Chapter 24 Nervous Systems
... inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. A receiving neuron’s membrane may receive signals - that are both excitatory and inhibitory. - from many different sending neurons. The summation of excitation and inhibition determines if a neuron will t ...
... inhibit a receiving cell’s activity by decreasing its ability to develop action potentials. A receiving neuron’s membrane may receive signals - that are both excitatory and inhibitory. - from many different sending neurons. The summation of excitation and inhibition determines if a neuron will t ...
LO Needs for Psych 112
... may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact [email protected] with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit http://open.umich.edu/privacy- ...
... may share and adapt this material. Copyright holders of content included in this material should contact [email protected] with any questions, corrections, or clarification regarding the use of content. For more information about how to cite these materials visit http://open.umich.edu/privacy- ...
Texture discrimination and unit recordings in the rat
... animal’s nose to the discriminandum, although actual whisker contact is monitored by a SuperVHS camera and measured offline using fieldby-field videographic analysis. Rats can be trained within 3 – 6 weeks at which time they perform 100 – 150 trials/day at a level of 80% correct. Unit recording from ...
... animal’s nose to the discriminandum, although actual whisker contact is monitored by a SuperVHS camera and measured offline using fieldby-field videographic analysis. Rats can be trained within 3 – 6 weeks at which time they perform 100 – 150 trials/day at a level of 80% correct. Unit recording from ...
Basic Forms of Learning Classical Conditioning Evidence of
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
Learning: The Cognitive Process Classical Conditioning
... -Disagree: Prove that media violence is not the major cause of youth violence. Think of other components that cause youth violence.( Argue that media violence helps America-Socially, ...
... -Disagree: Prove that media violence is not the major cause of youth violence. Think of other components that cause youth violence.( Argue that media violence helps America-Socially, ...
A1982NC82200001
... the discovery of the scalp-recorded movement-related potentials in man, studies of single neurons in monkeys trained to perform specific movements have contributed a substantial amount of information on the brain mechanisms underlying motor control. There is a close relationship between firing patte ...
... the discovery of the scalp-recorded movement-related potentials in man, studies of single neurons in monkeys trained to perform specific movements have contributed a substantial amount of information on the brain mechanisms underlying motor control. There is a close relationship between firing patte ...
Cortical and basal ganglia contributions to habit learning and
... the basal ganglia that includes two parallel structures known as the caudate nucleus and the putamen. The striatum receives massive and highly convergent input from almost all of cortex. It can be subdivided into associative and sensorimotor regions depending on the origins of this input. Roughly sp ...
... the basal ganglia that includes two parallel structures known as the caudate nucleus and the putamen. The striatum receives massive and highly convergent input from almost all of cortex. It can be subdivided into associative and sensorimotor regions depending on the origins of this input. Roughly sp ...
Introduction of the Nervous System
... the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually given is walking in a shallow pond and stepping on a sharp object. The foot immediately raises before you are voluntarily aware of pending dange ...
... the cerebrum where conscious thoughts are initiated. In humans: the polysynaptic reflex is the sudden movement to protect life and limb. An example usually given is walking in a shallow pond and stepping on a sharp object. The foot immediately raises before you are voluntarily aware of pending dange ...
Cerebellum - UCSD Cognitive Science
... • With time and practice control passes from effortful to effortless • Effects on equilibrium, posture, and muscle tone ...
... • With time and practice control passes from effortful to effortless • Effects on equilibrium, posture, and muscle tone ...
Nervous System - Anderson School District One
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Common Neurotransmitters: Criteria for Neurotransmitters, Key
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
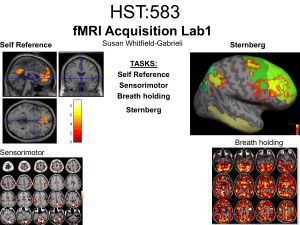
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
... additional auditory component so you see temporal lobe activation as well as motor and visual. In addition, the subject is responding with both hands so you see bilateral motor activation as opposed to only the left hemisphere motor (contralateral to response hand) ...
Slide 1
... spiking neural networks. Motivated by biological discoveries, many studies consider pulse-coupled neural networks with spike-timing as an essential component in ...
... spiking neural networks. Motivated by biological discoveries, many studies consider pulse-coupled neural networks with spike-timing as an essential component in ...
Neurons are - Vanderbilt University
... Functioning of the Brain • For example: groups of neurons called raphe nuclei, which use serotonin as a neurotransmitter, project to other nuclei and areas which are involved in “mood”; thus, mood can be influenced by drugs which affect levels of serotonin; drugs like Prozac elevate mood in some ind ...
... Functioning of the Brain • For example: groups of neurons called raphe nuclei, which use serotonin as a neurotransmitter, project to other nuclei and areas which are involved in “mood”; thus, mood can be influenced by drugs which affect levels of serotonin; drugs like Prozac elevate mood in some ind ...
