Rhymes, Songs, Stories and Fingerplays in Early Childhood
... learning a particular skill (not a new idea, but now supported by current brain research). • The brain is superactive between ages 4 and 10, called the "wonder years of learning." Brain research supports early education efforts and parental education efforts. ...
... learning a particular skill (not a new idea, but now supported by current brain research). • The brain is superactive between ages 4 and 10, called the "wonder years of learning." Brain research supports early education efforts and parental education efforts. ...
General anatomy [edit]
... respective nuclei. The obex marks the end of the 4th ventricle and the beginning of the central canal. The posterior intermediate sulci separates the fasciculi gracilis from the fasciculi cuneatus. Lateral to the fasciculi cuneatus is the lateral funiculus. Superior to the obex is the floor of the 4 ...
... respective nuclei. The obex marks the end of the 4th ventricle and the beginning of the central canal. The posterior intermediate sulci separates the fasciculi gracilis from the fasciculi cuneatus. Lateral to the fasciculi cuneatus is the lateral funiculus. Superior to the obex is the floor of the 4 ...
Music and the Brain: Areas and Networks
... the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as well as music. Language researchers describe a dual-stream pathway in speech and language processing. The two streams are dorsal and ventral: a dorsal stream projects from the superior tem ...
... the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as well as music. Language researchers describe a dual-stream pathway in speech and language processing. The two streams are dorsal and ventral: a dorsal stream projects from the superior tem ...
Neuron Preview
... features of M1 make it a particularly likely neocortical candidate site for implementation of motor binding. The intrinsic organization of M1 has distributed and overlapping movement representations, suggestive of intrinsic substrates for coordination (Sanes and Schieber, 2001). Additionally, M1 has ...
... features of M1 make it a particularly likely neocortical candidate site for implementation of motor binding. The intrinsic organization of M1 has distributed and overlapping movement representations, suggestive of intrinsic substrates for coordination (Sanes and Schieber, 2001). Additionally, M1 has ...
File
... • In the postcentral gyri • Receives sensory information from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints • Capable of spatial discrimination: identification of body region being stimulated ...
... • In the postcentral gyri • Receives sensory information from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints • Capable of spatial discrimination: identification of body region being stimulated ...
Functional Organization of the Neural Language System: Dorsal and
... Shafto, et al. 2010; Tyler et al. 2011), the controls showed significant clusters of activation in LpMTG and LIFG for stimuli that loaded on syntactic analysis, with the LIFG activity consisting of one cluster primarily located in BA45 and another primarily in BA44. Tracking between these clusters se ...
... Shafto, et al. 2010; Tyler et al. 2011), the controls showed significant clusters of activation in LpMTG and LIFG for stimuli that loaded on syntactic analysis, with the LIFG activity consisting of one cluster primarily located in BA45 and another primarily in BA44. Tracking between these clusters se ...
Cortical Functions Reference
... produce characteristic symptoms including: agraphesthesia, astereognosia, loss of vibration, proprioception, and fine touch (because the third-order neuron of the medial-lemniscal pathway cannot synapse in the cortex). It can also produce hemineglect, if it affects the non-dominant hemisphere. It co ...
... produce characteristic symptoms including: agraphesthesia, astereognosia, loss of vibration, proprioception, and fine touch (because the third-order neuron of the medial-lemniscal pathway cannot synapse in the cortex). It can also produce hemineglect, if it affects the non-dominant hemisphere. It co ...
Resolving sentence ambiguity with planning and working memory
... switching and selective attention as needed. These resources are supported in other, non-peri-Sylvian brain regions. The present study uses functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine this model during the comprehension of sentences with a temporary structural ambiguity. Functional neuro ...
... switching and selective attention as needed. These resources are supported in other, non-peri-Sylvian brain regions. The present study uses functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine this model during the comprehension of sentences with a temporary structural ambiguity. Functional neuro ...
The NTVA framework: Linking Cognition and Neuroscience
... In the Theory of Visual Attention (TVA) proposed by Bundesen (1990), both visual identification and selection of objects in the visual field consist in making visual categorizations. A visual categorization has the form "object x has feature i". A visual categorization is made when the categorizatio ...
... In the Theory of Visual Attention (TVA) proposed by Bundesen (1990), both visual identification and selection of objects in the visual field consist in making visual categorizations. A visual categorization has the form "object x has feature i". A visual categorization is made when the categorizatio ...
