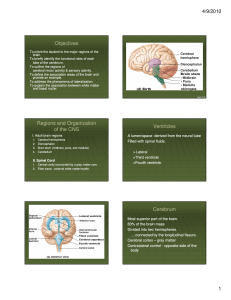
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The cerebral cortex is a thin, highly convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. The primary visual area is at the back occipi ...
... The cerebral cortex is a thin, highly convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres. The primary motor area is in the frontal lobe; this commands skeletal muscle. The primary somatosensory area is dorsal to the central sulcus or groove. The primary visual area is at the back occipi ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... Tour of the Brain - CNS Cerebrum - Responsible for consciousness. Divided into hemispheres & association areas. Controls: conscious mind, communication, memory and understanding, voluntary movements, creativity. Composed of primarily gray matter i.e. numerous cell bodies of neurons. ...
... Tour of the Brain - CNS Cerebrum - Responsible for consciousness. Divided into hemispheres & association areas. Controls: conscious mind, communication, memory and understanding, voluntary movements, creativity. Composed of primarily gray matter i.e. numerous cell bodies of neurons. ...
The Human Mirror Neuron System and Embodied
... network in humans, with links to the superior temporal sulcus (STS) (Fig. 3). We provide just a few examples here of this rather extensive literature (MolnarSzakacs et al., 2002; Rizzolatti and Craighero, 2004; Fadiga et al., 2005; Iacoboni, 2005). Fadiga and colleagues (1995) used transcranial magn ...
... network in humans, with links to the superior temporal sulcus (STS) (Fig. 3). We provide just a few examples here of this rather extensive literature (MolnarSzakacs et al., 2002; Rizzolatti and Craighero, 2004; Fadiga et al., 2005; Iacoboni, 2005). Fadiga and colleagues (1995) used transcranial magn ...
Lecture 36-40 - เว็บไซต์บุคลากรภาควิชาวิทยาการคอมพิวเตอร์
... Figure 15.1 P. 378 English sentences are incomplete descriptions of the information that are intended to convey. The same expression means different things in different context. No natural language program can be complete because of new words, expression, and meaning can be generated quite f ...
... Figure 15.1 P. 378 English sentences are incomplete descriptions of the information that are intended to convey. The same expression means different things in different context. No natural language program can be complete because of new words, expression, and meaning can be generated quite f ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. ...
... http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. ...
Psycholinguistics
... How are certain morphemes related? Do we store mono-morphemic words differently than polymorphemic words? (is there a “morpheme” place in the brain)? Are irregular morphemes stored differently than regular morphemes? ...
... How are certain morphemes related? Do we store mono-morphemic words differently than polymorphemic words? (is there a “morpheme” place in the brain)? Are irregular morphemes stored differently than regular morphemes? ...
The Brain and Its Disorders
... brain fit closely together • Only some molecules can pass through • Protects the brain from foreign molecules and hormones and neurotransmitters from other parts of the body • Can be damaged by infections, head trauma, high blood pressure, etc. ...
... brain fit closely together • Only some molecules can pass through • Protects the brain from foreign molecules and hormones and neurotransmitters from other parts of the body • Can be damaged by infections, head trauma, high blood pressure, etc. ...
1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
... The Nervous System • The most complex system • Coordinates activities of all body systems • Two divisions: The Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain & spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = all neural tissue not included in CNS ...
... The Nervous System • The most complex system • Coordinates activities of all body systems • Two divisions: The Central Nervous System (CNS) = brain & spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = all neural tissue not included in CNS ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain • They have sensory, motor, or both sensory and motor functions • Each nerve is identified by a number (I through XII) and a name ...
... • Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain • They have sensory, motor, or both sensory and motor functions • Each nerve is identified by a number (I through XII) and a name ...
Movement control system
... There’s another problem for the motor system. The length of a muscle, in this case the extensor muscles for the knee (quadriceps), is “pre-set” by the gamma system. But also pre-set is the length of the knee’s flexor muscles (hamstrings). So how does the knee ever extend? Shouldn’t a contraction the ...