What do my employees do? - College of Business, UNR
... Examples of Negative Reinforcement Focused on desirable behaviors that occur more frequently: If a clerical worker feels that being ahead is a favorable condition, the worker will be motivated to work hard in order to avoid the unpleasant state of being behind. An instructor deducts 10 points ...
... Examples of Negative Reinforcement Focused on desirable behaviors that occur more frequently: If a clerical worker feels that being ahead is a favorable condition, the worker will be motivated to work hard in order to avoid the unpleasant state of being behind. An instructor deducts 10 points ...
brain and spinal cord - Vanderbilt University
... Functioning of the Brain • For example: groups of neurons called raphe nuclei, which use serotonin as a neurotransmitter, project to other nuclei and areas which are involved in “mood”; thus, mood can be influenced by drugs which affect levels of serotonin; drugs like Prozac elevate mood in some ind ...
... Functioning of the Brain • For example: groups of neurons called raphe nuclei, which use serotonin as a neurotransmitter, project to other nuclei and areas which are involved in “mood”; thus, mood can be influenced by drugs which affect levels of serotonin; drugs like Prozac elevate mood in some ind ...
Unit 6 - Learning PP
... • Modeling has two basic components – – Observation – Imitation – Kids who observed models play violently with the Bobo doll were more likely to interact violently with the Bobo doll themselves – We can model prosocial or antisocial behaviors – Do violent TV shows and video games make people more li ...
... • Modeling has two basic components – – Observation – Imitation – Kids who observed models play violently with the Bobo doll were more likely to interact violently with the Bobo doll themselves – We can model prosocial or antisocial behaviors – Do violent TV shows and video games make people more li ...
Nonlinear Changes in Brain Activity During Continuous Word
... RT. Note that random-effects analyses did not reproduce some of the activations seen with our fixed-effects approach. The inverse relationship between the anterior cingulate cortex and individual or group RT was not significant when using random-effects analyses. The right PCC, however, did remain p ...
... RT. Note that random-effects analyses did not reproduce some of the activations seen with our fixed-effects approach. The inverse relationship between the anterior cingulate cortex and individual or group RT was not significant when using random-effects analyses. The right PCC, however, did remain p ...
Here
... action, causing the cursor to move. The brain gate system is a neuron motor prosthetic device consisting of an array of one hundred silicon microelectrodes; each electrode is 1mm long and thinner than a human hair. The electrodes are arranged less than half a millimeter apart on the array, which is ...
... action, causing the cursor to move. The brain gate system is a neuron motor prosthetic device consisting of an array of one hundred silicon microelectrodes; each electrode is 1mm long and thinner than a human hair. The electrodes are arranged less than half a millimeter apart on the array, which is ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... As described in the present Chapter, L-Dopa owes its efficacy to the fact that it forms part of the synthetic pathway for dopamine. For it to have an effect, there must be some DA neurons left in which DA can be synthesized. ...
... As described in the present Chapter, L-Dopa owes its efficacy to the fact that it forms part of the synthetic pathway for dopamine. For it to have an effect, there must be some DA neurons left in which DA can be synthesized. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Understanding ordinary unethical behavior: why people who value
... pay, their studies find that people lie when it pays, but only to the extent that they can do so without violating their perception of themselves as an honest person. This research advanced an important new perspective and has spawned significant follow-up research. Some of the follow-up work slight ...
... pay, their studies find that people lie when it pays, but only to the extent that they can do so without violating their perception of themselves as an honest person. This research advanced an important new perspective and has spawned significant follow-up research. Some of the follow-up work slight ...
Learning - Cloudfront.net
... Latent Learning Latent: hidden or concealed Tolman’s rats: – Rats learned about mazes in which they roamed even when they were unrewarded for doing so – Rats would acquire a cognitive map of the maze – Learning remained hidden until they were motivated to follow the rapid routes for food ...
... Latent Learning Latent: hidden or concealed Tolman’s rats: – Rats learned about mazes in which they roamed even when they were unrewarded for doing so – Rats would acquire a cognitive map of the maze – Learning remained hidden until they were motivated to follow the rapid routes for food ...
Memory - K-Dub
... (sniffing?). Dogs respond to immediate reinforcement. Humans have the ability to link a consequence to a behavior even if they aren’t linked sequentially in time. The piece of paper (money) can be a delayed reinforcer, paid a month later, yet still reinforcing if we link it to our performance. D ...
... (sniffing?). Dogs respond to immediate reinforcement. Humans have the ability to link a consequence to a behavior even if they aren’t linked sequentially in time. The piece of paper (money) can be a delayed reinforcer, paid a month later, yet still reinforcing if we link it to our performance. D ...