Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... left: language and logical thinking; right: visual and spatial functions • Integration: groups of coordinated cells • Differentiation: each neuron becomes specialized ...
... left: language and logical thinking; right: visual and spatial functions • Integration: groups of coordinated cells • Differentiation: each neuron becomes specialized ...
File
... are their functions? Answer: Sympathetic nervous system- “fight/flight”. Parasympathetic- “rest & digest”. ...
... are their functions? Answer: Sympathetic nervous system- “fight/flight”. Parasympathetic- “rest & digest”. ...
here - CNC
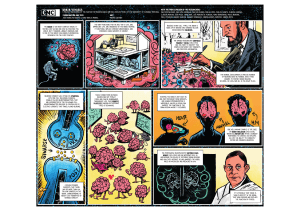
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
Visual Cortical Dynamics Charles Gilbert The Rockefeller University
... and the immediate information coming from the retina. These internal representations enable the brain’s analysis of scenes to be subject to topdown influences of attention, expectation, perceptual tasks, perceptual learning, working memory and motor commands. At the level of brain circuitry this pro ...
... and the immediate information coming from the retina. These internal representations enable the brain’s analysis of scenes to be subject to topdown influences of attention, expectation, perceptual tasks, perceptual learning, working memory and motor commands. At the level of brain circuitry this pro ...
Students know
... • Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
... • Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
Introduction to drugs and the brain
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
... Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences ...
nervous system
... Carries impulses from CNS to effector e.g. muscle to bring about movement or gland to bring about secretion of hormone e.g ADH ...
... Carries impulses from CNS to effector e.g. muscle to bring about movement or gland to bring about secretion of hormone e.g ADH ...
Nerves and the brain
... Cell body - contains the nucleus and other cell organelles. High level of cellular activity - means there is a large amount of endoplasmic reticulum - secretes protein visible in cytoplasm Dendrites - pick up messages using their extensive branches to increase the surface area of the ‘receiving end’ ...
... Cell body - contains the nucleus and other cell organelles. High level of cellular activity - means there is a large amount of endoplasmic reticulum - secretes protein visible in cytoplasm Dendrites - pick up messages using their extensive branches to increase the surface area of the ‘receiving end’ ...
The Nervous System
... coordination. BRAIN STEM – Controls some important automatic body functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure and digestion. NERVE – A bundle of neurons that act like an electrical cord moving signals through the nervous system. NUERONS – Specialized cells that send quick messages through ...
... coordination. BRAIN STEM – Controls some important automatic body functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure and digestion. NERVE – A bundle of neurons that act like an electrical cord moving signals through the nervous system. NUERONS – Specialized cells that send quick messages through ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... important to the processing of auditory and visual sensory information Process auditory sensations from the left and right ears Helps you visually locate objects and track their movements Substantia nigra: in midbrain; contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons ...
... important to the processing of auditory and visual sensory information Process auditory sensations from the left and right ears Helps you visually locate objects and track their movements Substantia nigra: in midbrain; contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons ...
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
... commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... Function of Central and Peripheral Systems ● integrating sensory information and responding accordingly ● The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body ● cells that detect information like smell and vision, exclusively motor cells, like the eyeballs and ...
... Function of Central and Peripheral Systems ● integrating sensory information and responding accordingly ● The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body ● cells that detect information like smell and vision, exclusively motor cells, like the eyeballs and ...
Neurotransmitters
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
INC-IEM Neuroengineering Seminar - 13-11-04
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
... Sensorycircuits (sight, touch, hearing, smell, taste) bring information to the nervous system, whereas motor circuits send information to muscles and glands. ...
The Nervous System
... 1. difficult to talk about 2. two fistfuls of pinkish/gray 3. wrinkled 4. consistency of cold oatmeal • 5. three pounds • 6. hugely complex • 7. four basic regions ...
... 1. difficult to talk about 2. two fistfuls of pinkish/gray 3. wrinkled 4. consistency of cold oatmeal • 5. three pounds • 6. hugely complex • 7. four basic regions ...
Vocabulary: Chapter 1 Body Control Systems Neuron
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
... muscles and organs. Retina- an area at the back of the eye that contains sensory receptors for light. Dendrite- part of a neuron that collects information from other neurons. Nerve impulse- message that travels from the dendrites of a neuron to the axon. Axon- part of the neuron that carries message ...
1-nervous_system
... form myelin sheaths around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
... form myelin sheaths around axons Holds neurons in place Speeds up transmission Can repair if damaged Keeps messages from being scrambled ...
The Nervous System
... collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
... collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
Brain-Powerpoint
... Predators tend to have larger brains than prey species. Mammals tend to have larger brains, and primates even more so. ...
... Predators tend to have larger brains than prey species. Mammals tend to have larger brains, and primates even more so. ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called neurotransmitters that trave ...
... - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called neurotransmitters that trave ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cortex enable our perceiving, thinking and speaking? 5. What have researchers learned ...
... 2. What are the lower-level brain structures, and what are their functions? 3. What is a "reward deficiency syndrome" and how might it explain addictive disorders? 4. How do neural networks within the cerebral cortex enable our perceiving, thinking and speaking? 5. What have researchers learned ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.