Brain Jokes (Questions)
... 1. What is a sleeping brain's favorite musical group (rock band)? 2. What does a brain do when it sees a friend across the street? 3. Where does a brain go on vacation? 4. What did the hippocampus say during its retirement speech? 5. Why did the action potential cross the optic chiasm? 6. What did t ...
... 1. What is a sleeping brain's favorite musical group (rock band)? 2. What does a brain do when it sees a friend across the street? 3. Where does a brain go on vacation? 4. What did the hippocampus say during its retirement speech? 5. Why did the action potential cross the optic chiasm? 6. What did t ...
The Neuron - University of Connecticut
... medulla - breathing, heartbeat, blood circulation pons - arousal and attention cerebellum - integration of muscles to perform fine movements, but no coordination / direction of these movements; balance cat transected above hindbrain: can move but not act midbrain: forms movements into acts; controls ...
... medulla - breathing, heartbeat, blood circulation pons - arousal and attention cerebellum - integration of muscles to perform fine movements, but no coordination / direction of these movements; balance cat transected above hindbrain: can move but not act midbrain: forms movements into acts; controls ...
Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... Synaptic Transmission Synaptic Transmission – Sequence of events in which ...
... Synaptic Transmission Synaptic Transmission – Sequence of events in which ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... exercising brain has unique methods of keeping itself fueled. What’s more, the finely honed energy balance that occurs in the brain appears to have implications ...
... exercising brain has unique methods of keeping itself fueled. What’s more, the finely honed energy balance that occurs in the brain appears to have implications ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Damages the outer part of some nerves This causes messages not to be sent properly It will affect your thinking and memory Cerebral Palsy Damage to the brain while the brain is growing No cure for either disease. Other disorders are Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy ...
... Damages the outer part of some nerves This causes messages not to be sent properly It will affect your thinking and memory Cerebral Palsy Damage to the brain while the brain is growing No cure for either disease. Other disorders are Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy ...
Chapter 02
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
PowerPoint Slides
... The contrast in architecture • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per second – Absolute arithmetic precision ...
... The contrast in architecture • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per second – Absolute arithmetic precision ...
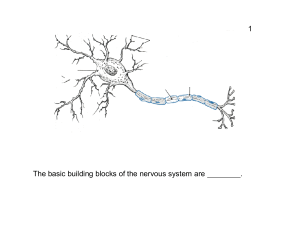
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... & toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch & body position ...
... & toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch & body position ...
Chapter 02_Quiz - Biloxi Public Schools
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
... sustained damage to his right cerebral hemisphere. This injury is most likely to reduce his ability to: • A) tell an angry face from a happy ...
Unit 3 Neuroscience and Behavior CHAPTER PREVIEW Our
... traverse the tiny synaptic gap between neurons and pass on excitatory or inhibitory messages. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system, which directs voluntary movements and reflexes, and the autonomic nerv ...
... traverse the tiny synaptic gap between neurons and pass on excitatory or inhibitory messages. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system, which directs voluntary movements and reflexes, and the autonomic nerv ...
Review
... Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. Describe the nervo ...
... Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. Describe the nervo ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... enriched-environment rats and the rats raised in bare cages. • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
... enriched-environment rats and the rats raised in bare cages. • B) Enriched-environment rats showed more stress and aggression. • C) Enriched-environment rats were able to ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
... biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
Overview of the Brain
... neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. • At the macroscopic level these nerve fibers form clusters in the brain creating distinct regions which after years of empirical study have been assigned different functions by scientists over the years. ...
... neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. • At the macroscopic level these nerve fibers form clusters in the brain creating distinct regions which after years of empirical study have been assigned different functions by scientists over the years. ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... Radiation is absorbed in different amounts depending on the density (“weight”) of the brain tissue Computers measure the amount of radiation absorbed and transform this information into a three-dimensional view of the brain ...
... Radiation is absorbed in different amounts depending on the density (“weight”) of the brain tissue Computers measure the amount of radiation absorbed and transform this information into a three-dimensional view of the brain ...
Neuroscience
... between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse If the message is for arm movement, the vesicles only release neurotransmitters invol ...
... between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse If the message is for arm movement, the vesicles only release neurotransmitters invol ...
PPT File - Holden R
... Spinocerebellar System • Carry proprioceptive information to cerebellum • Actual movements can be monitored and compared to cerebral information representing intended movement • Tracts – Posterior – Anterior ...
... Spinocerebellar System • Carry proprioceptive information to cerebellum • Actual movements can be monitored and compared to cerebral information representing intended movement • Tracts – Posterior – Anterior ...
Chapter 14
... Spinocerebellar System • Carry proprioceptive information to cerebellum • Actual movements can be monitored and compared to cerebral information representing intended movement • Tracts – Posterior – Anterior ...
... Spinocerebellar System • Carry proprioceptive information to cerebellum • Actual movements can be monitored and compared to cerebral information representing intended movement • Tracts – Posterior – Anterior ...
Lesson Plan
... conscious thought, executive thinking, decision-making and movement. This is the most unique to humans and more developed in humans than in animals. If you damage this, you will have trouble working socially and creatively as well as experience impairments with movements, depending on the part of th ...
... conscious thought, executive thinking, decision-making and movement. This is the most unique to humans and more developed in humans than in animals. If you damage this, you will have trouble working socially and creatively as well as experience impairments with movements, depending on the part of th ...
neurotransmitter
... A neurotransmitter used by the spinal cord neurons to control muscles and by many neurons in the brain to regulate memory. In most instances, acetylcholine is excitatory. ...
... A neurotransmitter used by the spinal cord neurons to control muscles and by many neurons in the brain to regulate memory. In most instances, acetylcholine is excitatory. ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.