The Nervous System
... Impulses that go to the brain are? Ascending or Descending The gaps between the myelin in a neuron are called? ________________ The gaps that exist between two neurons are called _____________________ The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found is the __________________ What is “fight or fligh ...
... Impulses that go to the brain are? Ascending or Descending The gaps between the myelin in a neuron are called? ________________ The gaps that exist between two neurons are called _____________________ The part of the neuron where the nucleus is found is the __________________ What is “fight or fligh ...
File
... • F. Two divisions of the Nervous System – 1. CNS – Central Nervous System • A. includes brain and spinal cord • B. there are billions of neurons in the brain • C. the spinal cord is made up of bundles of ...
... • F. Two divisions of the Nervous System – 1. CNS – Central Nervous System • A. includes brain and spinal cord • B. there are billions of neurons in the brain • C. the spinal cord is made up of bundles of ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... your life that have experienced or struggled with a nervous system disorder. What were the symptoms and struggles? After you finish, get out your notes. ...
... your life that have experienced or struggled with a nervous system disorder. What were the symptoms and struggles? After you finish, get out your notes. ...
Slide ()
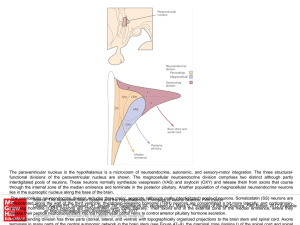
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... reasoning to reach the speed of numerical calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
... reasoning to reach the speed of numerical calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
Slide ()
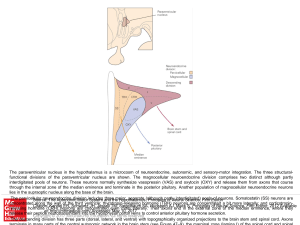
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Chapter 6
... 6. The ______ controls movement and cognitive processes that require precise timing. (6) 7. What is the difference between gray matter and white matter? (7) 8. What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system and what are their functions? (7) 9. How many neurons are in the mammalian brain? ...
... 6. The ______ controls movement and cognitive processes that require precise timing. (6) 7. What is the difference between gray matter and white matter? (7) 8. What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system and what are their functions? (7) 9. How many neurons are in the mammalian brain? ...
Chapter 3 Neuroscience and Behavior
... some dendrites have more branches than others; this allows the neuron to receive more information 3. axon-- thin, tube-like structure that extends out from the cell body Sends information from neuron to other neurons, a gland, or a muscle Not all neurons have axons, and the ones that do have axons h ...
... some dendrites have more branches than others; this allows the neuron to receive more information 3. axon-- thin, tube-like structure that extends out from the cell body Sends information from neuron to other neurons, a gland, or a muscle Not all neurons have axons, and the ones that do have axons h ...
Review questions: Neuroanatomy
... Vasomotor (nerves having muscular control of the blood vessel walls) Centre, Centres for cough, gag, swallow, and vomit. 2. Describe how the sensation of being touched is dealt with in the 3 functional areas of the cerebral cortex. 3. Explain what is meant by the term “the emotional brain”. 4. Defin ...
... Vasomotor (nerves having muscular control of the blood vessel walls) Centre, Centres for cough, gag, swallow, and vomit. 2. Describe how the sensation of being touched is dealt with in the 3 functional areas of the cerebral cortex. 3. Explain what is meant by the term “the emotional brain”. 4. Defin ...
The Nervous System
... nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. • Humans of 12 pairs of cranial nerves attached to the b ...
... nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. • Humans of 12 pairs of cranial nerves attached to the b ...
The Nervous System When you caught the ruler with your fingers
... The brain is the center of the nervous system and coordinates all of the body’s activities. It is the most complex organ in the human body. The brain is made up of approximately 100 billion nerve cells (neurons). The three major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Surrou ...
... The brain is the center of the nervous system and coordinates all of the body’s activities. It is the most complex organ in the human body. The brain is made up of approximately 100 billion nerve cells (neurons). The three major parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Surrou ...
Answers
... 1. A neuron is a ___NERVE___ cell. The brain is made up of about _100__billion neurons. 2. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body in some ways such as: a. Neurons are surrounded by a ________MEMBRANE_______________________. b. Neurons have a ______NUCLEUS____________ that contains __GENES___ ...
