The Brain: How does it work?
... Secret Life of the Brain (PBS) http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/index.html Seeing, Hearing, and Smelling - http://www.hhmi.org/senses/ Neuroscience for Kids http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html The Musical Brain http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/music.html Kidshealth - http:/ ...
... Secret Life of the Brain (PBS) http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/index.html Seeing, Hearing, and Smelling - http://www.hhmi.org/senses/ Neuroscience for Kids http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html The Musical Brain http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/music.html Kidshealth - http:/ ...
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
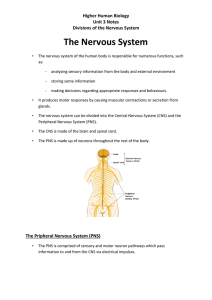
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
3 Medical Terminology - MedicalScienceTwoCCP
... 1. What are the two divisions of the Nervous system? And what are they composed of? 2. Why is the autonomic division of the nervous system important? Give an example 3. Using a soccer player as an example, give an example of 8 different things that the nervous system does to help the player perform. ...
... 1. What are the two divisions of the Nervous system? And what are they composed of? 2. Why is the autonomic division of the nervous system important? Give an example 3. Using a soccer player as an example, give an example of 8 different things that the nervous system does to help the player perform. ...
Neuroplasticity - Bakersfield College
... Have unlimited capacity for self renewal Can become any kind of mature cell ...
... Have unlimited capacity for self renewal Can become any kind of mature cell ...
Class
... a. momentarily becomes less negative, or even positive b. suddenly becomes even more positive than it was during the resting state c. momentarily changes from positive to negative d. suddenly becomes even more negative than it was during the resting state ...
... a. momentarily becomes less negative, or even positive b. suddenly becomes even more positive than it was during the resting state c. momentarily changes from positive to negative d. suddenly becomes even more negative than it was during the resting state ...
The Brain
... the brain and spinal cord, and is also found throughout the ventricle (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thought, lear ...
... the brain and spinal cord, and is also found throughout the ventricle (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thought, lear ...
Dynamic Decision Making in Complex Task Environments
... environments as the project continues. • Bridges to investigations concerned with decision making processes in real-life situations (e.g. those faced by air-traffic controllers and pilots). ...
... environments as the project continues. • Bridges to investigations concerned with decision making processes in real-life situations (e.g. those faced by air-traffic controllers and pilots). ...
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... 2. Vibrations move through middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes) 3. Stapes vibrates causing oval window (separates middle from inner ear) to move back and forth 4. Cochlea is filled with fluid and lined with tiny hair cells 5. Vibrations cause fluid inside to move like a wave against hair cells 6. Hai ...
... 2. Vibrations move through middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes) 3. Stapes vibrates causing oval window (separates middle from inner ear) to move back and forth 4. Cochlea is filled with fluid and lined with tiny hair cells 5. Vibrations cause fluid inside to move like a wave against hair cells 6. Hai ...
Two Point Discrimination Lab
... 1. Identify the three different types of neurons and describe their functions. ...
... 1. Identify the three different types of neurons and describe their functions. ...
Reuptake, or re-uptake, is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by
... neurotransmitters are too large and hydrophilic to diffuse through the membrane, specific transport proteins are necessary for the reabsorption of neurotransmitters. Much research, both biochemical and structural, has been performed to obtain clues about the mechanism of reuptake. ...
... neurotransmitters are too large and hydrophilic to diffuse through the membrane, specific transport proteins are necessary for the reabsorption of neurotransmitters. Much research, both biochemical and structural, has been performed to obtain clues about the mechanism of reuptake. ...
The Nervous System
... B. Neurons are made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites and axons. ...
... B. Neurons are made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites and axons. ...
Chapter 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Neurons don’t actually touch. Instead they are separated by a microscopic gap between the terminal button of one neuron and the _19_ (2 words) of another neuron. This gap is called the _20_ (2 words). • Electrical signals can’t jump this gap. Instead, the neuron that is sending the message across ...