... There’s another problem for the motor system. The length of a muscle, in this case the extensor muscles for the knee (quadriceps), is “pre-set” by the gamma system. But also pre-set is the length of the knee’s flexor muscles (hamstrings). So how does the knee ever extend? Shouldn’t a contraction the ...
COURSE: 7065
... Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works Neurons---nerve cells in the brain that control body functions Dend ...
... Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works Neurons---nerve cells in the brain that control body functions Dend ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...
Seminars of Interest
... control of his left hand. Why the left hand? The lesion occurred above the pyramidal decussation, where the corticospinal fibers cross, so a lesion on the right pyramid would affect the left side. A lesion below the site of decussation would affect fine motor movement on the same side as the lesion. ...
... control of his left hand. Why the left hand? The lesion occurred above the pyramidal decussation, where the corticospinal fibers cross, so a lesion on the right pyramid would affect the left side. A lesion below the site of decussation would affect fine motor movement on the same side as the lesion. ...
Biosocial Development - Austin Community College District
... children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
... children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
test1short answer - answer key
... 4. Disorders of righting – difficulties in achieving a standing position 5. Disorders of locomotion – difficulty initiating stepping. Festination – tendency to engage in behavior at faster and faster speeds. 6. Disturbances of speech – aprosodia 7. Akinesia – absence of movement (e.g., blank facial ...
... 4. Disorders of righting – difficulties in achieving a standing position 5. Disorders of locomotion – difficulty initiating stepping. Festination – tendency to engage in behavior at faster and faster speeds. 6. Disturbances of speech – aprosodia 7. Akinesia – absence of movement (e.g., blank facial ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... • Other senses similar The visual fields NOT the eyes cross over!!! ...
... • Other senses similar The visual fields NOT the eyes cross over!!! ...
Force field adaptation based on musulo
... 2004 and of CREST, JST since 2004 to 2014. His research interests include human motor control theory, human interface, brain machine interface and their applications. He is a member of Society for Neuroscience, IEICE, VRSJ and JNNS. ...
... 2004 and of CREST, JST since 2004 to 2014. His research interests include human motor control theory, human interface, brain machine interface and their applications. He is a member of Society for Neuroscience, IEICE, VRSJ and JNNS. ...
Nervous System
... Disease of unknown cause that manifests as multiple hard plaques of degeneration of insulating layer of nerve fibers in the central nervous system, allowing short circuiting of nerve impulses Patients may suffer paralysis, blindness, or sensory disturbances Affects about 400,000 people in United Sta ...
... Disease of unknown cause that manifests as multiple hard plaques of degeneration of insulating layer of nerve fibers in the central nervous system, allowing short circuiting of nerve impulses Patients may suffer paralysis, blindness, or sensory disturbances Affects about 400,000 people in United Sta ...
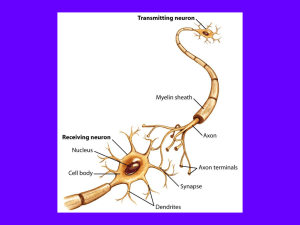
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
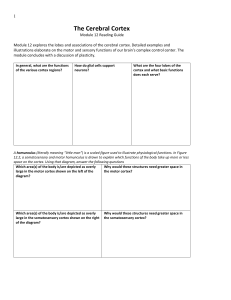
The Cerebral Cortex
... In which lobe is the motor cortex located? How does the location of the motor cortex help us to better understand the function? ...
... In which lobe is the motor cortex located? How does the location of the motor cortex help us to better understand the function? ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... • Function: The Insulin and Glycogen y g in the Pancreas help to keep the level of glucose in the blood stable. • Disorders: When the Pancreas fails to produce or properly use Insulin, it can cause a ...
... • Function: The Insulin and Glycogen y g in the Pancreas help to keep the level of glucose in the blood stable. • Disorders: When the Pancreas fails to produce or properly use Insulin, it can cause a ...
Brain Development
... – Occurs as a result of idiosyncratic individual experiences across the lifespan • Ex: String musicians have more connections in the area of the cortex representing the fingers of the left hand ...
... – Occurs as a result of idiosyncratic individual experiences across the lifespan • Ex: String musicians have more connections in the area of the cortex representing the fingers of the left hand ...