the brain - Dr Magrann
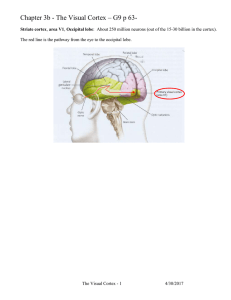
... I can identify them as keys. Within this region is an area called Brodmann areas 18 and 19. Damage to this area results in an inability to recognize what one sees. The person can see a chair in their way, move around it, but they can’t identify the object as a chair. Some people with this damage can ...
... I can identify them as keys. Within this region is an area called Brodmann areas 18 and 19. Damage to this area results in an inability to recognize what one sees. The person can see a chair in their way, move around it, but they can’t identify the object as a chair. Some people with this damage can ...
Printable
... a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin respo ...
... a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin respo ...
File
... Who is Wilder Penfield and how did he contribute to our understanding of the brain? Where is the site of intellectual processes in the brain? What 3 types of neurons are involved in reflex responses and in what order do nerve impulses travel through them? What is the difference between a voluntary m ...
... Who is Wilder Penfield and how did he contribute to our understanding of the brain? Where is the site of intellectual processes in the brain? What 3 types of neurons are involved in reflex responses and in what order do nerve impulses travel through them? What is the difference between a voluntary m ...
Consciousness, Literature and the Arts
... nonetheless provides eloquent and extensive access to Consciousness wrestling with the idea of human thought and actions being able to intervene, interrupt, and elaborate on 'Nature's' relentless cycles of birth, copulation, and death; the left hemisphere's persistent jockeying of the right hemisphe ...
... nonetheless provides eloquent and extensive access to Consciousness wrestling with the idea of human thought and actions being able to intervene, interrupt, and elaborate on 'Nature's' relentless cycles of birth, copulation, and death; the left hemisphere's persistent jockeying of the right hemisphe ...
BA 352 lecture ch8
... Behavior is purposive rather than random - People exhibit both positive (work done on time) and negative (arrive late for work) behavior for a reason Motivation arouses people to do something - People are unlikely to change a behavior or do something different unless they are motivated to do so Moti ...
... Behavior is purposive rather than random - People exhibit both positive (work done on time) and negative (arrive late for work) behavior for a reason Motivation arouses people to do something - People are unlikely to change a behavior or do something different unless they are motivated to do so Moti ...
Cognitive behavioral approach
... Within behavioral approach, the focus is placed directly on the athlete’s inappropriate behavior and ...
... Within behavioral approach, the focus is placed directly on the athlete’s inappropriate behavior and ...
Week 14 Lecture - PSY 310-1
... Within behavioral approach, the focus is placed directly on the athlete’s inappropriate behavior and ...
... Within behavioral approach, the focus is placed directly on the athlete’s inappropriate behavior and ...
Unit 3 Biological Bases of Behavior 11_12
... control his emotions or his obscene language. Autopsy revealed that the relationship between ...
... control his emotions or his obscene language. Autopsy revealed that the relationship between ...
In operant conditioning
... OPERANT CONDITIONING In operant conditioning (also a type of associative learning), people and animals learn to do certain things—and not to do others—because of the results of what they do. In other words, they learn from the consequences of their actions. ...
... OPERANT CONDITIONING In operant conditioning (also a type of associative learning), people and animals learn to do certain things—and not to do others—because of the results of what they do. In other words, they learn from the consequences of their actions. ...
Learning Unit Study Guide
... 10. How can classical conditioning be used to treat phobias today? (2 methods in applications of classical conditioning on pg. 133-135) ...
... 10. How can classical conditioning be used to treat phobias today? (2 methods in applications of classical conditioning on pg. 133-135) ...
Operant Conditioning
... or "an item presented" is, since it's something that's added to the animal's environment ...
... or "an item presented" is, since it's something that's added to the animal's environment ...
Examining the Role of BIS/BAS, Peer Relationships, and Negative
... • Fleming, C. B., Mason, A. W., Mazza, J. J., Abbott, R. D. & Catalano, R. F. (2008). Latent growth modeling of the relationship between depressive symptoms and substance abuse use during adolescence. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 22, 186-197. • Gray, J. A. (1987). The physiology of fear and st ...
