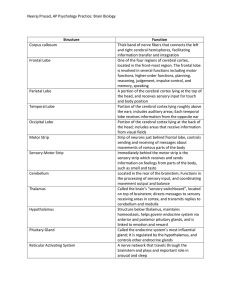
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... Located at the base of the brainstem; Controls many essential involuntary functions such as heartbeat and breathing Region of frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the control of speech Region of the frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the comprehension of speech A fa ...
... Located at the base of the brainstem; Controls many essential involuntary functions such as heartbeat and breathing Region of frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the control of speech Region of the frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the comprehension of speech A fa ...
Central nervous system (CNS)
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
9 Functions of the Middle Prefrontal Cortex
... feel secure and to develop well. Through out our life we need attunement to feel close and connected. ...
... feel secure and to develop well. Through out our life we need attunement to feel close and connected. ...
6. Brain Lateralization
... 3. Linguistic theory: This is based on the view that the primary function of the LH is language. On the basis of several studies of deaf people who communicate using ASL, it has been found that the signing ability is lost if a person suffers damage to the LH. Moreover, the person can make use of ot ...
... 3. Linguistic theory: This is based on the view that the primary function of the LH is language. On the basis of several studies of deaf people who communicate using ASL, it has been found that the signing ability is lost if a person suffers damage to the LH. Moreover, the person can make use of ot ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.