The Nervous System - AP Psychology-NWHS
... - Average adult brain weighs about 3 lbs -Contains about 100 billion neurons - The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult males ...
... - Average adult brain weighs about 3 lbs -Contains about 100 billion neurons - The spinal cord is about 43 cm long in adult women and 45 cm long in adult males ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... 2. Define Neuron: Neurons are the cells responsible for passing chemical and electrical signals along the pathways of the brain and Nervous System Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings o ...
... 2. Define Neuron: Neurons are the cells responsible for passing chemical and electrical signals along the pathways of the brain and Nervous System Click through the slide show about how “The Reward Pathways Reinforce Behavior”. 3. What is the central job of the reward pathway? driving our feelings o ...
MSdoc, 459KB
... behaving and also ways of changing this behaviour. The brain is really the enlarged anterior part of the vertebrate CNS, which is enclosed within the cranium of the skull. It is composed of billions of interconnected neurons that transmit information to one another and to peripheral neurons througho ...
... behaving and also ways of changing this behaviour. The brain is really the enlarged anterior part of the vertebrate CNS, which is enclosed within the cranium of the skull. It is composed of billions of interconnected neurons that transmit information to one another and to peripheral neurons througho ...
The human brain is nature`s most complex operating system, but
... computers are enormously powerful in their own way, and can outperform humans in very complex tasks. IBM’s ‘Watson’ computer proved that it could beat humans in quiz contests, and is now being used to assist cancer diagnosis and treatment. The IBM-sponsored Blue Brain project in Switzerland has atte ...
... computers are enormously powerful in their own way, and can outperform humans in very complex tasks. IBM’s ‘Watson’ computer proved that it could beat humans in quiz contests, and is now being used to assist cancer diagnosis and treatment. The IBM-sponsored Blue Brain project in Switzerland has atte ...
You*ve had a concussion! How to return a player to the
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
... Neurons are basically like on/off switches of a light switch. Neurons are either resting or shooting an electrical impulse down a wire called an axon. Each of the neurons spit out chemicals that trigger other neurons. ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... carrying impulse from receptor to CNS____________________________neurons-found in a ganglion outside CNS;dendrite endings of sensory neurons are usually associated with specialized recptors activated by specific nearby ...
... carrying impulse from receptor to CNS____________________________neurons-found in a ganglion outside CNS;dendrite endings of sensory neurons are usually associated with specialized recptors activated by specific nearby ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is –70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has changed enough, about +10 ...
... • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is –70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has changed enough, about +10 ...
1. Semester Introduction to functional neurobiology
... information technology (2) Employ the modern bio-, nano-, computer technology to simultaneously study a multitude of neurons ...
... information technology (2) Employ the modern bio-, nano-, computer technology to simultaneously study a multitude of neurons ...
Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... Nerve impulses result from the flow of ions across their plasma membranes. – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, ...
... Nerve impulses result from the flow of ions across their plasma membranes. – The electrical potential across the membrane is known as the membrane potential or resting potential. – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, ...
Central Nervous System
... Loss of motor skills; strength and ability unaffected Practice rewires Visual cortex Primary: functional blindness Association: can see, but not comprehend Language areas Broca’s: speech production Wernike’s: speech comprehension ...
... Loss of motor skills; strength and ability unaffected Practice rewires Visual cortex Primary: functional blindness Association: can see, but not comprehend Language areas Broca’s: speech production Wernike’s: speech comprehension ...
Cognitive Psychology
... properties of neurons, how they share information and what-not, and try to understand how these properties can lead to complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use ...
... properties of neurons, how they share information and what-not, and try to understand how these properties can lead to complex computations. (opponent processes, how feature detectors are calculated). • Computational modeling - Neural networks are computer models of how groups of neurons behave. Use ...
Neurological Systemppt
... Analyze the function of the nervous system. Discuss characteristics and treatment of common nervous system disorders. ...
