This file has Chapter II: Structural differentiation of the brain • Neural
... Second, at least since the morphological work of Baer (1828), it has been suspected that there is a common basic structural plan of the vertebrate brain. The extent to which this may be true, and the nature of this plan, are fundamental issues that deserve consideration from time to time. And third, ...
... Second, at least since the morphological work of Baer (1828), it has been suspected that there is a common basic structural plan of the vertebrate brain. The extent to which this may be true, and the nature of this plan, are fundamental issues that deserve consideration from time to time. And third, ...
Affective Computing
... • Basic, distinct emotion circuits in the brain – Distinct emotional patterns can be evoked by stimulating electrically particular subcortical areas responsible for basic emotions • Cortical regions largely free of such effects ...
... • Basic, distinct emotion circuits in the brain – Distinct emotional patterns can be evoked by stimulating electrically particular subcortical areas responsible for basic emotions • Cortical regions largely free of such effects ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... between two seemingly mutually exclusive requirements: The model for a single neuron must be: 1) computationally simple, yet 2) capable of producing rich firing patterns exhibited by real biological neurons. Using biophysically accurate Hodgkin–Huxley-type models is computationally prohibitive, sinc ...
... between two seemingly mutually exclusive requirements: The model for a single neuron must be: 1) computationally simple, yet 2) capable of producing rich firing patterns exhibited by real biological neurons. Using biophysically accurate Hodgkin–Huxley-type models is computationally prohibitive, sinc ...
Brain Day Volunteer Instructor Guide
... Taste receptors are clustered into taste buds on our tongue, all over our mouth on the roof of our mouth, epiglottis and upper esophagus. At the top of each taste bud is an opening called a taste pore. This is where the taste bud comes into contact with food molecules to recognize four basic tastes: ...
... Taste receptors are clustered into taste buds on our tongue, all over our mouth on the roof of our mouth, epiglottis and upper esophagus. At the top of each taste bud is an opening called a taste pore. This is where the taste bud comes into contact with food molecules to recognize four basic tastes: ...
Simple model of spiking neurons
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
... Hoppensteadt and Izhikevich [1] and Wang [2] have proposed network models where the neural activity is described by differential equations. Both architectures can be used for pattern recognition via associative memory, which occurs when a group of neurons fires synchronously. These models were inspi ...
fMRI can see M1, premotor activity Corresponding to Individual
... activity of individual muscles. Further, it is believed that the spatial resolution of noninvasive brain imaging modalities is not sufficient to isolate neural activity related to individual muscles. However, this study shows that it is possible to reconstruct a quantitative mapping from functional ...
... activity of individual muscles. Further, it is believed that the spatial resolution of noninvasive brain imaging modalities is not sufficient to isolate neural activity related to individual muscles. However, this study shows that it is possible to reconstruct a quantitative mapping from functional ...
Module_10vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... – Spontaneous recovery • tendency for the conditioned response to reappear after being extinguished, even though there have been no further conditioning trials ...
... – Spontaneous recovery • tendency for the conditioned response to reappear after being extinguished, even though there have been no further conditioning trials ...
PDF - Stanford University
... maintenance of these symptoms, over the past two decades investigators have used neuroimaging techniques to examine the neural substrates of MDD. In this review we present findings from this body of research, identifying the major brain regions or structures that have been implicated in depression a ...
... maintenance of these symptoms, over the past two decades investigators have used neuroimaging techniques to examine the neural substrates of MDD. In this review we present findings from this body of research, identifying the major brain regions or structures that have been implicated in depression a ...
Albert Bandura Paper
... person. Bandura believes that children imitate models or, “individuals that are observed,” (McLeod). There are many models for children while they’re growing up. Children are influenced by their parents, peers, teachers, and characters on television. These models influence a child’s behavior that th ...
... person. Bandura believes that children imitate models or, “individuals that are observed,” (McLeod). There are many models for children while they’re growing up. Children are influenced by their parents, peers, teachers, and characters on television. These models influence a child’s behavior that th ...
Continuous reinforcement
... independently at the same time for two or more different behaviors ◦ organism has a choice of behaviors and schedules ◦ CONC VI 15 sec VI 60 sec: Can choose to respond to the VI 15 second schedule OR the VI 60 sec. schedule ...
... independently at the same time for two or more different behaviors ◦ organism has a choice of behaviors and schedules ◦ CONC VI 15 sec VI 60 sec: Can choose to respond to the VI 15 second schedule OR the VI 60 sec. schedule ...
A novel neuroprosthetic interface with the peripheral nervous system
... important to have an architecture that minimizes surgical complexity and recovery time, provides a hospitable environment for nerve survival and lends itself to rapid learning. Over the past several decades, a variety of architectures that target both the CNS and PNS have been developed. CNS-based a ...
... important to have an architecture that minimizes surgical complexity and recovery time, provides a hospitable environment for nerve survival and lends itself to rapid learning. Over the past several decades, a variety of architectures that target both the CNS and PNS have been developed. CNS-based a ...
Inhalant Prevention Education
... psychoactive effects when misused. Most inhalants are readily available, inexpensive or free, and usually legal to purchase and possess. Many youth do not perceive them as harmful and don’t understand the consequences. To learn more about inhalants prior to teaching this lesson, please take the 15-m ...
... psychoactive effects when misused. Most inhalants are readily available, inexpensive or free, and usually legal to purchase and possess. Many youth do not perceive them as harmful and don’t understand the consequences. To learn more about inhalants prior to teaching this lesson, please take the 15-m ...
Center for Health Education Wellness | Homewood Student Affairs
... medication in the body over a period of time). These medications have a paradoxically calming and “focusing” effect on individuals with ADHD. Researchers speculate that because methylphenidate amplifies the release of dopamine, it can improve attention and ...