... • Neurons don’t actually touch. Instead they are separated by a microscopic gap between the terminal button of one neuron and the _19_ (2 words) of another neuron. This gap is called the _20_ (2 words). • Electrical signals can’t jump this gap. Instead, the neuron that is sending the message across ...
Neuroscience Journal Club
... brain areas by a topographically similar matrix of cell rings. (A, B) Barrels: aggregates of cell rings in layer IV of the cerebral cortex . Barrel cortex: area in the somatosensory cortex (C) where neurons are grouped in barrel- like arrangements, with a hollow center of lesser cell density surroun ...
... brain areas by a topographically similar matrix of cell rings. (A, B) Barrels: aggregates of cell rings in layer IV of the cerebral cortex . Barrel cortex: area in the somatosensory cortex (C) where neurons are grouped in barrel- like arrangements, with a hollow center of lesser cell density surroun ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... We know the algorithms that the vestibular system uses. We know (sort of) how it’s implemented at the neural level. We know the algorithm for echolocation. We know (mainly) how it’s implemented at the neural level. We know the algorithm for computing x+y. We know (mainly) how it might be implemented ...
... We know the algorithms that the vestibular system uses. We know (sort of) how it’s implemented at the neural level. We know the algorithm for echolocation. We know (mainly) how it’s implemented at the neural level. We know the algorithm for computing x+y. We know (mainly) how it might be implemented ...
neuron…
... Your brain is about the size of a cantaloupe and is wrinkled like a walnut. Your brain feels like a ripe avocado and looks pink because of the blood running through it. The baby’s brain grows 3x in size during its first year. At birth, the human brain weighs 4/5 of a pound, while an adult’s weighs a ...
... Your brain is about the size of a cantaloupe and is wrinkled like a walnut. Your brain feels like a ripe avocado and looks pink because of the blood running through it. The baby’s brain grows 3x in size during its first year. At birth, the human brain weighs 4/5 of a pound, while an adult’s weighs a ...
neurons
... • Inhibition from another neuron causes a brief decrease in voltage (IPSP) threshold resting potential EPSP IPSP time (milliseconds) ...
... • Inhibition from another neuron causes a brief decrease in voltage (IPSP) threshold resting potential EPSP IPSP time (milliseconds) ...
This guide is for middle and high school students participating... of the Human Brain and Sheep Brain Dissections. Programs... Distance Learning Program
... Anatomy of the Human Brain/Sheep Brain Dissection This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Brain and Sheep Brain Dissections. Programs will be presented by an AIMS Anatomy Specialist. In this activity students will become more familiar with the ana ...
... Anatomy of the Human Brain/Sheep Brain Dissection This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Brain and Sheep Brain Dissections. Programs will be presented by an AIMS Anatomy Specialist. In this activity students will become more familiar with the ana ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... and the outside is positively charged. There is approximately a -65 mV potential difference across the membrane. This charge difference is due to the action of the sodium-potassium pump that actively transports sodium out of and potassium into the axon. Action Potential An action potential is a rapi ...
... and the outside is positively charged. There is approximately a -65 mV potential difference across the membrane. This charge difference is due to the action of the sodium-potassium pump that actively transports sodium out of and potassium into the axon. Action Potential An action potential is a rapi ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Element of the Nervous System Each nerve is a bundle of neurons (sends electrical messages to the body’s organs and muscles). ...
... Element of the Nervous System Each nerve is a bundle of neurons (sends electrical messages to the body’s organs and muscles). ...
Document
... – A region in the left temporal lobe that is important to language, particularly the semantic content in speech – Wernicke’s aphasia: serious disruptions in comprehension • Speak fairly grammatical sentences that are almost devoid of meaning ...
... – A region in the left temporal lobe that is important to language, particularly the semantic content in speech – Wernicke’s aphasia: serious disruptions in comprehension • Speak fairly grammatical sentences that are almost devoid of meaning ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.