Module 21 Operant Conditioning
... Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. ...
... Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: food & sex. Conditionered (or secondary) reinforcer: a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. ...
A quantitative theory of neural computation Cambridge, MA 02138
... The classical model of vision in cortex is as a hierarchy. As one ascends it the complexity of the items represented by a neuron increases, as does their invariance to size, translation, etc. We hypothesize that the higher levels of the vision hierarchy require the capabilities of some form of hiera ...
... The classical model of vision in cortex is as a hierarchy. As one ascends it the complexity of the items represented by a neuron increases, as does their invariance to size, translation, etc. We hypothesize that the higher levels of the vision hierarchy require the capabilities of some form of hiera ...
lec #2 By: Lubna Al-Marmori
... inferior part of brain stem then directly make crossing, then it complete its way until reach thalamus, then synap as 3rd order neuron -The axons of 3rd order neurons pass through internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the Postcentral gyrus of cerebral cortex - u should know the difference bet ...
... inferior part of brain stem then directly make crossing, then it complete its way until reach thalamus, then synap as 3rd order neuron -The axons of 3rd order neurons pass through internal capsule and corona radiata to reach the Postcentral gyrus of cerebral cortex - u should know the difference bet ...
History and Approaches - Airport Senior High School
... Evolutionary Perceptive • The principles of evolution and knowledge we currently have about evolution are used in this perspective to look at the way the mind works and why it works as it does. • Behavior is seen has having and adaptive or survival value. ...
... Evolutionary Perceptive • The principles of evolution and knowledge we currently have about evolution are used in this perspective to look at the way the mind works and why it works as it does. • Behavior is seen has having and adaptive or survival value. ...
Slide 1
... 1. Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) 2. Variable-interval schedule: Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals, which produces slow, steady responses. (e.g., pop quiz.) ...
... 1. Fixed-interval schedule: Reinforces a response only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) 2. Variable-interval schedule: Reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals, which produces slow, steady responses. (e.g., pop quiz.) ...
MOTIVATION500
... – The essence of Maslow’s Need Hierarchy is that basic human needs are organized into a HIERARCHY of 5 needs ...
... – The essence of Maslow’s Need Hierarchy is that basic human needs are organized into a HIERARCHY of 5 needs ...
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW QUESTIONS:
... Adrenergic receptor activation: Alpha and Beta adrenergic receptors. Alpha receptors have affinity for binding noradrenaline. A1 – activation increases Ca2+ in cell, causing excitatory response which contracts peripheral blood vessels shunting blood to brain and other needed organs. A2 – activation ...
... Adrenergic receptor activation: Alpha and Beta adrenergic receptors. Alpha receptors have affinity for binding noradrenaline. A1 – activation increases Ca2+ in cell, causing excitatory response which contracts peripheral blood vessels shunting blood to brain and other needed organs. A2 – activation ...
BEHAVIORISM JOHN BROADUS WATSON (1878
... • POSITIVE REINFORCER - Is any stimulus that is given or added to increase the response • NEGATIVE REINFORCER- Is any stimulus that results in the increased frequency of a response when it is withdrawn or removed • PUNISHMENT • Is a consequence intended to result in reduced responses * Skinner also ...
... • POSITIVE REINFORCER - Is any stimulus that is given or added to increase the response • NEGATIVE REINFORCER- Is any stimulus that results in the increased frequency of a response when it is withdrawn or removed • PUNISHMENT • Is a consequence intended to result in reduced responses * Skinner also ...
Psychology312-2_002 - Northwestern University
... by John and Morrell in the ‘61 reviews. B) problem of choosing electrode sites and neural parameters for study. C) Correlation approach: let animals do their own thing and see what neural events from what sites correlate. That’s not controlled science. D) Time base issues: Learning takes days ...
... by John and Morrell in the ‘61 reviews. B) problem of choosing electrode sites and neural parameters for study. C) Correlation approach: let animals do their own thing and see what neural events from what sites correlate. That’s not controlled science. D) Time base issues: Learning takes days ...
sanjay sood - UCLA Anderson School of Management
... Shi Zhang, revising for resubmission to Journal of Marketing Research. “The Effects of Branding Strategies and Product Experience on Brand Evaluations” with Kevin Lane Keller, revising for resubmission to Journal of Marketing. “On Self Referencing Differences in Judgment and Choice,” with Mark Foreh ...
... Shi Zhang, revising for resubmission to Journal of Marketing Research. “The Effects of Branding Strategies and Product Experience on Brand Evaluations” with Kevin Lane Keller, revising for resubmission to Journal of Marketing. “On Self Referencing Differences in Judgment and Choice,” with Mark Foreh ...
Chapter 6: Learning (Operant Conditioning)
... Discriminative Stimuli and Stimuli Control STIMULUS DISCRIMINATION occurs when an organism learns to make a particular response in the presence of one stimulus but not another. When this occurs, the response is under stimulus control. e.g., Although you are repeatedly rewarded for telling jokes duri ...
... Discriminative Stimuli and Stimuli Control STIMULUS DISCRIMINATION occurs when an organism learns to make a particular response in the presence of one stimulus but not another. When this occurs, the response is under stimulus control. e.g., Although you are repeatedly rewarded for telling jokes duri ...
What drives the plasticity of brain tissues?