... Analyze the function of the nervous system. Discuss characteristics and treatment of common nervous system disorders. ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD
... Dorsal part forms the ALAR plate , cell bodies in which form the dorsal gray columns. In transverse section, appear as Dorsal horn. Ventral part forms the BASAL plate, cell bodies of which form the ventral and lateral gray columns. In transverse section, appear as ventral and lateral horns respectiv ...
... Dorsal part forms the ALAR plate , cell bodies in which form the dorsal gray columns. In transverse section, appear as Dorsal horn. Ventral part forms the BASAL plate, cell bodies of which form the ventral and lateral gray columns. In transverse section, appear as ventral and lateral horns respectiv ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... – Stem-like part of the base of the brain connected to spinal cord – Consists of: midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata – Functions to: control the flow of messages between the brain and body; control breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness; and identify if one is awake/aler ...
... – Stem-like part of the base of the brain connected to spinal cord – Consists of: midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata – Functions to: control the flow of messages between the brain and body; control breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness; and identify if one is awake/aler ...
Too little
... The Brain and Neural Networks Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
... The Brain and Neural Networks Interconnected neurons form networks in the brain. Theses networks are complex and modify with growth and experience. ...
File - firestone falcons
... The brain can be divided into three major regions: • Hindbrain – includes the cerebellum and two structures found in the lower part of the brainstem: the medulla and the pons • Midbrain – is the segment of the brainstem that lies between the hindbrain and the forebrain • Forebrain – is the largest a ...
... The brain can be divided into three major regions: • Hindbrain – includes the cerebellum and two structures found in the lower part of the brainstem: the medulla and the pons • Midbrain – is the segment of the brainstem that lies between the hindbrain and the forebrain • Forebrain – is the largest a ...
SV3 Neuroscience n Behavior Oct 5 09
... Hindbrain – oldest part of the brain CEREBELLUM - coordination of movement and balance MEDULLA - controls vegetative function PONS - sleep, arousal, and connects cerebellum with the brain stem THALAMUS - structure through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral ...
... Hindbrain – oldest part of the brain CEREBELLUM - coordination of movement and balance MEDULLA - controls vegetative function PONS - sleep, arousal, and connects cerebellum with the brain stem THALAMUS - structure through which all sensory information (except smell) must pass to get to the cerebral ...
nervous system
... puzzle; they’ll do it in 30 mins. The next day, they don’t recognize the puzzle, but they do it in 20 mins, the next day in 10. Therefore, they are learning by motor memory. They can learn their route from home to the market by repetition. But they can’t make a detour, and if anything bumps them off ...
... puzzle; they’ll do it in 30 mins. The next day, they don’t recognize the puzzle, but they do it in 20 mins, the next day in 10. Therefore, they are learning by motor memory. They can learn their route from home to the market by repetition. But they can’t make a detour, and if anything bumps them off ...
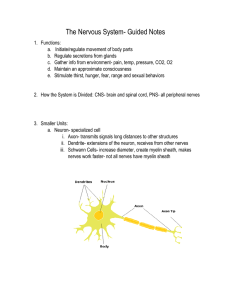
Nervous System Guided Notes
... i. Two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic systems ii. Sympathetic= fight or flight iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal organs to muscles, brain and heart. v. Bronchi open to allow more air into the lungs vi. Pupils dilate- all in ...
... i. Two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic systems ii. Sympathetic= fight or flight iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal organs to muscles, brain and heart. v. Bronchi open to allow more air into the lungs vi. Pupils dilate- all in ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... activityis based at the University of Florida where is the Director of Behavioural Neurology. This new book is co-authored with Donda; beginning with a preface acknowledging the Harvard Medical School graduate William James as one of the first modern scientists 'to investigate religious experience a ...
... activityis based at the University of Florida where is the Director of Behavioural Neurology. This new book is co-authored with Donda; beginning with a preface acknowledging the Harvard Medical School graduate William James as one of the first modern scientists 'to investigate religious experience a ...
Brain Bark
... abstract information like music, colors or shapes and to synthesize experiences by giving a quick, general sense of what is happening ...
... abstract information like music, colors or shapes and to synthesize experiences by giving a quick, general sense of what is happening ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.