Function
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
Function
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
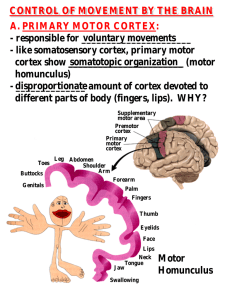
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... the following 3 premotor areas: - supplementary motor area: ________________ Internal stimuli - premotor cortex: _______________________ Guided by external stimuli - cingulate motor areas:Guided ____________________ by emotional states Prefrontal cortex (very important for planning ________ ________ ...
... the following 3 premotor areas: - supplementary motor area: ________________ Internal stimuli - premotor cortex: _______________________ Guided by external stimuli - cingulate motor areas:Guided ____________________ by emotional states Prefrontal cortex (very important for planning ________ ________ ...
day2-morning2
... of a stimulus or message- both the auditory and visual message. • The hearing process is based on a complex set of physical interactions between the ear and the brain. • Besides using the hearing mechanism, we listen through our visual system. We observe a person’s facial expression, posture, moveme ...
... of a stimulus or message- both the auditory and visual message. • The hearing process is based on a complex set of physical interactions between the ear and the brain. • Besides using the hearing mechanism, we listen through our visual system. We observe a person’s facial expression, posture, moveme ...
An Associator Network Approach to Robot Learning by Imitation
... from structural complexity. Although, it is not fully understood why certain regions of the brain are associated with specific cognitive function, the performance achieved would not be possible without this type of modularity [23]. Research into the form that regional brain modularity takes has focu ...
... from structural complexity. Although, it is not fully understood why certain regions of the brain are associated with specific cognitive function, the performance achieved would not be possible without this type of modularity [23]. Research into the form that regional brain modularity takes has focu ...
Natural language processing Prof. Pushpak Bhattacharyya
... The opposite process is called morphology generation or morphology syntheses. We have a root word and from the root word we should be able to produce the word form. Again to take an example in English, suppose the root word is transport, we transport some material. Now, if I say that this word tran ...
... The opposite process is called morphology generation or morphology syntheses. We have a root word and from the root word we should be able to produce the word form. Again to take an example in English, suppose the root word is transport, we transport some material. Now, if I say that this word tran ...
Lecture 11: Chapter 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory
... • Corticospinal pathway contain 3 pairs of ...
... • Corticospinal pathway contain 3 pairs of ...
neurons
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft ...
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... perceive as pitch) and amplitude or intensity (which we perceive as loudness). Verbal sounds such as words are mainly processed in the primary auditory cortex of the left hemisphere and nonverbal sounds (such as music) are mainly processed in the primary auditory cortex of the right hemisphere. Dama ...
... perceive as pitch) and amplitude or intensity (which we perceive as loudness). Verbal sounds such as words are mainly processed in the primary auditory cortex of the left hemisphere and nonverbal sounds (such as music) are mainly processed in the primary auditory cortex of the right hemisphere. Dama ...
1. Materials and Methods
... these statements seem trivial, understanding what brain mechanisms reside behind the brain’s capacity to extract a single meaning – ‘knocking’ – from such different modalities is far from trivial. The ventral premotor cortex (area F5, Fig. 1A) of the monkey contains a class of neurons called ‘audiov ...
... these statements seem trivial, understanding what brain mechanisms reside behind the brain’s capacity to extract a single meaning – ‘knocking’ – from such different modalities is far from trivial. The ventral premotor cortex (area F5, Fig. 1A) of the monkey contains a class of neurons called ‘audiov ...
MIrror neuRons based RObot Recognition - LIRA-Lab
... have been found also in area PF of the inferior parietal lobule, which is bidirectionally connected with area F5 (Fogassi, Gallese, Fadiga, & Rizzolatti, 1998). Therefore, mirror neurons seem to be identical to canonical neurons in terms of motor properties, but they radically differ from the canoni ...
... have been found also in area PF of the inferior parietal lobule, which is bidirectionally connected with area F5 (Fogassi, Gallese, Fadiga, & Rizzolatti, 1998). Therefore, mirror neurons seem to be identical to canonical neurons in terms of motor properties, but they radically differ from the canoni ...
File
... ◦ neurotransmitter produced in the presynaptic knob and stored in vesicles. ◦ when an action potential reaches the presynaptic knob the vesicles rupture releasing their contents (acetylcholine) into the synaptic cleft ◦ The acetylcholine diffuses across the synapse and binds to receptor sites on the ...
... ◦ neurotransmitter produced in the presynaptic knob and stored in vesicles. ◦ when an action potential reaches the presynaptic knob the vesicles rupture releasing their contents (acetylcholine) into the synaptic cleft ◦ The acetylcholine diffuses across the synapse and binds to receptor sites on the ...

![General anatomy [edit]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000712414_1-9f164978a5775158fafd921c8e3d4cef-300x300.png)