... 1. A neuron is a ___NERVE___ cell. The brain is made up of about _100__billion neurons. 2. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body in some ways such as: a. Neurons are surrounded by a ________MEMBRANE_______________________. b. Neurons have a ______NUCLEUS____________ that contains __GENES___ ...
Chapter 2 – Biology of the Mind
... 1. What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? 2. How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? 3. How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmission? 4. What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? 5. How ...
... 1. What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? 2. How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? 3. How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmission? 4. What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? 5. How ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... hearing loss after only a few minutes of exposure. Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance clubs, it is not only the acoust ...
... hearing loss after only a few minutes of exposure. Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance clubs, it is not only the acoust ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Brain and behavior are two of the most interesting subjects in science; biopsychology focuses on brain/behavior relationships. Psychology is a study of human behaviour. While, Biopsychologists study how the brain and the rest of the nervous system determine what we perceive, feel, think, say, ...
... Brain and behavior are two of the most interesting subjects in science; biopsychology focuses on brain/behavior relationships. Psychology is a study of human behaviour. While, Biopsychologists study how the brain and the rest of the nervous system determine what we perceive, feel, think, say, ...
AHISA PASTORAL CARE CONFERENCE, 2006
... • It contains about 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) which are responsible for all our mental activity. These make up the grey matter of the brain ...
... • It contains about 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) which are responsible for all our mental activity. These make up the grey matter of the brain ...
Document
... • May play role in regulation of autonomic functions such as respiration and vomiting ...
... • May play role in regulation of autonomic functions such as respiration and vomiting ...
The Nervous System
... by the brain. • However, a reflex is controlled by the spinal cord. • A reflex is a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus. • An example, if you touch a really hot object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds by sending impulses to your arm m ...
... by the brain. • However, a reflex is controlled by the spinal cord. • A reflex is a rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus. • An example, if you touch a really hot object with your hand. The impulse is sent to the spinal cord immediately. The spinal cord responds by sending impulses to your arm m ...
Nervous System 2
... peripheral location they innervate?) c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you ...
... peripheral location they innervate?) c. Which is primarily involved in energy conservation and basic self-maintenance, and which in rapid mobilization of energy (fight or flight) d. Know major effects of each, including specific effects on specific organs. Note that these are easier to learn if you ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... c. Reflexes are much faster than regular responses. Give an explanation by using the structure of a reflex arc to help you. ...
... c. Reflexes are much faster than regular responses. Give an explanation by using the structure of a reflex arc to help you. ...
Nervous System Nervous system
... The axons in spinal cord allow the brain to communicate with PNS The axons of sensory neurons in skin and muscles carry impulses to the spinal cord The spinal cord relays these impulses to the brain The brain interprets these impulses as pain, temperature, or other sensations and responds to the sit ...
... The axons in spinal cord allow the brain to communicate with PNS The axons of sensory neurons in skin and muscles carry impulses to the spinal cord The spinal cord relays these impulses to the brain The brain interprets these impulses as pain, temperature, or other sensations and responds to the sit ...
Frequently asked questions Psychology 1010.06M A Biologically-Oriented
... Verbal left hemisphere ...
... Verbal left hemisphere ...
Unit 2 The Brain
... – A. Action Potential – B. Inhibitory Potential – C. Excitatory Potential – D. Graded Potential – E. Neuron Potential ...
... – A. Action Potential – B. Inhibitory Potential – C. Excitatory Potential – D. Graded Potential – E. Neuron Potential ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... • It is a progressive disorder that currently has no cure. However new treatments have been shown effective in slowing the progression and dealing with symptoms. • Symptoms vary depending on the regions of nervous tissue affected. (Blurred vision, weakness, change in sensation, etc…) ...
... • It is a progressive disorder that currently has no cure. However new treatments have been shown effective in slowing the progression and dealing with symptoms. • Symptoms vary depending on the regions of nervous tissue affected. (Blurred vision, weakness, change in sensation, etc…) ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... by the astounding complexity and intricate activity of the brain and nervous system. Most signals are excitatory, somewhat like pushing a neuron’s accelerator. Some are inhibitory, more like pushing its brake. Myers is making a comparison between the effect of a neuron firing and the effect of speed ...
... by the astounding complexity and intricate activity of the brain and nervous system. Most signals are excitatory, somewhat like pushing a neuron’s accelerator. Some are inhibitory, more like pushing its brake. Myers is making a comparison between the effect of a neuron firing and the effect of speed ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.