Chapter 03: Neuroscience and behaviour PowerPoint
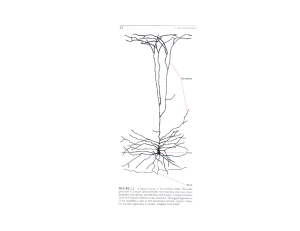
... • Dendrites — “tree” • Cell body — “soma” • Axon — “myelin” ...
... • Dendrites — “tree” • Cell body — “soma” • Axon — “myelin” ...
Ch.02
... Brainstem the oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. Responsible for automatic survival functions. ...
... Brainstem the oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. Responsible for automatic survival functions. ...
Verlamde man bestuurt computer via gedachten
... check e-mail and play computer games using his thoughts. The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they r ...
... check e-mail and play computer games using his thoughts. The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they r ...
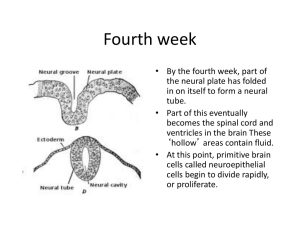
Fourth week
... Back to the structures in the growing brain 2nd and 3rd month • The growing brain is beginning to take shape. • The hindbrain gives rise to the medulla oblongata and the pons (part of the brain stem), which are involved in many functions essential to life, such as breathing and heartbeat. • The cer ...
... Back to the structures in the growing brain 2nd and 3rd month • The growing brain is beginning to take shape. • The hindbrain gives rise to the medulla oblongata and the pons (part of the brain stem), which are involved in many functions essential to life, such as breathing and heartbeat. • The cer ...
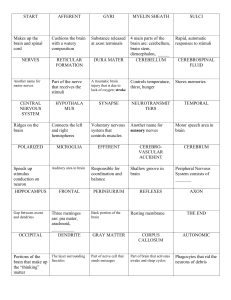
Health - Nervous System Review
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
... 1. Largest part of the brain where learning, intelligence, and judgment occur 3. Sweet, sour, salty, and bitter 5. Nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal column 6. Carries messages to your brain and spinal cord from receptors in your skin 8. Special cell in our skin that allows us to s ...
Chapter 12
... Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
... Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
NS Review
... 23. During a what**** potential the cell is negative outside & positive inside? 24. During depolarization the blank *** channels open. 25. The Na/K pump reestablishes the what *** potential. 26. A bruise to the brain which could be mild to severe is called what? 27. The substance released at axonal ...
... 23. During a what**** potential the cell is negative outside & positive inside? 24. During depolarization the blank *** channels open. 25. The Na/K pump reestablishes the what *** potential. 26. A bruise to the brain which could be mild to severe is called what? 27. The substance released at axonal ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
... 6. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a neuron, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ pe ...
the central nervous system
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
... coverings called the meninges and are bathed in cerebrospinal fluids. ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
... ¾ An electroencephalogram records the different patterns in the electrical activity of the brain produced during sleep and arousal. ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... is the largest part ofthe brain, where cognitive functions as well as many of the motor functions of the brain are carried out. 16. The nerves in the connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. 17. The primary visual cortex, where vision registers, and association areas involved in t ...
... is the largest part ofthe brain, where cognitive functions as well as many of the motor functions of the brain are carried out. 16. The nerves in the connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. 17. The primary visual cortex, where vision registers, and association areas involved in t ...
History of Psychology - Western Washington University
... • Do you think your brain today is the same as it was when you were born? Why or why not? ...
... • Do you think your brain today is the same as it was when you were born? Why or why not? ...
10-5 Infant Biosocial Development
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
... Germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods Teratogens: critical period, threshold, interaction Birth process ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Nervous System study guide
... The three main parts are: the brain, spinal cord (medulla) and nerves (neurons). The brain (master control center) has three main parts: 1. Cerebrum: largest area. Controls thinking, memory, senses, and feelings 2. Cerebellum: under the back part of the cerebrum. Controls balance and movement. 3. Br ...
... The three main parts are: the brain, spinal cord (medulla) and nerves (neurons). The brain (master control center) has three main parts: 1. Cerebrum: largest area. Controls thinking, memory, senses, and feelings 2. Cerebellum: under the back part of the cerebrum. Controls balance and movement. 3. Br ...
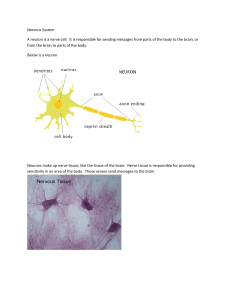
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
... Below you will find a plastic model of the brain. The brain is responsible for sending and receiving all the signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... Overview of organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems • Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a particular function • Muscle, Epithelial, Nervous, and Connective tissues • The human body is composed of 11 organ systems. ...
... Overview of organization Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems • Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a particular function • Muscle, Epithelial, Nervous, and Connective tissues • The human body is composed of 11 organ systems. ...
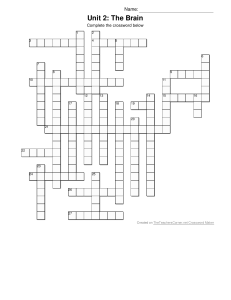
Crossword Puzzle
... 26. a series of x-ray photographs of the brain taken from different positions and analyzed by computer, creating an image that represents a slice through the brain 27. located just behind the forehead, these lobes are involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments ...
... 26. a series of x-ray photographs of the brain taken from different positions and analyzed by computer, creating an image that represents a slice through the brain 27. located just behind the forehead, these lobes are involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.