... (Withers and Greenough, 1989). Taken with the study above, these results indicate that learning or some other aspect of training-related activity drives morphological change in neurons. Both experiments make clear that nonspecific effects such as globally-acting hormonal or metabolic differences, w ...
... (Withers and Greenough, 1989). Taken with the study above, these results indicate that learning or some other aspect of training-related activity drives morphological change in neurons. Both experiments make clear that nonspecific effects such as globally-acting hormonal or metabolic differences, w ...
Operantmine
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
Lecture 3
... areas of the cb are necessary for spatial reasoning, keeping muscle tone during voluntary movement or reflexes • people can't walk in a coordinated smooth manner after cb lesion ie they appear to walk as if drunk ...
... areas of the cb are necessary for spatial reasoning, keeping muscle tone during voluntary movement or reflexes • people can't walk in a coordinated smooth manner after cb lesion ie they appear to walk as if drunk ...
PSYC550 Communication and Movement
... internal division of the globus pallidus, and the ventral anterior/ventrolateral thalamic nuclei; has an inhibitory effect on movement. • indirect pathway (in basal ganglia) – The pathway that includes the caudate nucleus and putamen, the internal division of the globus pallidus, and the ventral ant ...
... internal division of the globus pallidus, and the ventral anterior/ventrolateral thalamic nuclei; has an inhibitory effect on movement. • indirect pathway (in basal ganglia) – The pathway that includes the caudate nucleus and putamen, the internal division of the globus pallidus, and the ventral ant ...
conditioned
... or mental processes Behaviorists: reject mental processes and focus only on what can be observed. Cognitive psychologists: in addition to behavior, learning requires that we make inferences about hidden mental processes ...
... or mental processes Behaviorists: reject mental processes and focus only on what can be observed. Cognitive psychologists: in addition to behavior, learning requires that we make inferences about hidden mental processes ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning Notes
... Discovery: Pavlov when he began ringing a bell at the same time he showed his dog food. ...
... Discovery: Pavlov when he began ringing a bell at the same time he showed his dog food. ...
Posterior Parietal Cortex: Space…and Beyond
... require different responses at home (answer the phone) than when dining in a restaurant (let the host or hostess get it). If we were unable to take such contextual cues into account when planning voluntary actions, every stimulus would lead to a highly predictable reflex-like response that could be ...
... require different responses at home (answer the phone) than when dining in a restaurant (let the host or hostess get it). If we were unable to take such contextual cues into account when planning voluntary actions, every stimulus would lead to a highly predictable reflex-like response that could be ...
Learning - Gordon State College
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
... Defined performance goals and immediate reinforcement at work Parenting – reward good behavior, ignore whining, time-out ...
Module II
... better understanding of possible interdisciplinary approachesin T & I such as cognitive & neurocognitive processes as well as issues related to affective sciences & emotions. Participants will be given a fundamental orientation on those domains with practical applications and will have the opportuni ...
... better understanding of possible interdisciplinary approachesin T & I such as cognitive & neurocognitive processes as well as issues related to affective sciences & emotions. Participants will be given a fundamental orientation on those domains with practical applications and will have the opportuni ...
Overview of Addiction Related Brain Regions Nucleus Accumbens
... limbic system. In humans and other animals, this subcortical brain structure is linked to both fear responses and pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males ...
... limbic system. In humans and other animals, this subcortical brain structure is linked to both fear responses and pleasure. Its size is positively correlated with aggressive behavior across species. In humans, it is the most sexually-dimorphic brain structure, and shrinks by more than 30% in males ...
Operant Conditioning - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
Ear to Auditory Cortex
... vibrations in air, water, or solid material. The number of sound waves that pass through a given point in one second is called the sound’s frequency. • When your sensory system experiences the physical sensation of frequency, you also have the psychological experience of pitch. High-pitched sounds a ...
... vibrations in air, water, or solid material. The number of sound waves that pass through a given point in one second is called the sound’s frequency. • When your sensory system experiences the physical sensation of frequency, you also have the psychological experience of pitch. High-pitched sounds a ...
Language Processing in the Brain
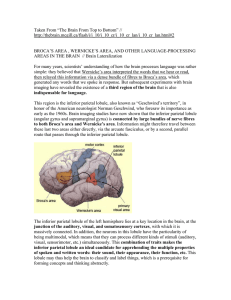
... imaging have revealed the existence of a third region of the brain that is also indispensable for language. This region is the inferior parietal lobule, also known as “Geschwind’s territory”, in honor of the American neurologist Norman Geschwind, who foresaw its importance as early as the 1960s. Bra ...
... imaging have revealed the existence of a third region of the brain that is also indispensable for language. This region is the inferior parietal lobule, also known as “Geschwind’s territory”, in honor of the American neurologist Norman Geschwind, who foresaw its importance as early as the 1960s. Bra ...
- Cambridge Center for Behavioral Studies
... demonstrate how well CyberRat simulates a live rat under similar experimental conditions. Ray argues that the cumulative records and tabulated overall operant data generated by CyberRat show great fidelity to the operant behaviors generated by live rats under the same experimental conditions. That i ...
... demonstrate how well CyberRat simulates a live rat under similar experimental conditions. Ray argues that the cumulative records and tabulated overall operant data generated by CyberRat show great fidelity to the operant behaviors generated by live rats under the same experimental conditions. That i ...