... • Fleming, C. B., Mason, A. W., Mazza, J. J., Abbott, R. D. & Catalano, R. F. (2008). Latent growth modeling of the relationship between depressive symptoms and substance abuse use during adolescence. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 22, 186-197. • Gray, J. A. (1987). The physiology of fear and st ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
2009_Computers_Brains_Extra_Mural
... such as face recognition [..]. An algorithm to solve a face recognition task is one of the holy grails of computer science. At present, we do not know precisely how single neurons are involved in this computation. An essential first step is feature extraction from the image, which clearly involves a ...
... such as face recognition [..]. An algorithm to solve a face recognition task is one of the holy grails of computer science. At present, we do not know precisely how single neurons are involved in this computation. An essential first step is feature extraction from the image, which clearly involves a ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... depends or is contingent upon what happens next, or the consequences (whether it be a reinforcer/reward or punishment) Consequences: Animals & humans learns that performing or emitting some behavior is followed by a consequence (reward or punishment) that increases or decreases the chances of perf ...
... depends or is contingent upon what happens next, or the consequences (whether it be a reinforcer/reward or punishment) Consequences: Animals & humans learns that performing or emitting some behavior is followed by a consequence (reward or punishment) that increases or decreases the chances of perf ...
Behaviorism: An In-Depth Perspective 1 Running head
... concerned with retention, focuses on the ability to remember what one has witnessed or observed. The third step, regarding reproduction, addresses the ability of an individual to recreate a specific observed behavior. Lastly, the fourth step of Bandura’s social learning theory explains motivation, o ...
... concerned with retention, focuses on the ability to remember what one has witnessed or observed. The third step, regarding reproduction, addresses the ability of an individual to recreate a specific observed behavior. Lastly, the fourth step of Bandura’s social learning theory explains motivation, o ...
Innate/Learned Behavior Powerpoint
... What did this prove? Pavlov's experiment proved that all animals could be trained or conditioned to expect a consequence on the results of previous experience. ...
... What did this prove? Pavlov's experiment proved that all animals could be trained or conditioned to expect a consequence on the results of previous experience. ...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury 9th Annual Fall
... • 3T MRI- done at centers using higher resolution than 1.5 T evalute white matter tracts and cortex ...
... • 3T MRI- done at centers using higher resolution than 1.5 T evalute white matter tracts and cortex ...
Jackson Rancheria Casino Shooting
... ____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS. ____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons ____ 6. Gaps in a myelin sheath ____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS ____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscl ...
... ____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS. ____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons ____ 6. Gaps in a myelin sheath ____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS ____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscl ...
Why light
... Both sets of kittens were then tested by placing them in an environment with both types of orientation. Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens raised in horizontal environments ignored the vertically oriented parts of their envi ...
... Both sets of kittens were then tested by placing them in an environment with both types of orientation. Kittens raised in vertical environments ignored the horizontally oriented parts of their environments. Kittens raised in horizontal environments ignored the vertically oriented parts of their envi ...
The Synergy between Bioinformatics and Cognitive Informatics
... artificial intelligence problems without necessarily creating a model of a real biological system. Biological neural networks are made up of real biological neurons that are connected or functionally-related in the peripheral nervous system or the central nervous system. A biological neuron may have ...
... artificial intelligence problems without necessarily creating a model of a real biological system. Biological neural networks are made up of real biological neurons that are connected or functionally-related in the peripheral nervous system or the central nervous system. A biological neuron may have ...
Neurons and Astrocytes
... because the neurons have successfully created a "bike riding" pathway. • Scientists think these “pathways” are created by a type of Glial cell called the astrocytes! ...
... because the neurons have successfully created a "bike riding" pathway. • Scientists think these “pathways” are created by a type of Glial cell called the astrocytes! ...
Operant Conditioning and Cognitive Learning
... chimpanzee in a cage with a banana on the ground just out of his reach outside of the cage. After a period of inaction, the chimp suddenly grabbed the stick in the cage, poked it through the cage, and dragged the banana within reach. This type of learning is called: (A) Insight (B) Latent (C) Cognit ...
... chimpanzee in a cage with a banana on the ground just out of his reach outside of the cage. After a period of inaction, the chimp suddenly grabbed the stick in the cage, poked it through the cage, and dragged the banana within reach. This type of learning is called: (A) Insight (B) Latent (C) Cognit ...