... medication in the body over a period of time). These medications have a paradoxically calming and “focusing” effect on individuals with ADHD. Researchers speculate that because methylphenidate amplifies the release of dopamine, it can improve attention and ...
Structural Loop Between the Cerebellum and the Superior Temporal
... landmarks for cerebro-cerebellar connections known from previous neuroanatomical and DTI studies (e.g., Brodal 1978, 1979; Glickstein et al. 1985, 1994; Schmahmann and Pandya 1991; Dum and Strick 2003; Evrard and Craig 2008; Salmi et al. 2010). This suggests anatomical plausibility of the DTI finding ...
... landmarks for cerebro-cerebellar connections known from previous neuroanatomical and DTI studies (e.g., Brodal 1978, 1979; Glickstein et al. 1985, 1994; Schmahmann and Pandya 1991; Dum and Strick 2003; Evrard and Craig 2008; Salmi et al. 2010). This suggests anatomical plausibility of the DTI finding ...
Regulation of Respiration
... person breathes deeply for a short interval and then breathes slightly or not at all for an additional interval most common – Cheyne-Stokes breathing (slowly waxing and waning respiration occurring about every 40 to 60 seconds) ...
... person breathes deeply for a short interval and then breathes slightly or not at all for an additional interval most common – Cheyne-Stokes breathing (slowly waxing and waning respiration occurring about every 40 to 60 seconds) ...
a place for behavior in ecological epigenetics
... example, in addition to a more established mode of epigenetic inheritance through the germline, epigenetically based behaviors can be transmitted to offspring through parental care (Avital and Jablonka 2000; Day and Bonduriansky 2011). Understanding how environmental (e.g., offspring environment) an ...
... example, in addition to a more established mode of epigenetic inheritance through the germline, epigenetically based behaviors can be transmitted to offspring through parental care (Avital and Jablonka 2000; Day and Bonduriansky 2011). Understanding how environmental (e.g., offspring environment) an ...
The elephant brain in numbers
... elephant brain, in particular, at 4.5–5 kg, is about 3–4 times larger than the human brain (Manger et al., 2009). Another possibility was the relative mass of the cerebral cortex measured as a percentage of brain mass—but although this value is indeed largest in the human brain, it is only marginall ...
... elephant brain, in particular, at 4.5–5 kg, is about 3–4 times larger than the human brain (Manger et al., 2009). Another possibility was the relative mass of the cerebral cortex measured as a percentage of brain mass—but although this value is indeed largest in the human brain, it is only marginall ...
learning - khollington
... Situational cues are repeatedly paired with the drug’s effects (UCS), which elicits a compensatory response that is opposite to the drug’s effect (UCR). After several pairings the situational cues become CS. Exposure to the CS will now elicit a conditioned compensatory response (CCR). The heroine ...
... Situational cues are repeatedly paired with the drug’s effects (UCS), which elicits a compensatory response that is opposite to the drug’s effect (UCR). After several pairings the situational cues become CS. Exposure to the CS will now elicit a conditioned compensatory response (CCR). The heroine ...
Chapter 5 Powerpoint - Destiny High School
... Punishments only suppress behavior—doesn’t teach more desirable behavior Punishments often stir up unpleasant emotions that can impede learning the behavior we want to be substituted EX: when children are scolded fro mispronouncing a word child may become frightened and confused and then they ...
... Punishments only suppress behavior—doesn’t teach more desirable behavior Punishments often stir up unpleasant emotions that can impede learning the behavior we want to be substituted EX: when children are scolded fro mispronouncing a word child may become frightened and confused and then they ...
melanin in the body
... whose primary signal is dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical signal sent between neurons and cells controlling many different roles of the brain. It has extremely powerful affects on the brain processes that control emotional responses, the ability to feel pleasure and pain, our mood, attention and lear ...
... whose primary signal is dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical signal sent between neurons and cells controlling many different roles of the brain. It has extremely powerful affects on the brain processes that control emotional responses, the ability to feel pleasure and pain, our mood, attention and lear ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Rates of up to 10,000 bar-presses an hour recorded Medial forebrain bundle passing through lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum An animal will self-stimulate for more than 24 hrs continuously without rest, and will cross electrified grid to gain access to lever Other brain centers are aver ...
... Rates of up to 10,000 bar-presses an hour recorded Medial forebrain bundle passing through lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum An animal will self-stimulate for more than 24 hrs continuously without rest, and will cross electrified grid to gain access to lever Other brain centers are aver ...
Learning Theory - Amanda K. Jones
... to let the dog outside. The sitting behavior is positively reinforced because the dog gets to go outside and have fun. Keep in mind that positive reinforcement does not always result in positive behavior. For example, a people-loving dog may see a neighbor walking down the sidewalk. The dog pulls on ...
... to let the dog outside. The sitting behavior is positively reinforced because the dog gets to go outside and have fun. Keep in mind that positive reinforcement does not always result in positive behavior. For example, a people-loving dog may see a neighbor walking down the sidewalk. The dog pulls on ...
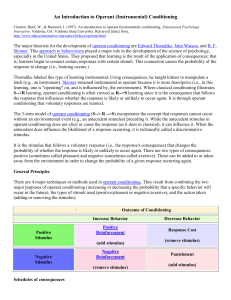
Operant conditioning
... The Premack Principle, often called "grandma's rule," states that a high frequency activity can be used to reinforce low frequency behavior. Access to the preferred activity is contingent on completing the lowfrequency behavior. The high frequency behavior to use as a reinforcer can be determined by ...
... The Premack Principle, often called "grandma's rule," states that a high frequency activity can be used to reinforce low frequency behavior. Access to the preferred activity is contingent on completing the lowfrequency behavior. The high frequency behavior to use as a reinforcer can be determined by ...